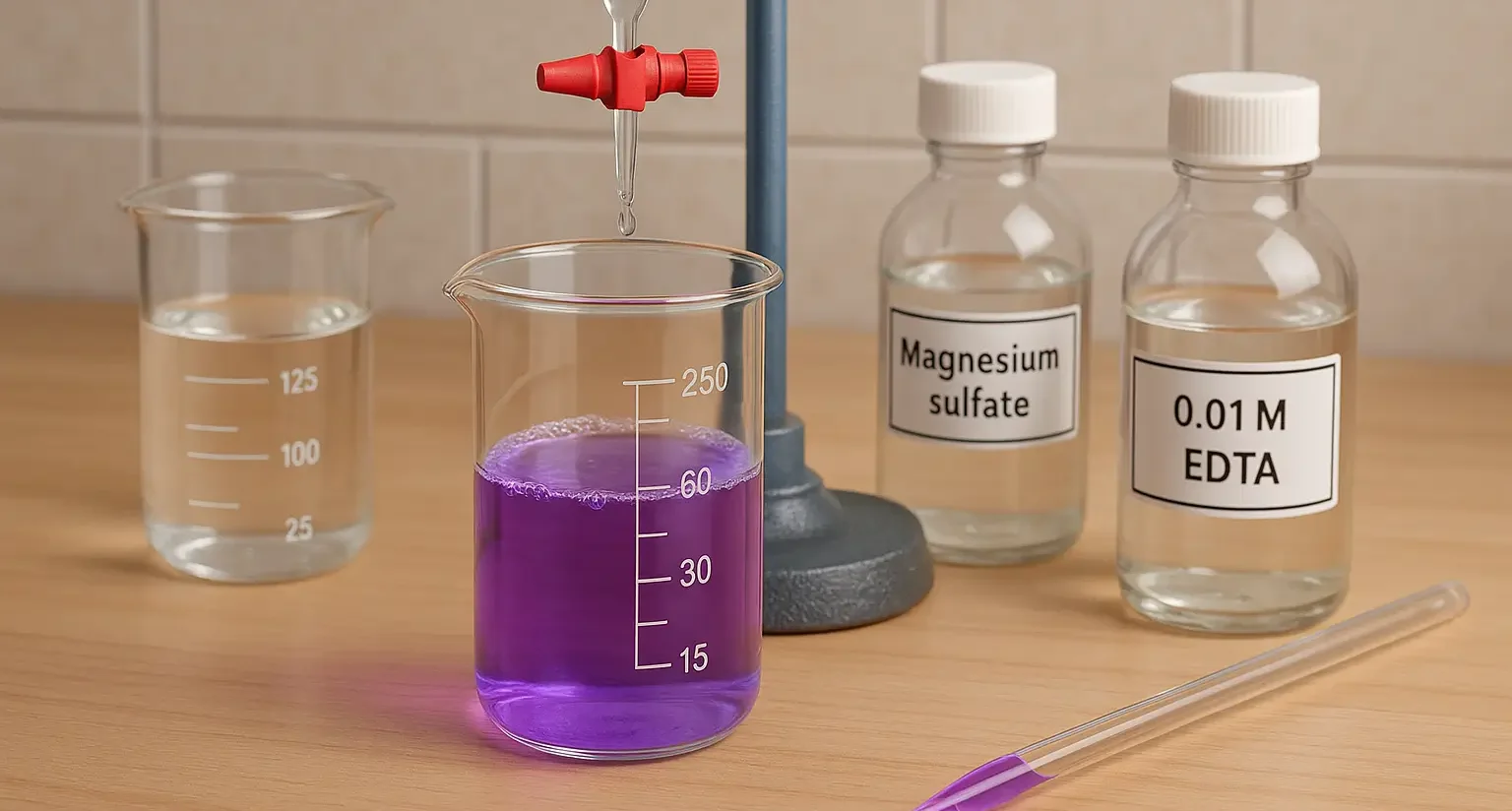
Estimation of Magnesium Sulfate by Complexometric Titration
Estimations of magnesium sulfate by complexometric titration involves titrating with EDTA using Eriochrome Black T as an indicator to determine magnesium content. Introduction of Estimation of Magnesium Sulfate by Complexometric Titration: Estimation of Magnesium Sulfate by Complexometric Titration In pharmaceutical analysis, the estimations of magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄) is done using complexometric titration with EDTA as … Read more