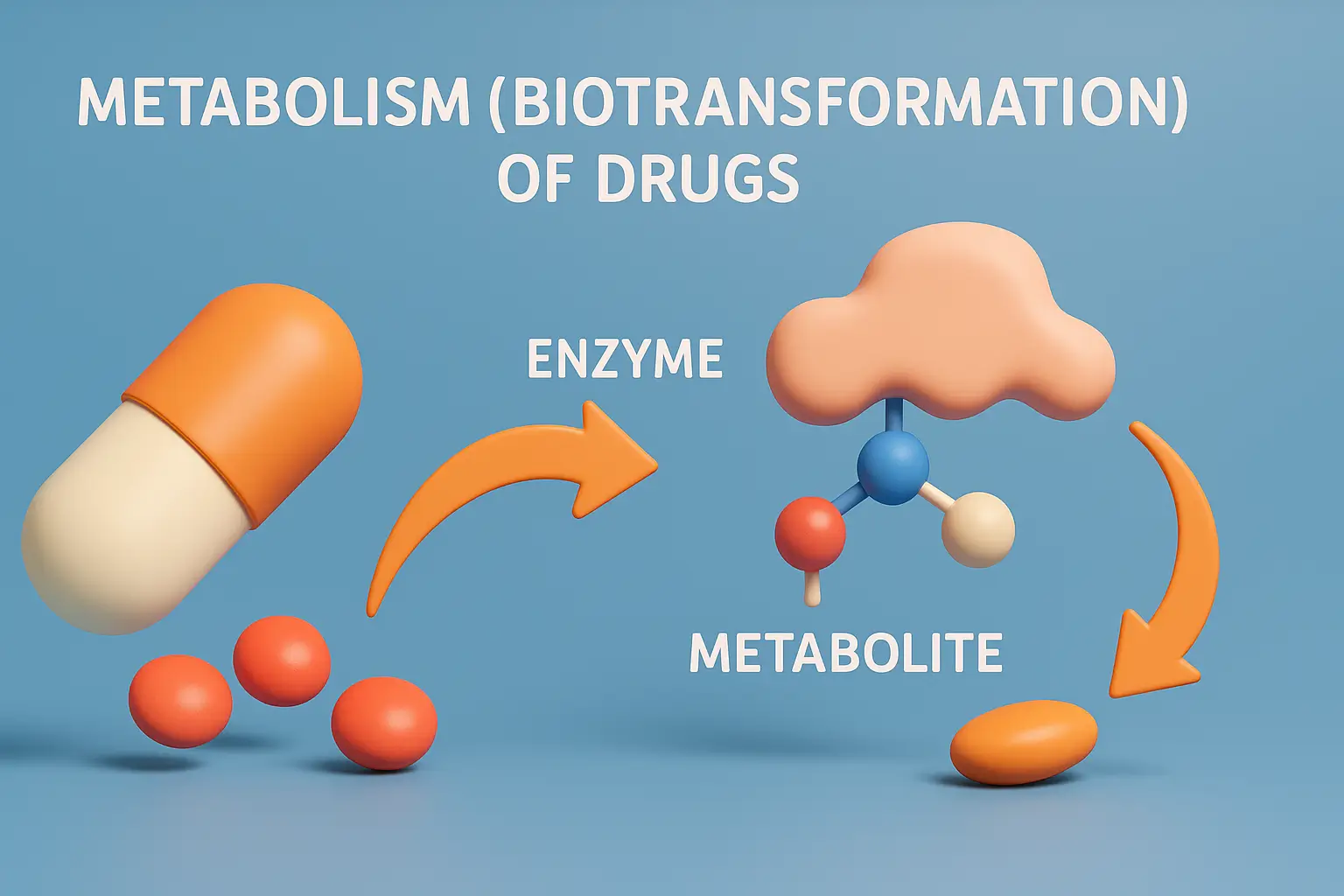
