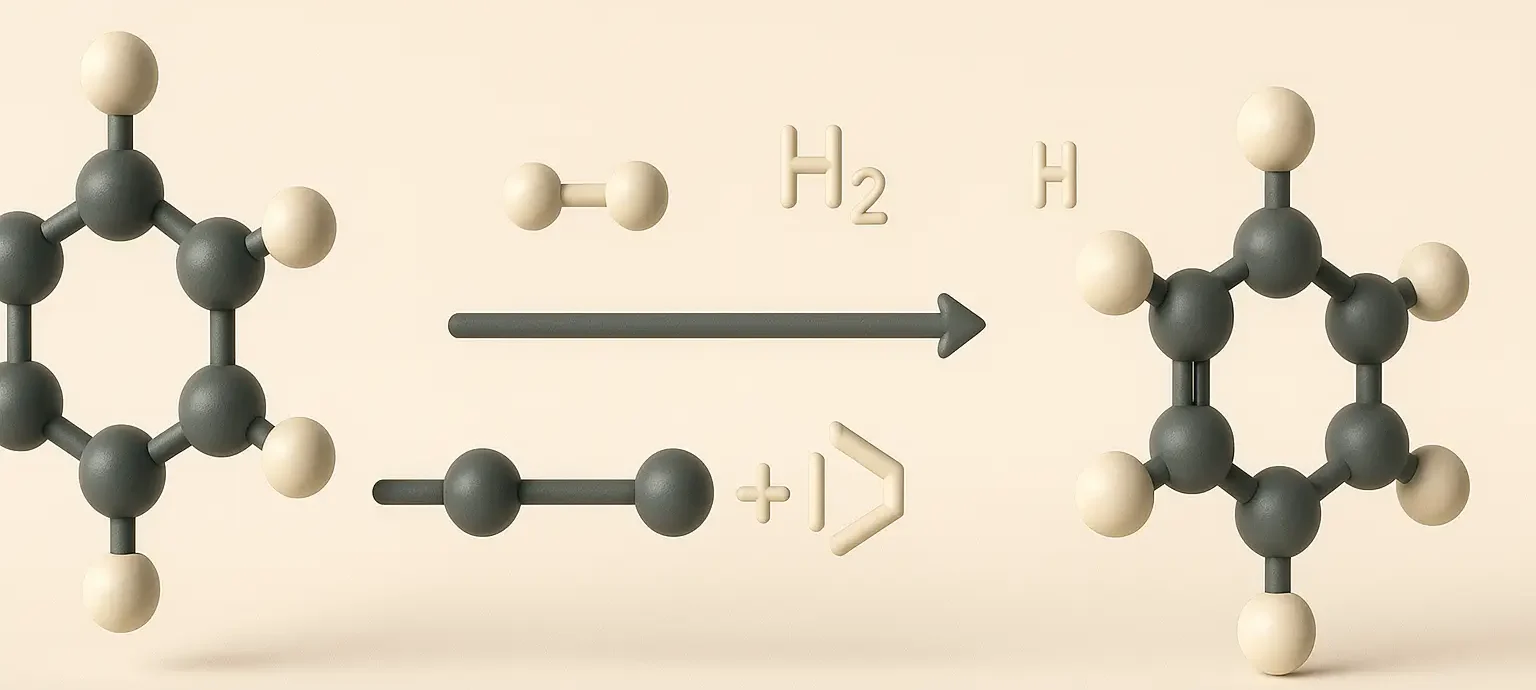Cycloalkanes: General Methods of Preparation
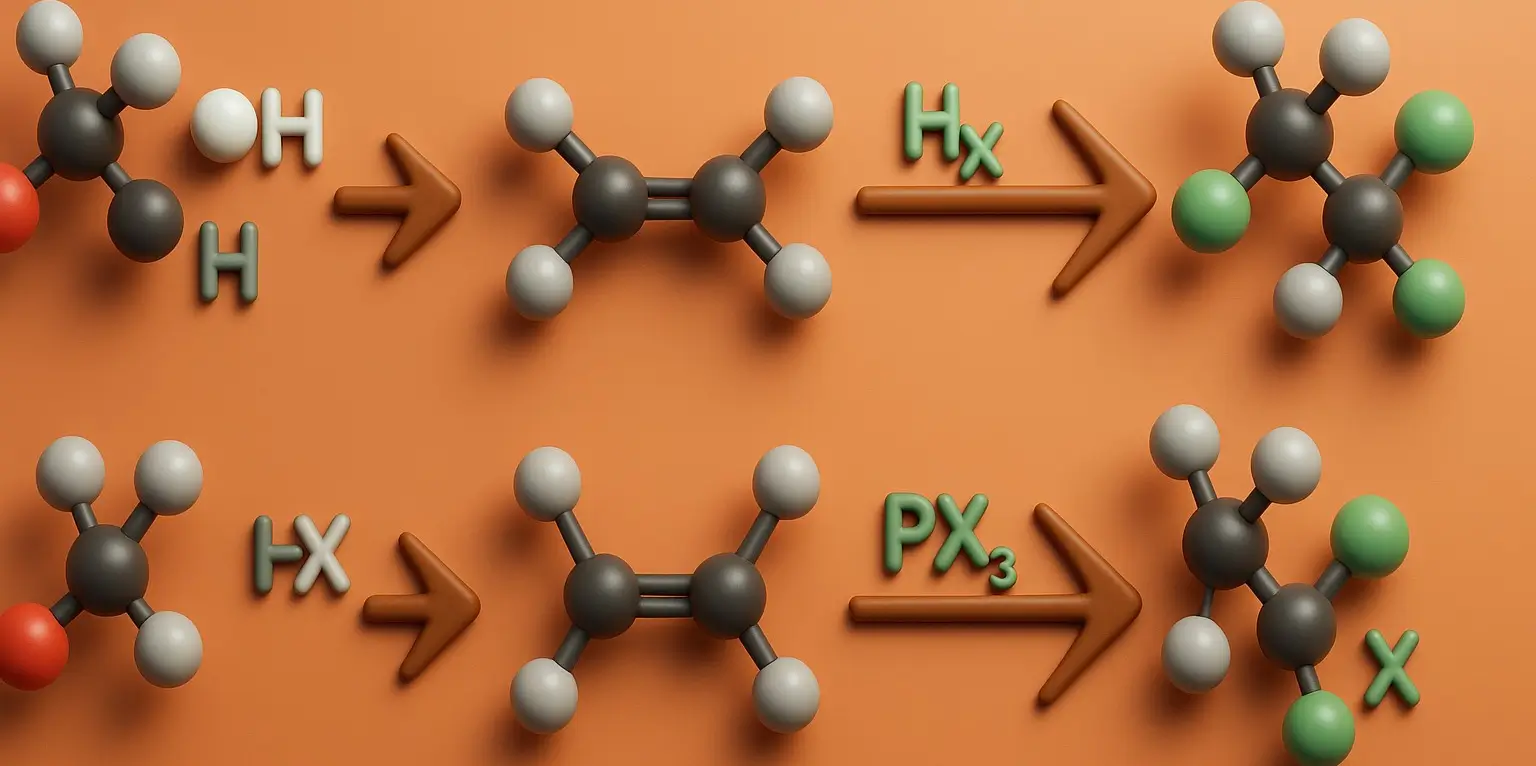
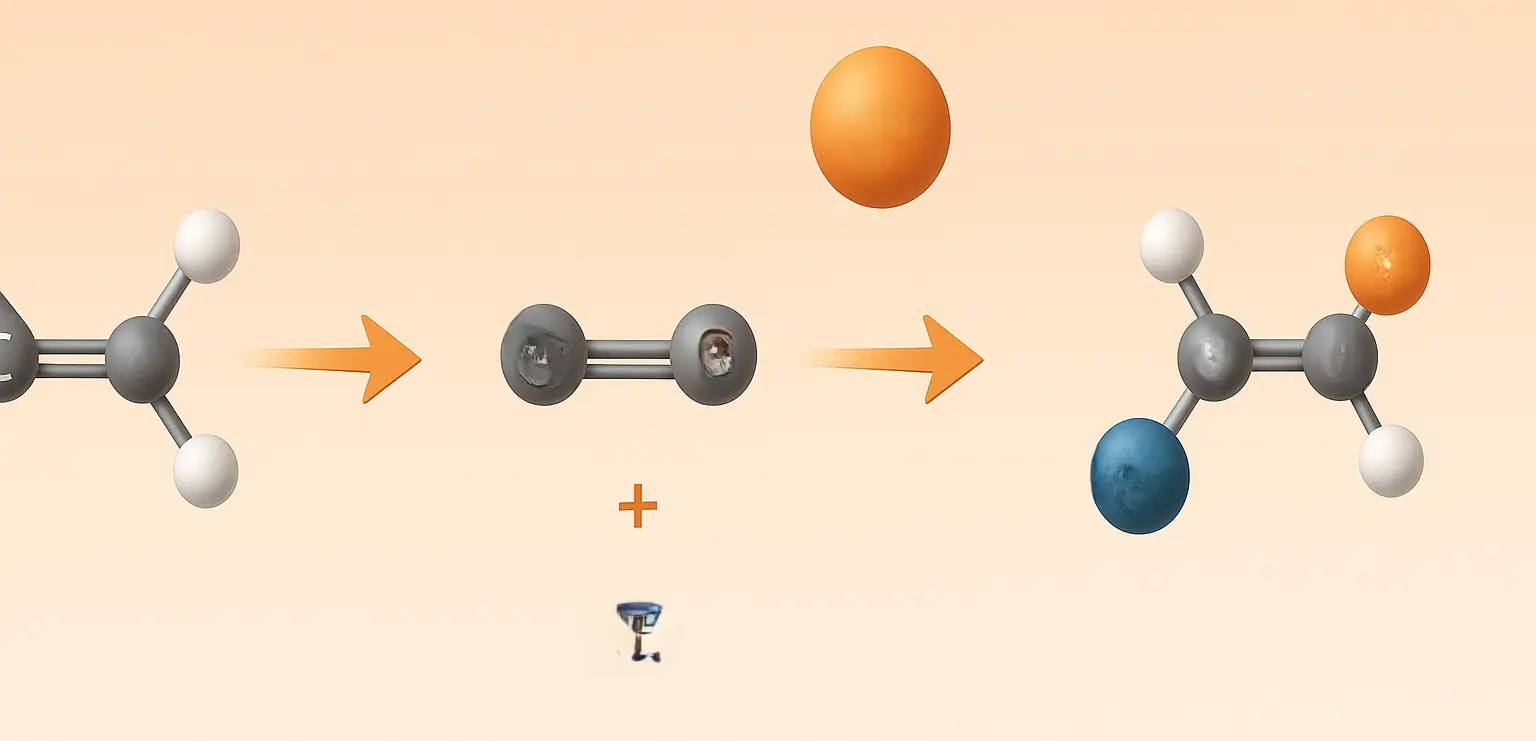
Cycloalkanes Methods of Preparation Generally, there are four Cycloalkanes Methods of Preparation which are stated below with the examples: 1. Hydrogenation of Aromatic Compounds: Process: Aromatic compounds like benzene can be hydrogenated in the presence of a catalyst (usually nickel, palladium, or platinum) under high pressure to produce cycloalkanes. Example: C6H6 (benzene) + 3H2 → Ni, heat … Read more