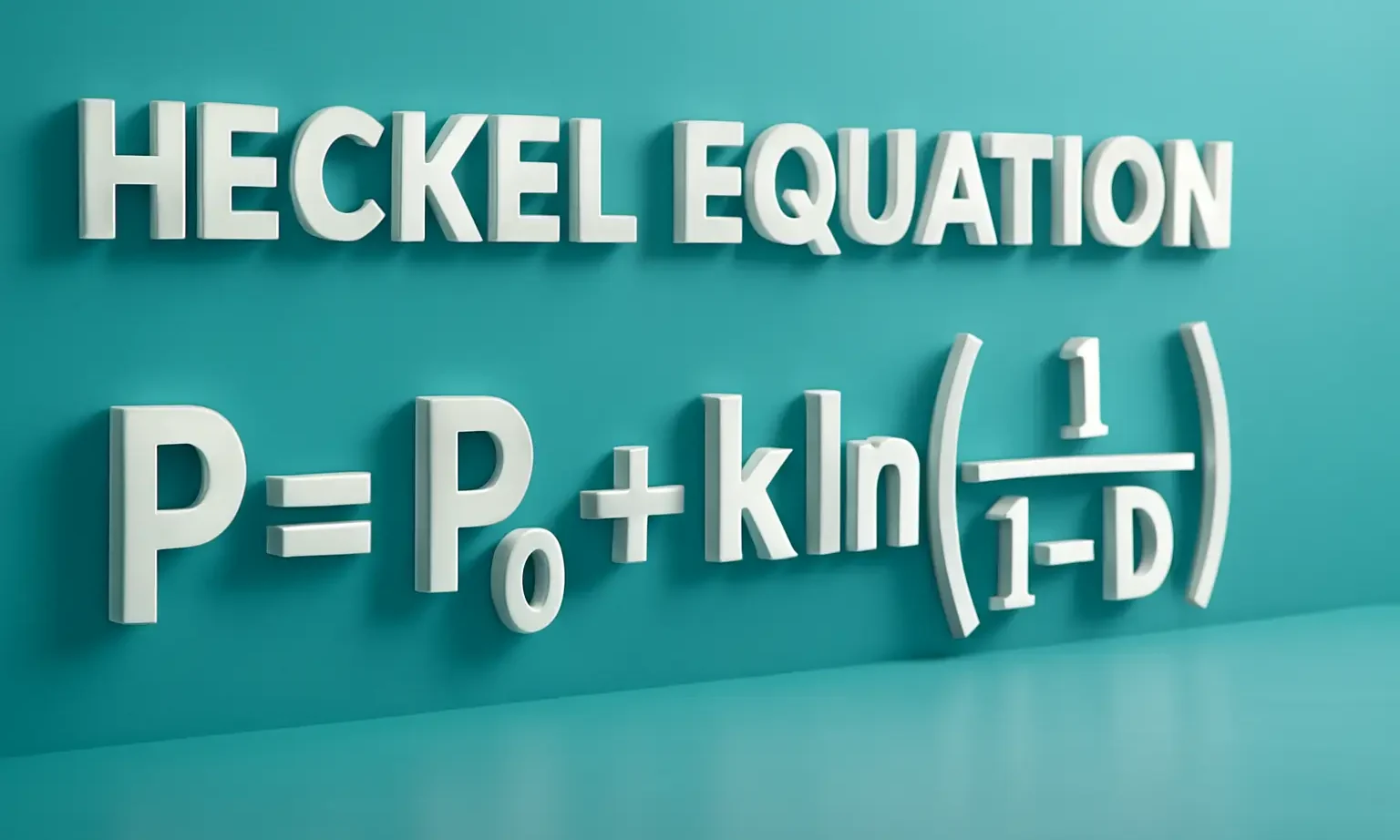Interfacial Properties Of Suspended Particles
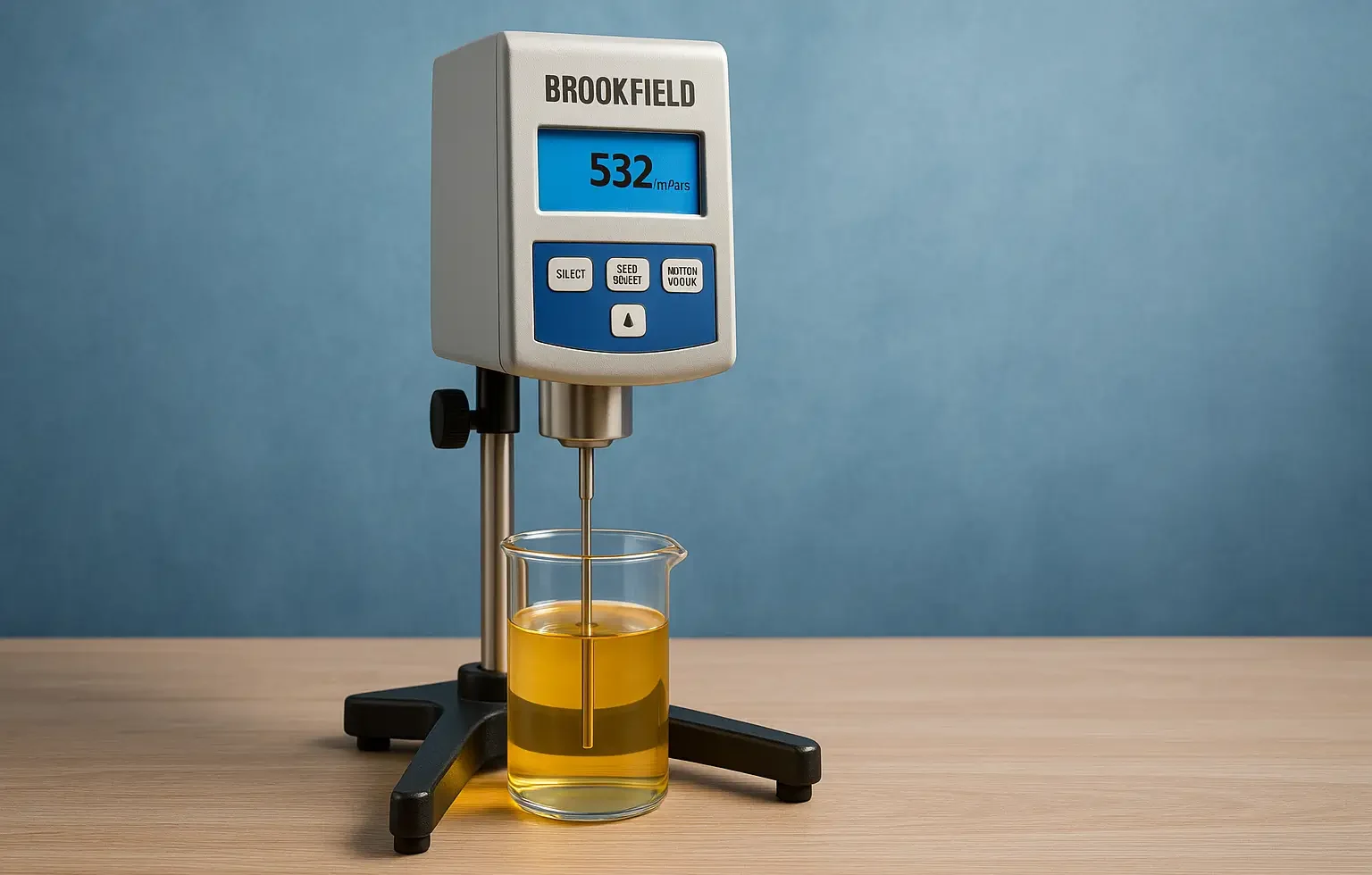
Interfacial Properties of Suspended Particles are key in drug formulation, emulsions, and colloidal systems. It influences, aggregation, and dispersion in suspensions. At the interface between suspended particles and the surrounding liquid, several key properties affect the behavior and stability of the suspension: Interfacial Tension Exists between the solid particle surface and the liquid. Higher tension … Read more