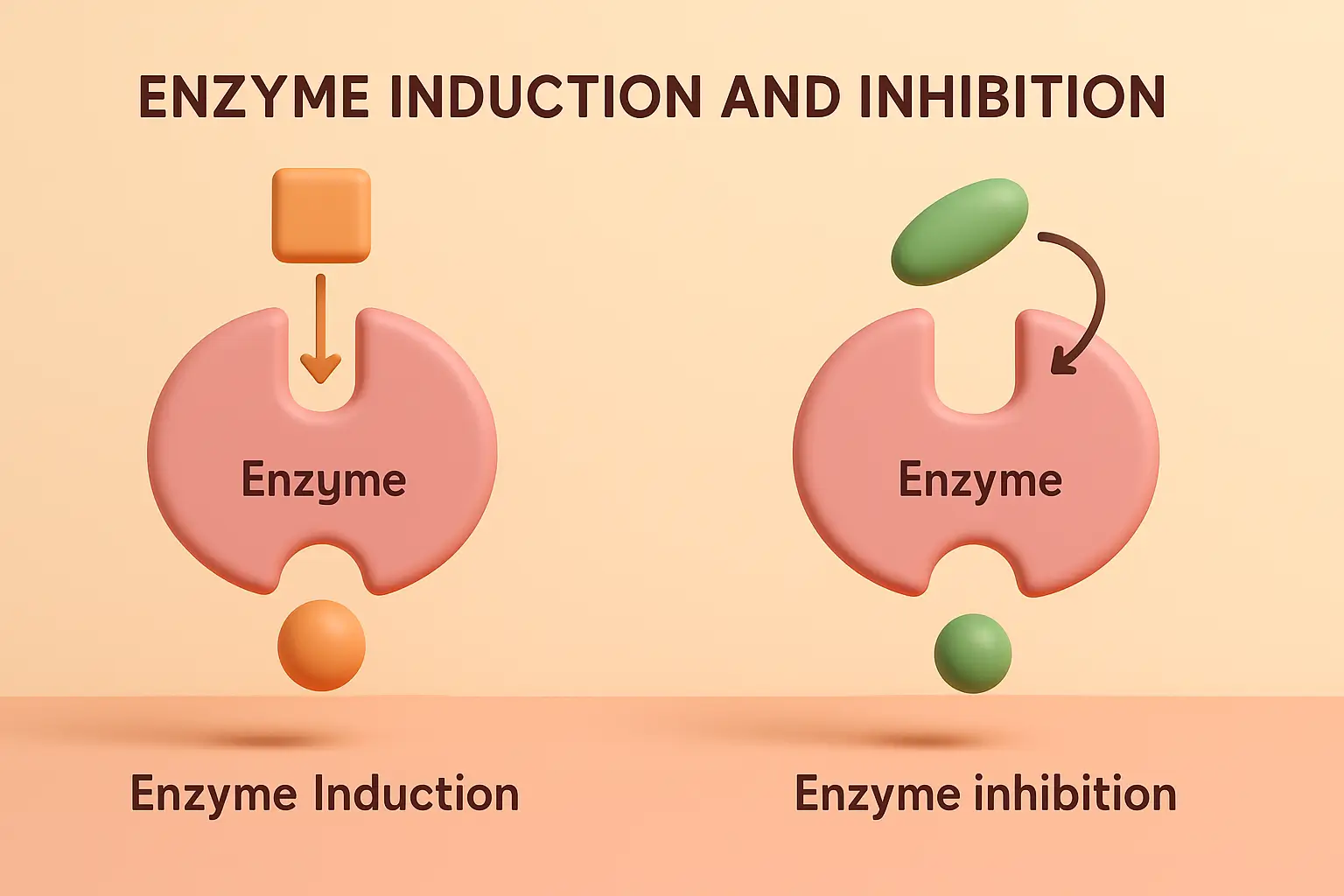
