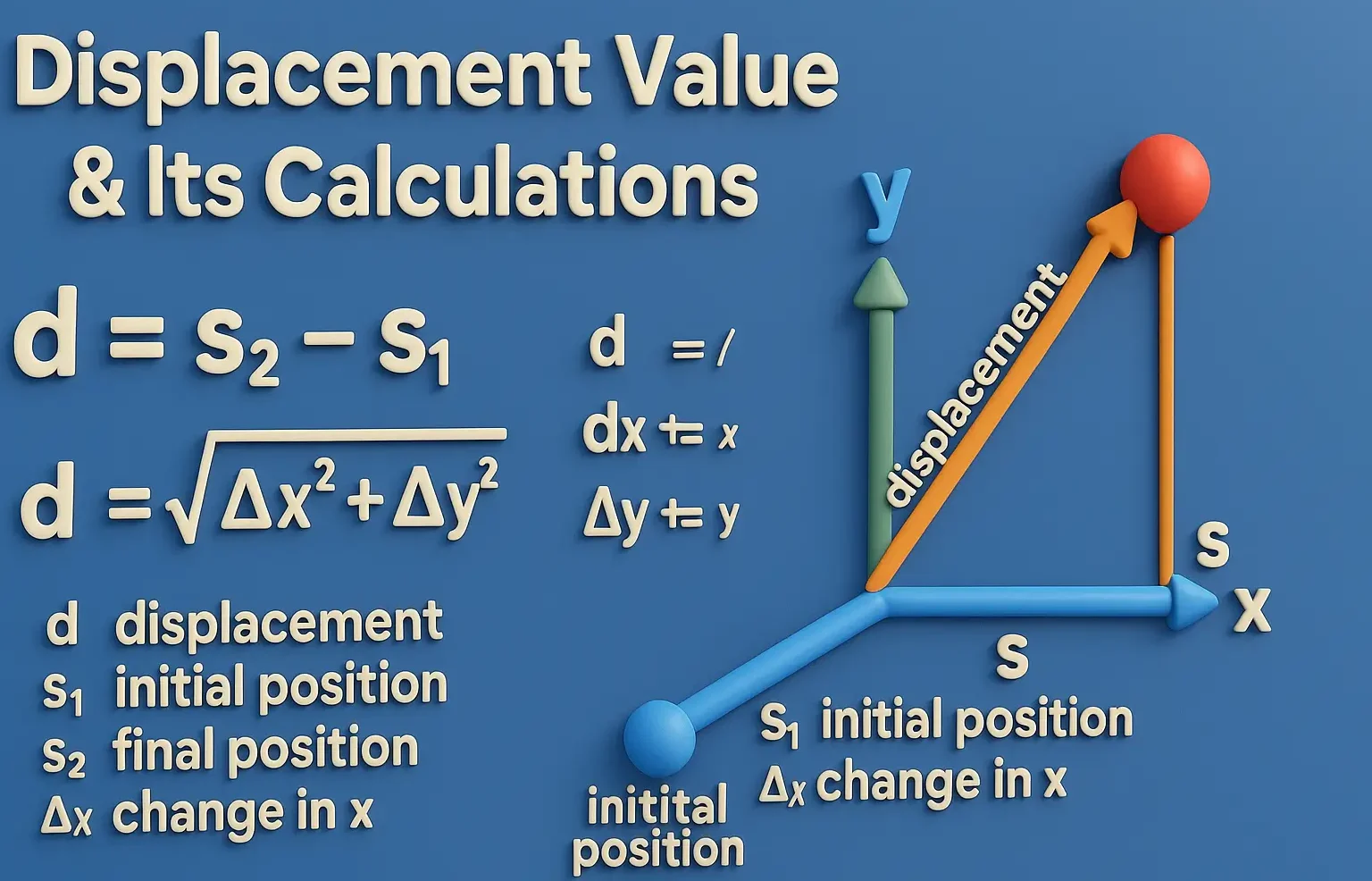
Displacement value and its calculations
Displacement value (D.V.) is a crucial concept in the preparation of suppositories, particularly when using the fusion molding method. It helps determine the amount of suppository base required to incorporate a specific amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) while maintaining the desired weight of the suppository. Key Concepts: Displacement Value (D.V.): The amount of suppository … Read more