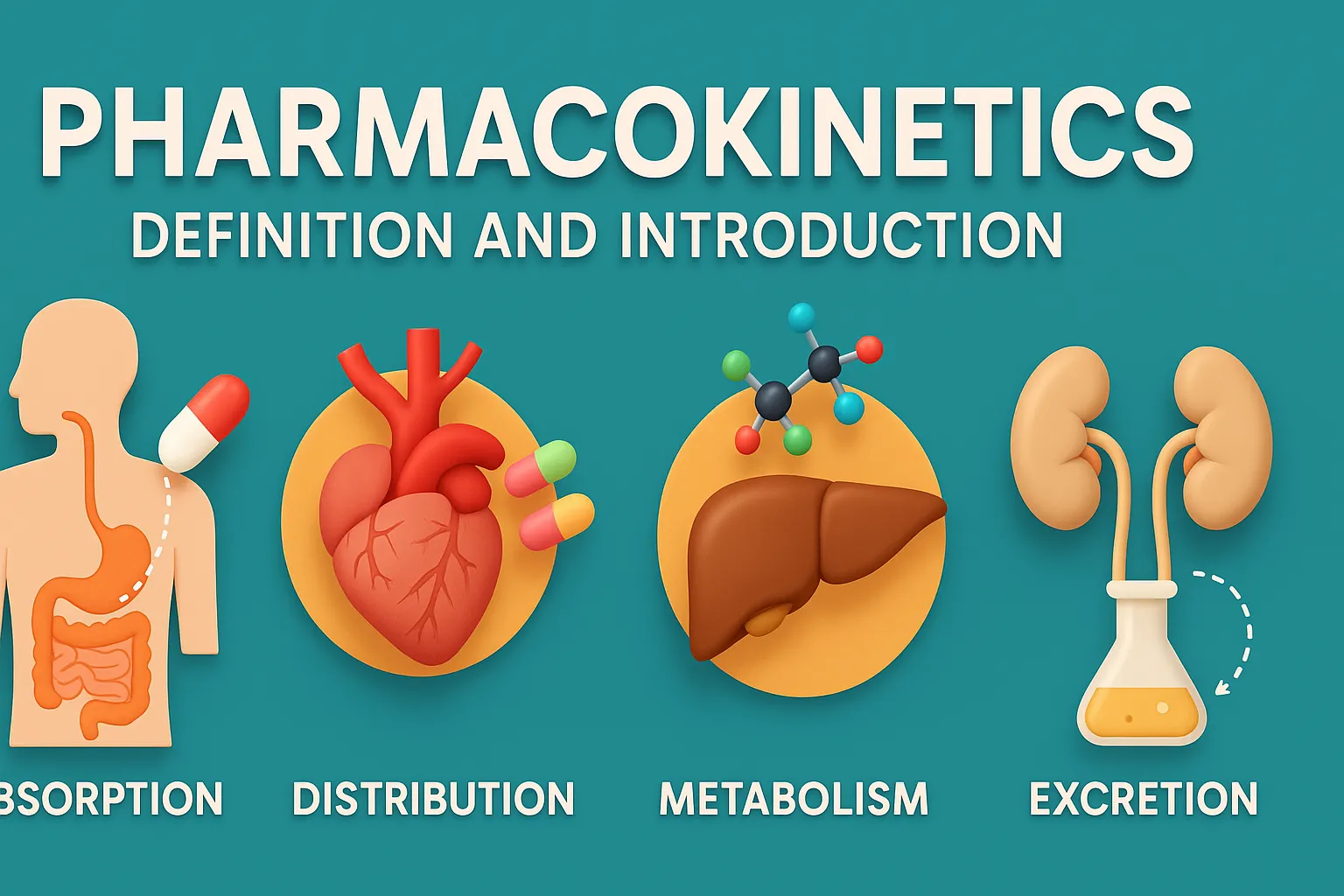
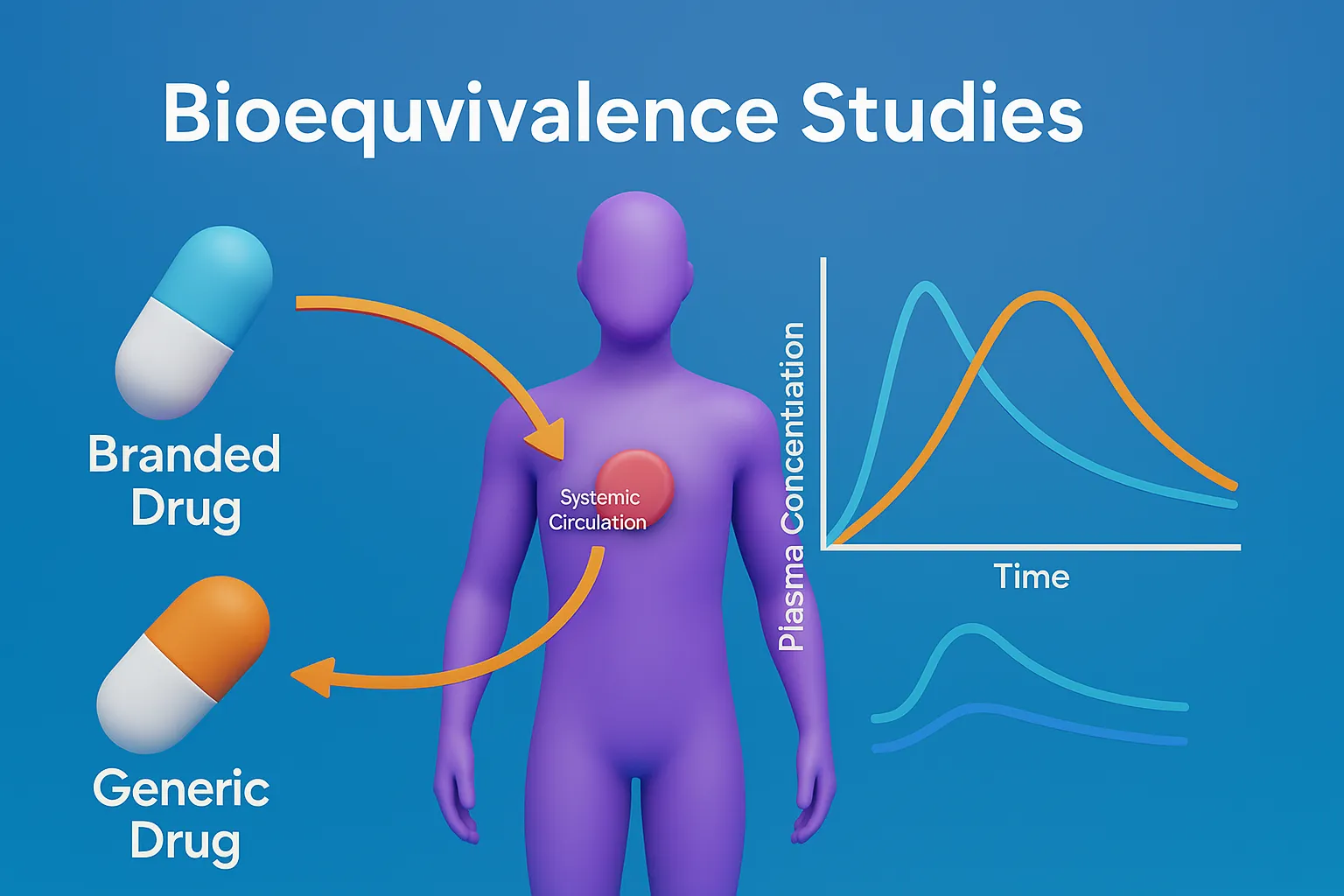
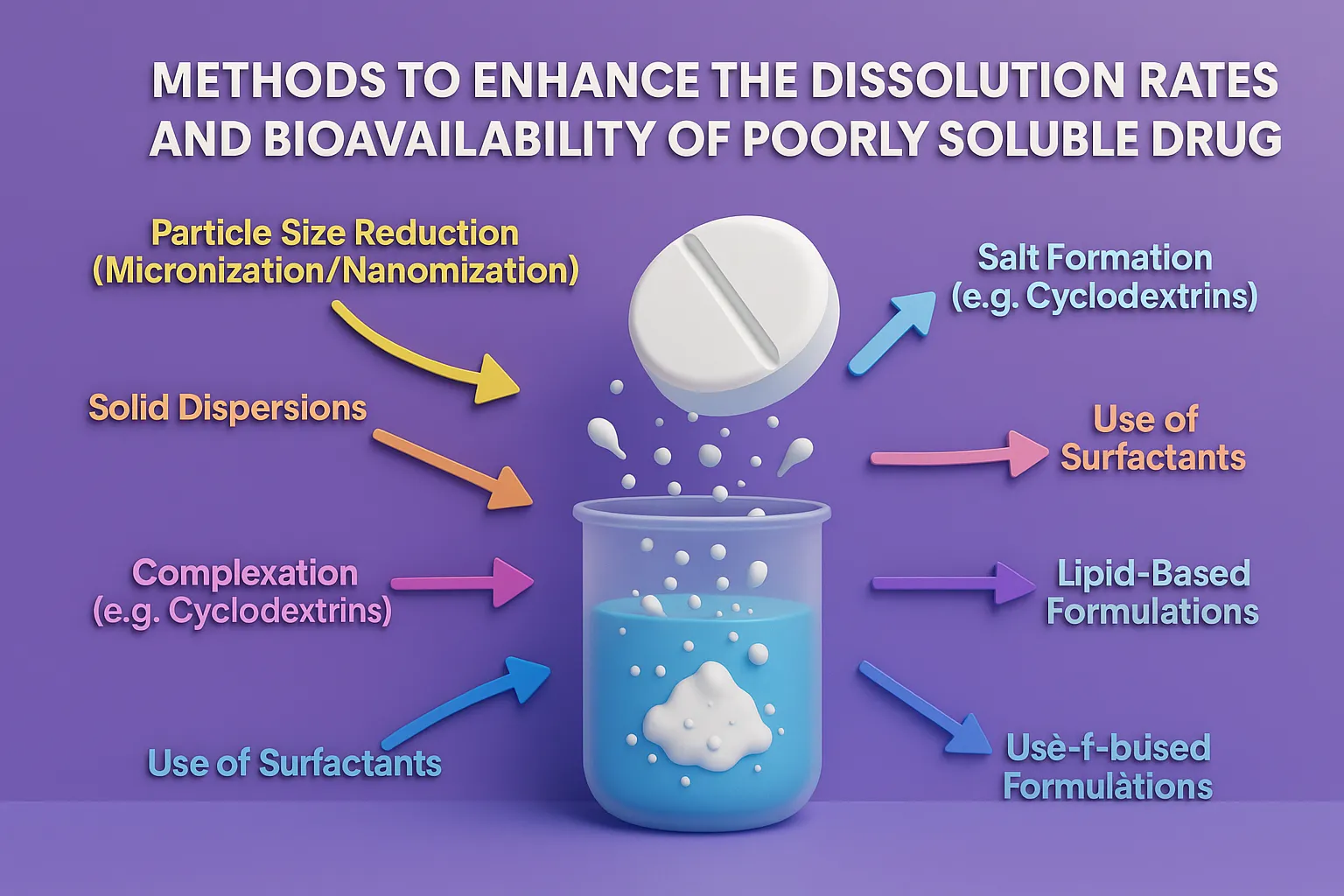
Alligation in Pharmaceutical Calculations
Alligation in Pharmaceutical Calculations is a method used in pharmacy to calculate the proportions of solutions of different strengths needed to achieve a desired concentration. It’s useful in compounding and preparing pharmaceutical mixtures. Alligation Medial This method calculates the average strength of a mixture based on the quantities and concentrations of the individual solutions. Formula: … Read more