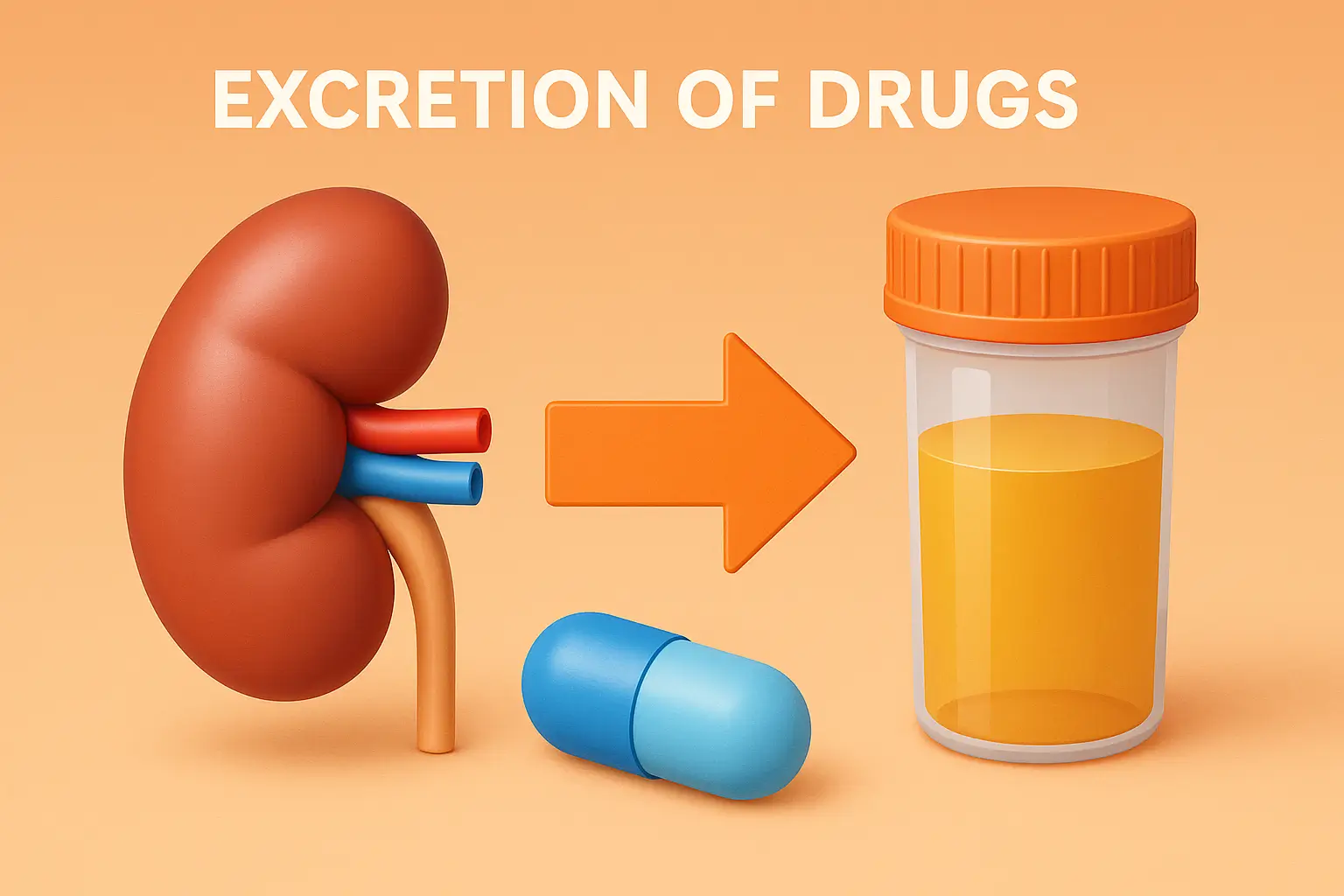
