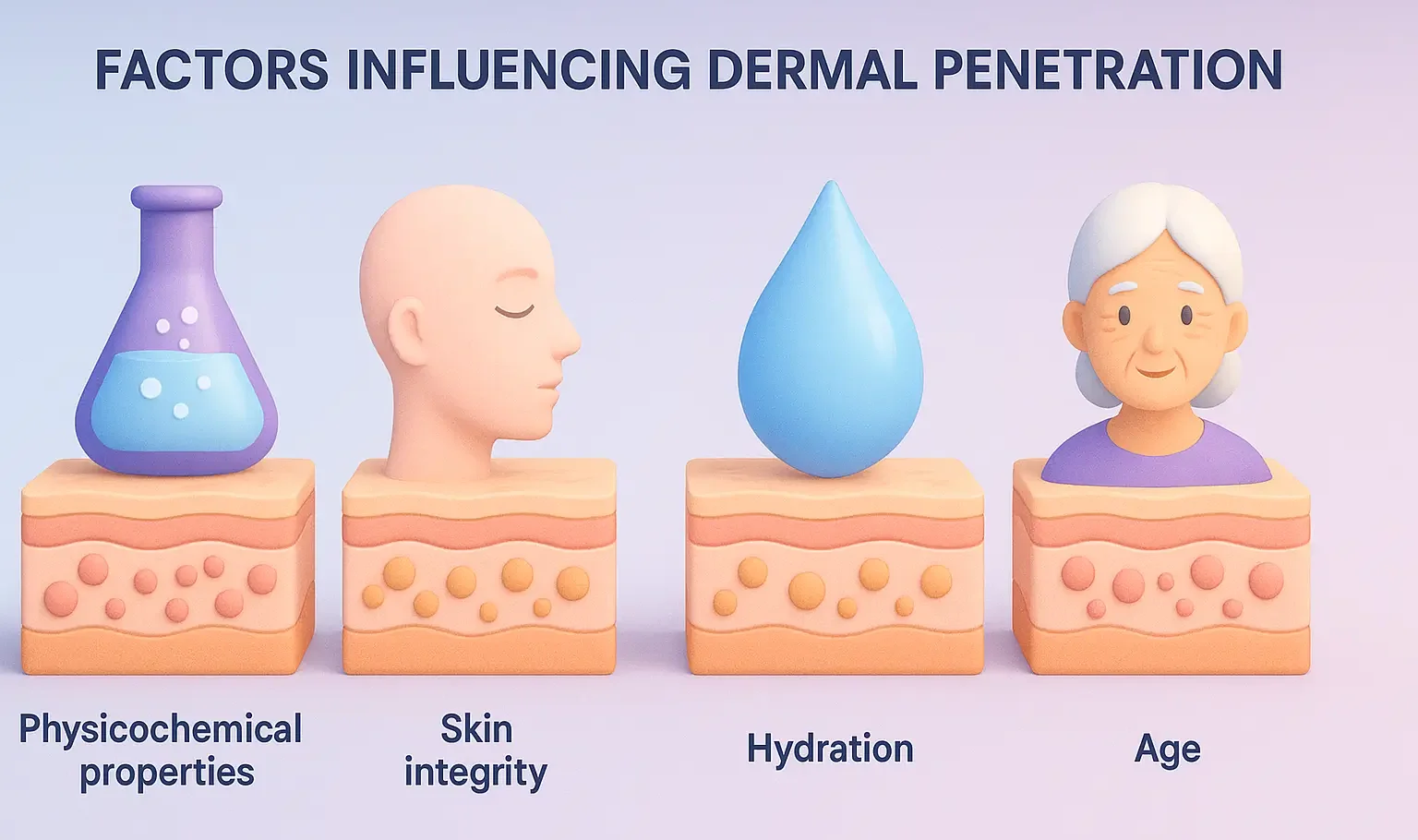
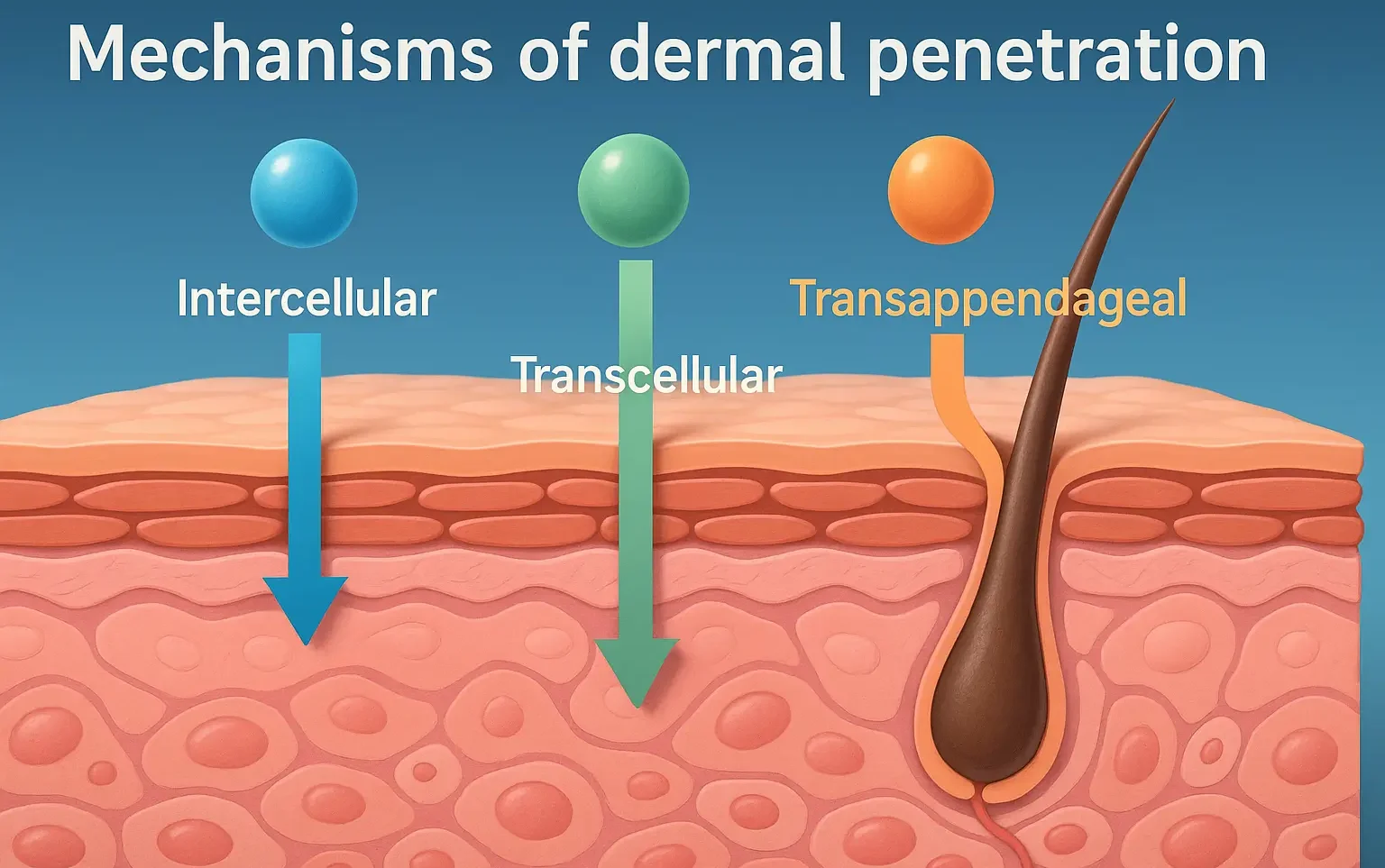
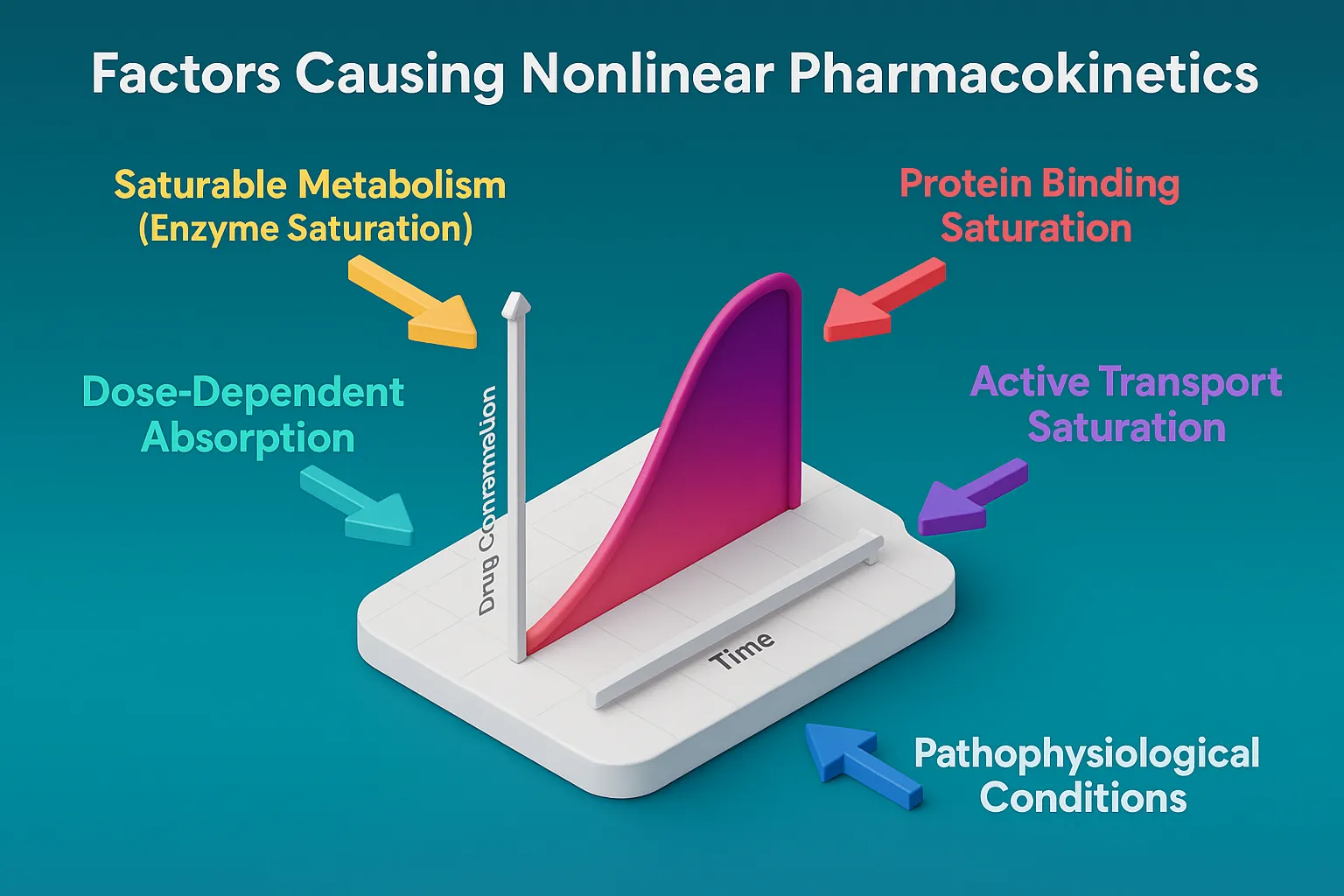
Excipients used in semi solid dosage forms
Excipients are inactive ingredients added to enhance the physical properties, stability, and patient acceptability of semisolid dosage forms. Common types include: Bases: Provide structure and consistency. They can be lipophilic (e.g., petrolatum, lanolin) or hydrophilic (e.g., polyethylene glycols). Gelling Agents: Form the gel structure in semisolids. Examples include carbomers, hydroxyethyl cellulose, and xanthan gum. Emulsifying … Read more