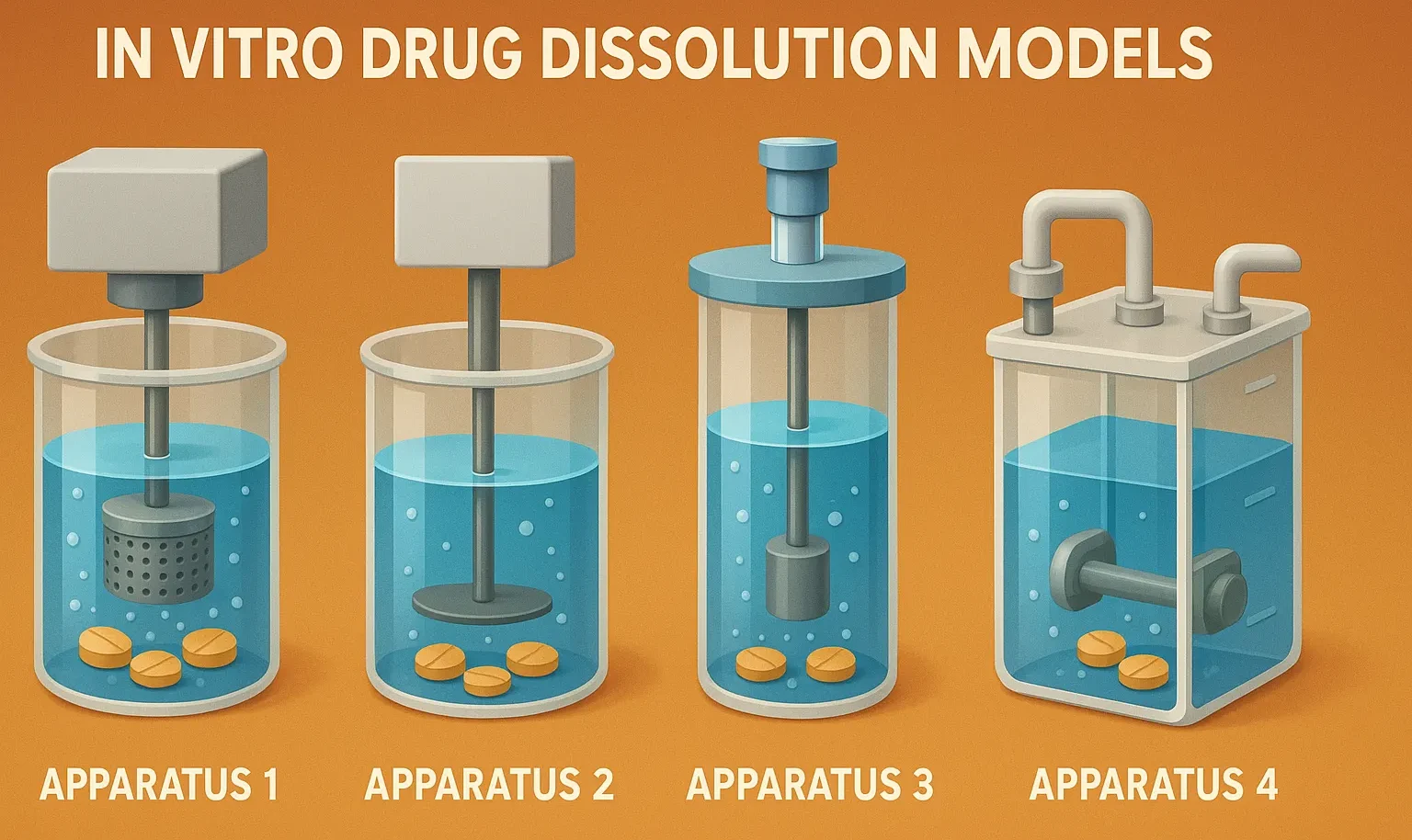
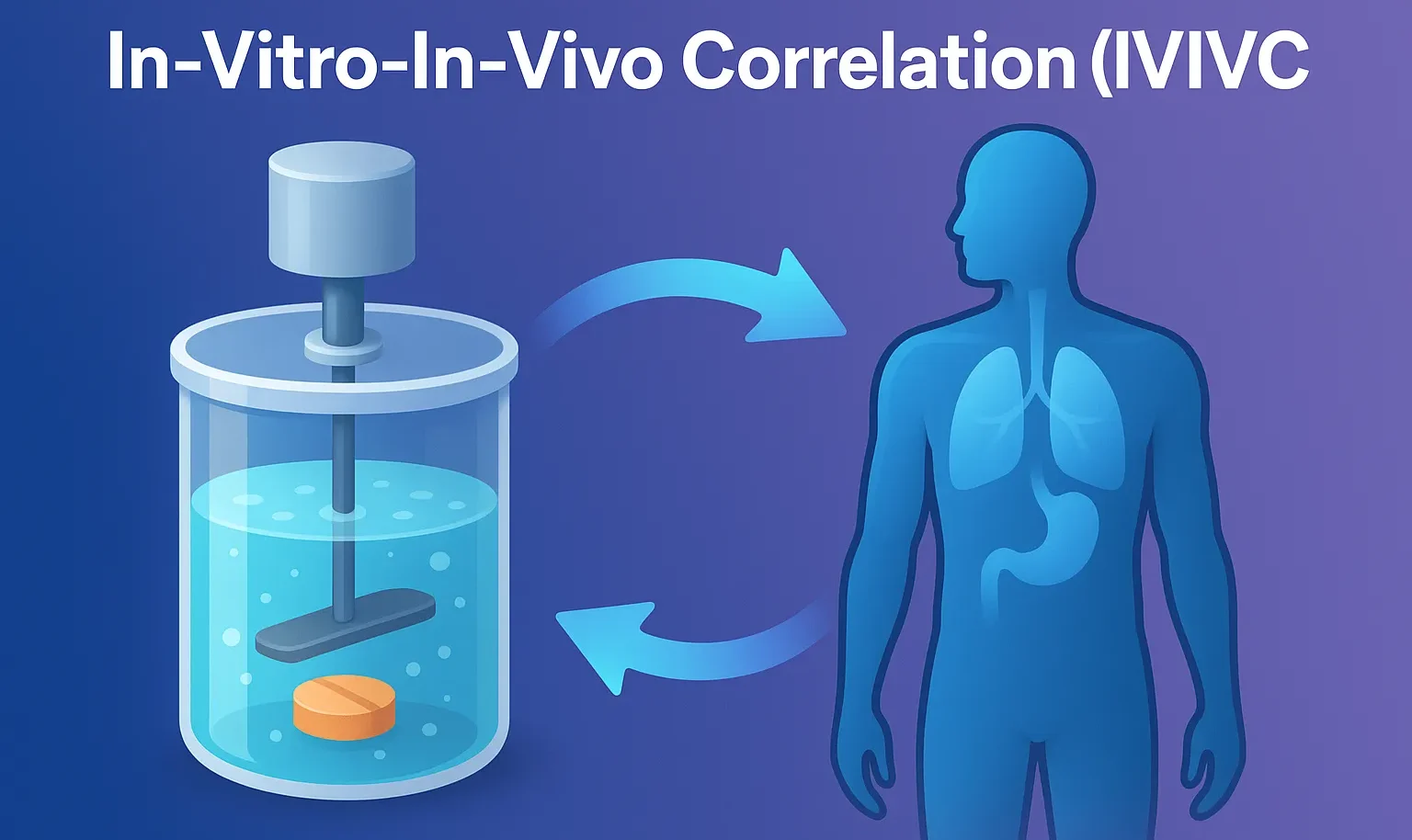
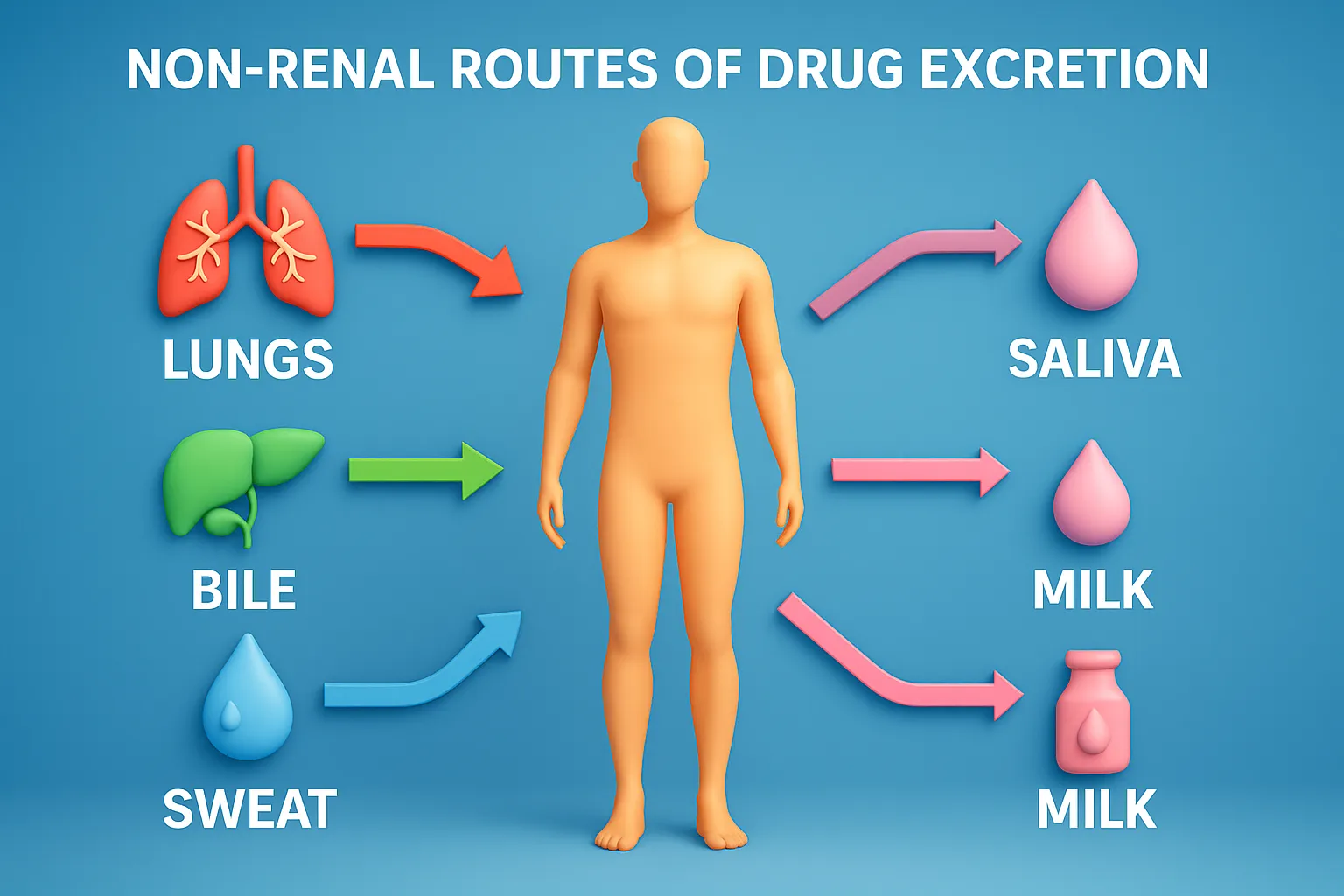
In-vitro drug dissolution models
In vitro drug dissolution models evaluate drug release from dosage forms using methods like USP apparatus for bioavailability prediction. In-vitro drug dissolution models In-vitro drug dissolution models are essential in pharmaceutical research to study drug release from formulations like tablets and capsules. These models help predict drug dissolution, absorption, and bioavailability, ensuring consistent drug quality. … Read more