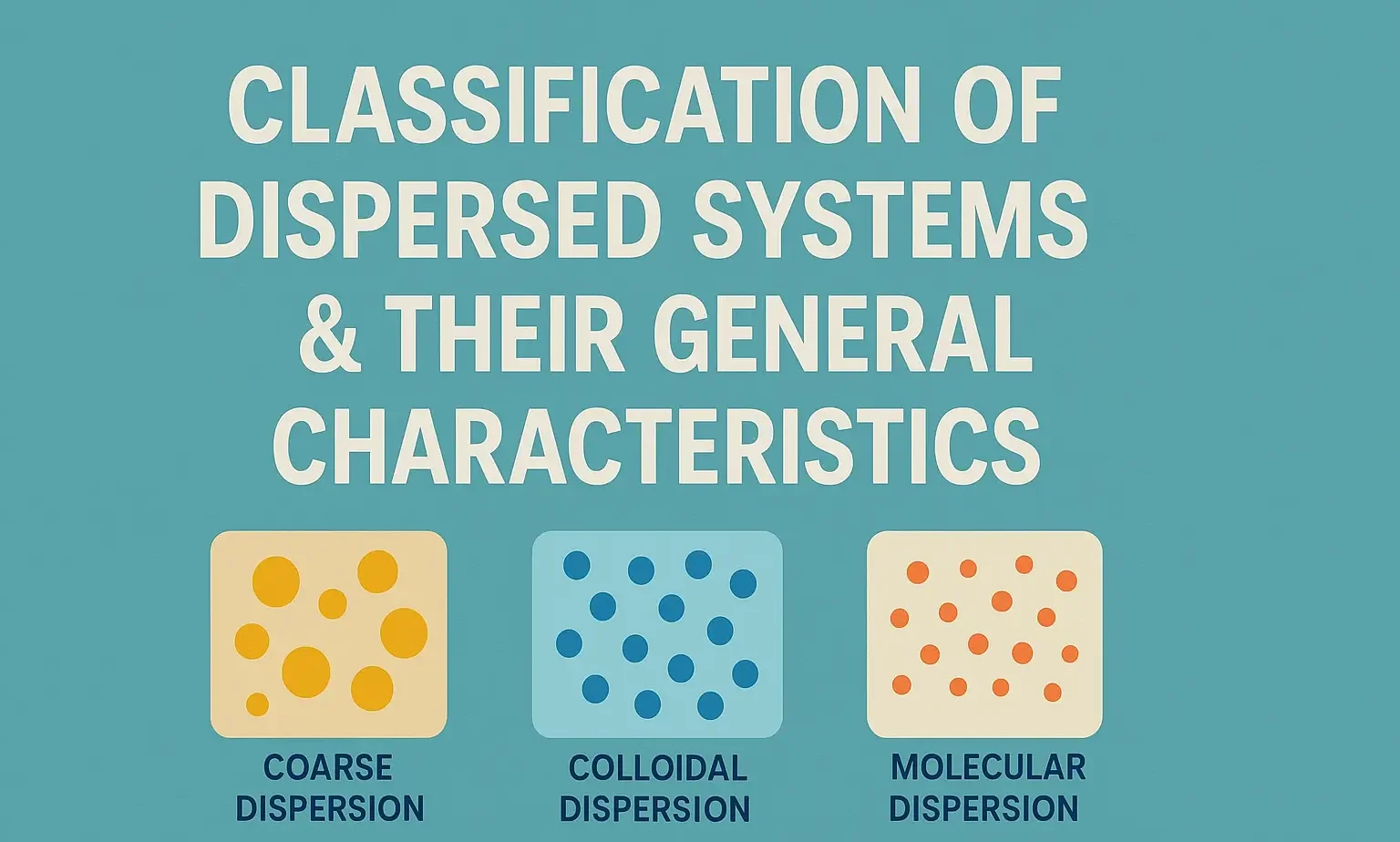
Comparative Account of General Properties of Colloids
Comparative Account of General Properties of Colloids explains optical, electrical, and mechanical behaviors. Comparative Account of General Properties of Colloids highlights differences between lyophilic and lyophobic sols. Property Lyophilic Colloids Lyophobic Colloids Association Colloids (Micelles) Affinity for Medium Strong Very weak or none Amphiphilic (both water-loving and -hating parts) Ease of Formation Easily formed by … Read more