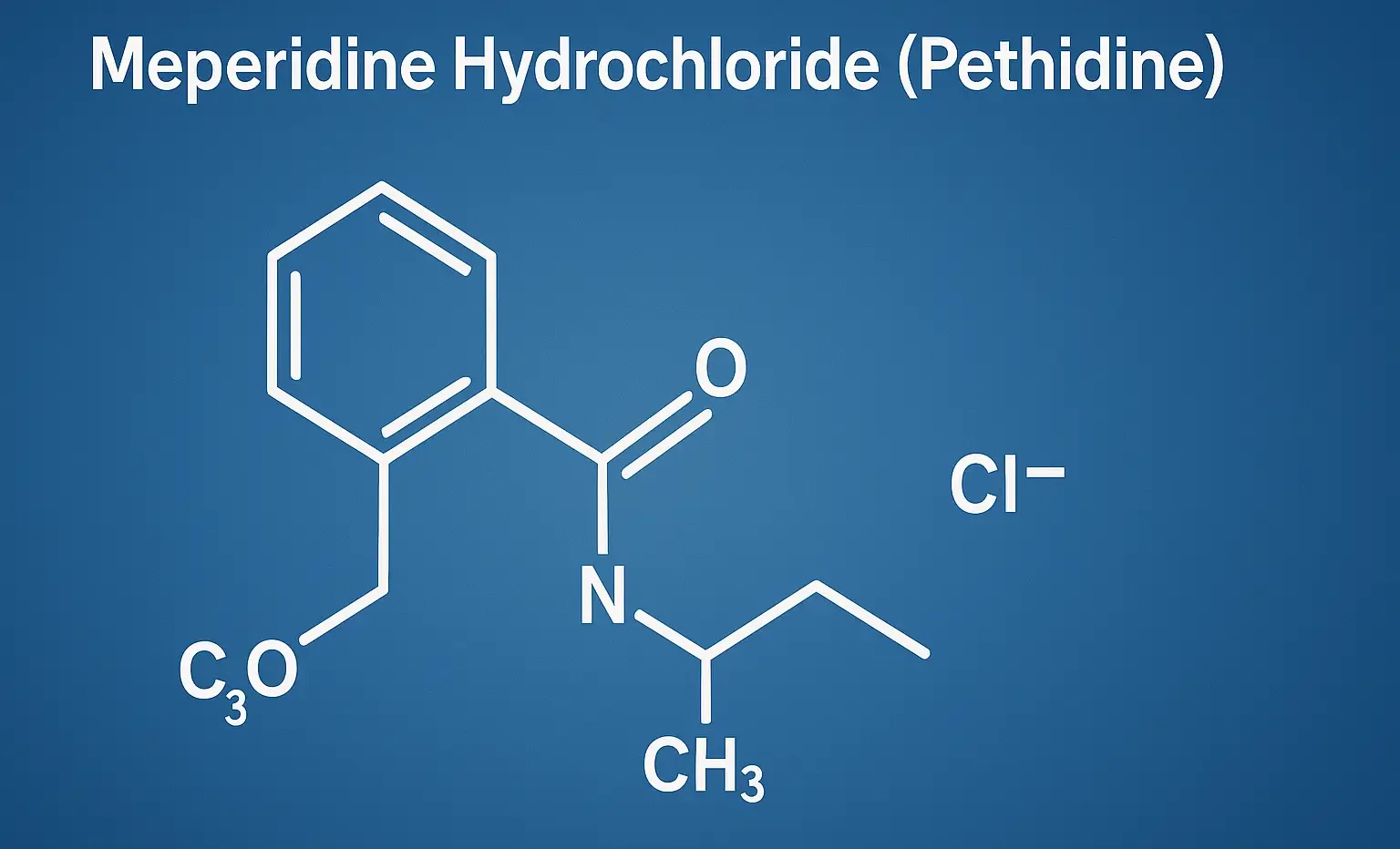
Methadone Hydrochloride
Methadone Hydrochloride manages opioid dependence and chronic pain with long-lasting effects. It acts as a μ-opioid receptor agonist with NMDA antagonism for analgesia. Chemical Formula: C₂₁H₂₇NO·HCl Mechanism of Action: Full μ-opioid receptor agonist Also, NMDA antagonist and inhibits monoamine reuptake Very long half-life (15–60 hrs) → minimal withdrawal fluctuations Uses of Methadone Hydrochloride: Opioid maintenance … Read more