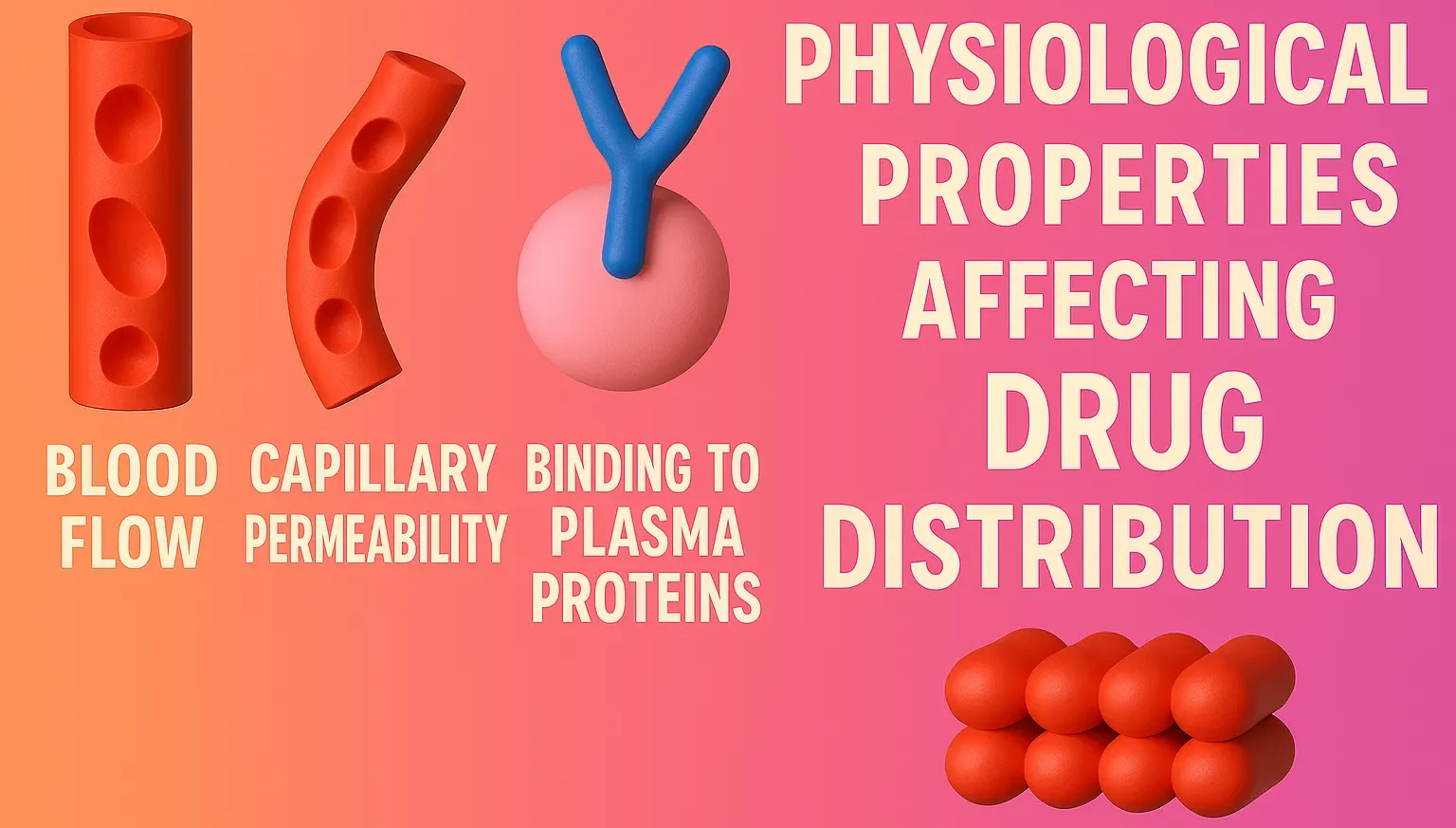
Physiological Properties Affecting Drug Distribution
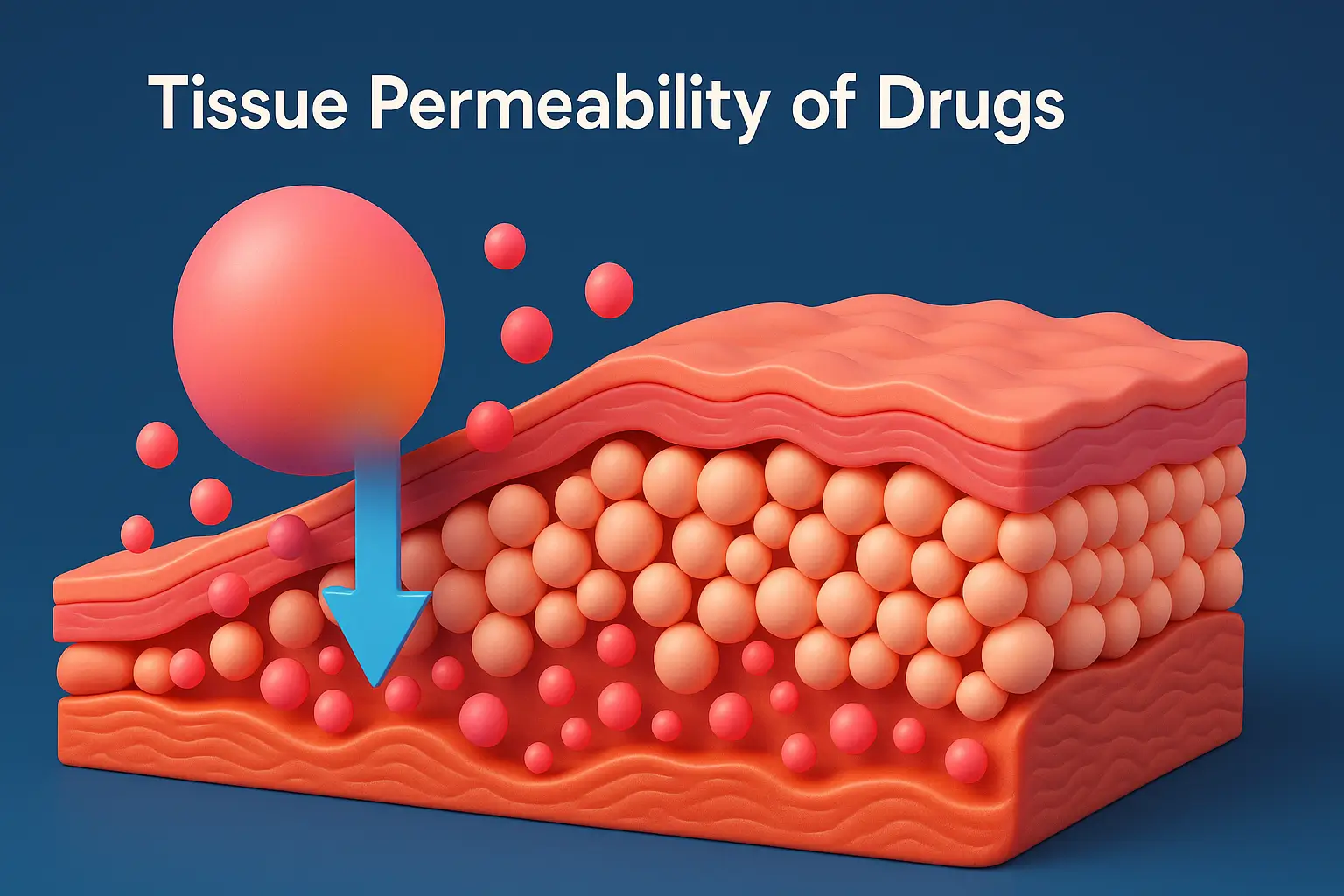
Physiological Properties Affecting Drug Distribution include blood flow, tissue permeability, protein binding, and body water content. Physiological Properties Affecting Drug Distribution The distribution of a drug in the body is influenced by several physiological properties: Lipid Solubility Highly lipid-soluble drugs (e.g., diazepam, propofol) distribute more readily into lipid-rich tissues like the brain and adipose tissue. … Read more