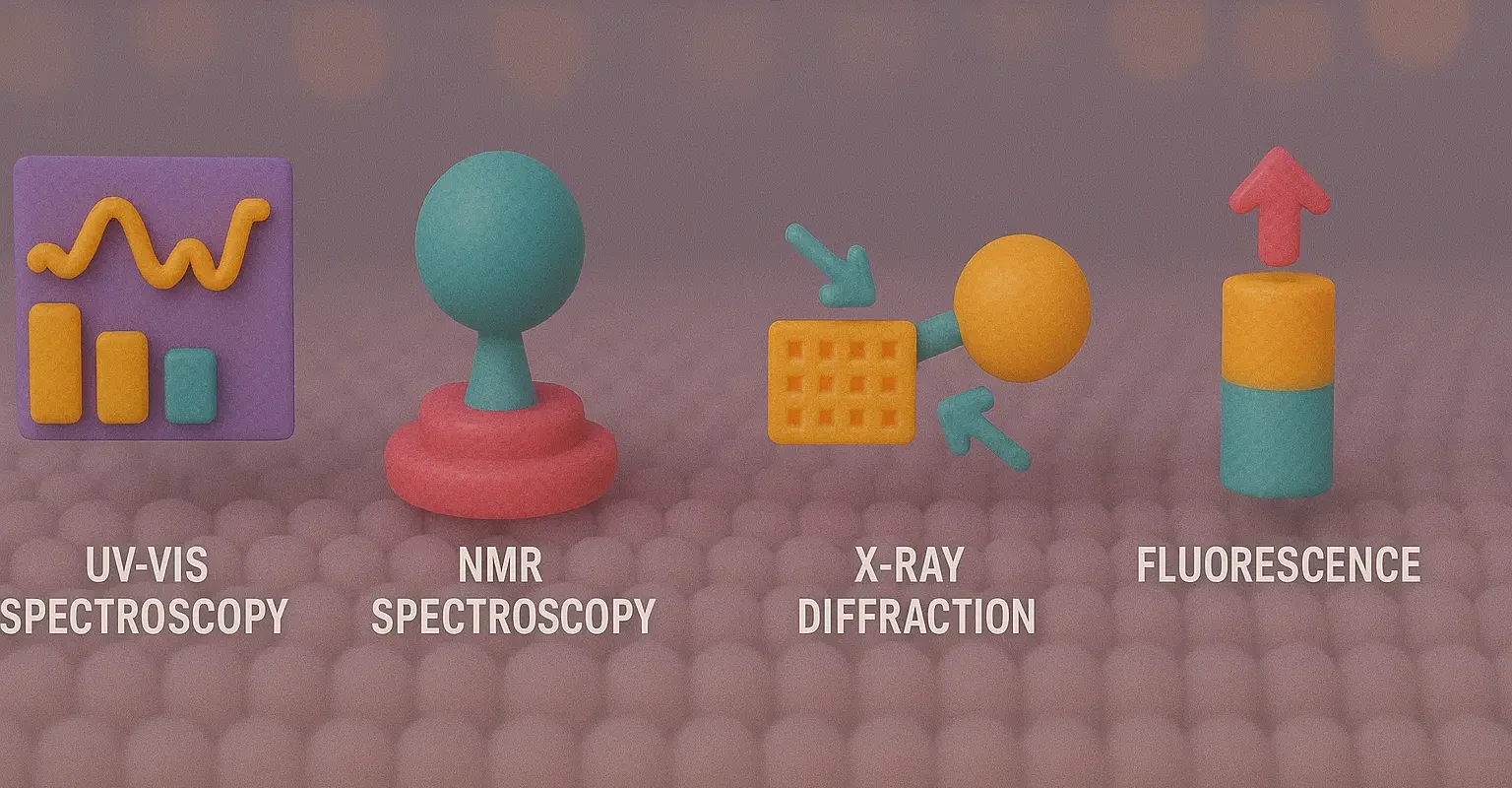
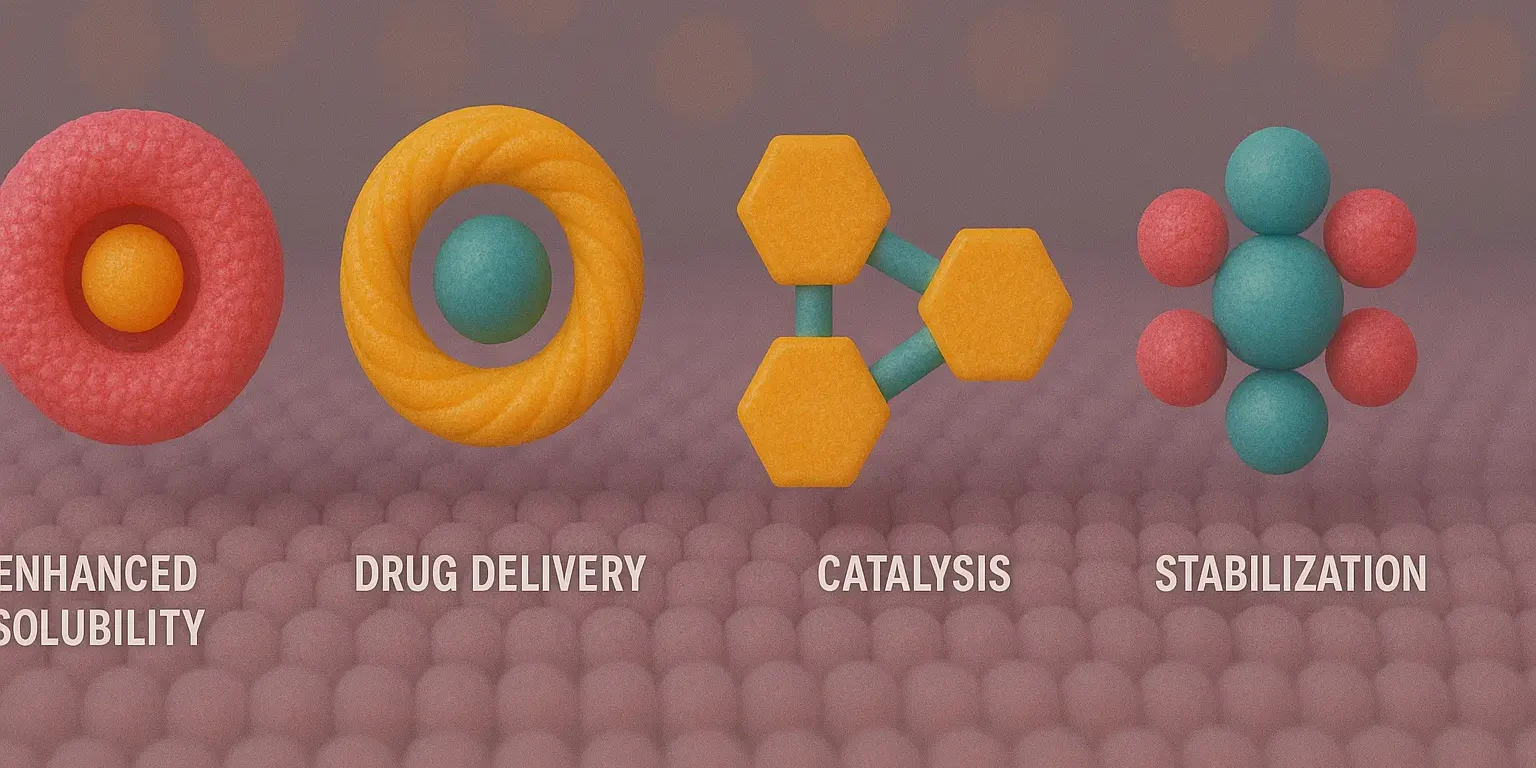
Methods of Analysis for Complexes
Methods of Analysis for Complexes analysis explores the formation, stoichiometry, and stability of complexes between a central atom (typically a metal ion) and ligands. This understanding is essential in fields like chemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. Below are four primary methods used to analyze complexation: 1. Method of Continuous Variation (Job’s Method) Overview: Job’s Method determines … Read more