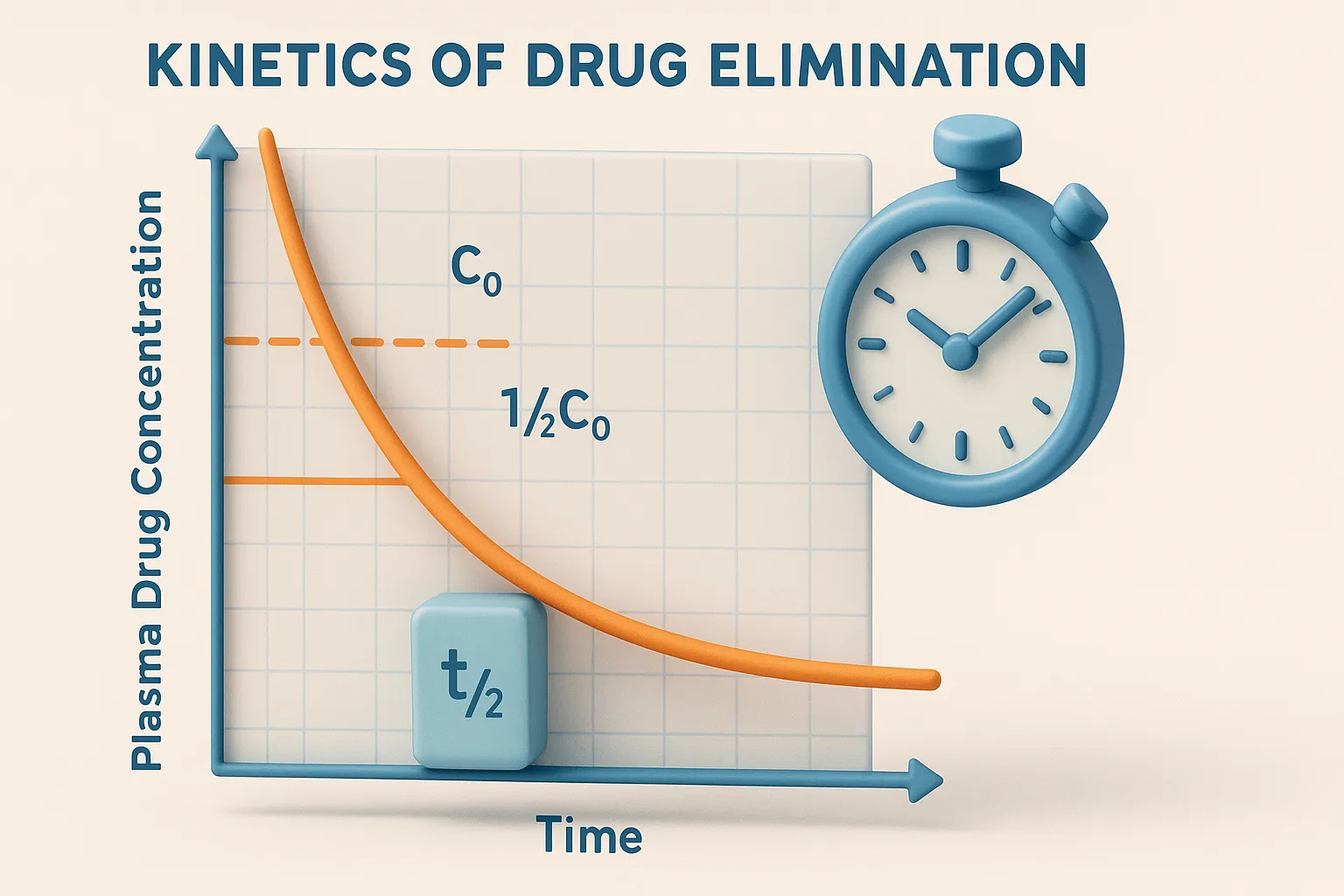
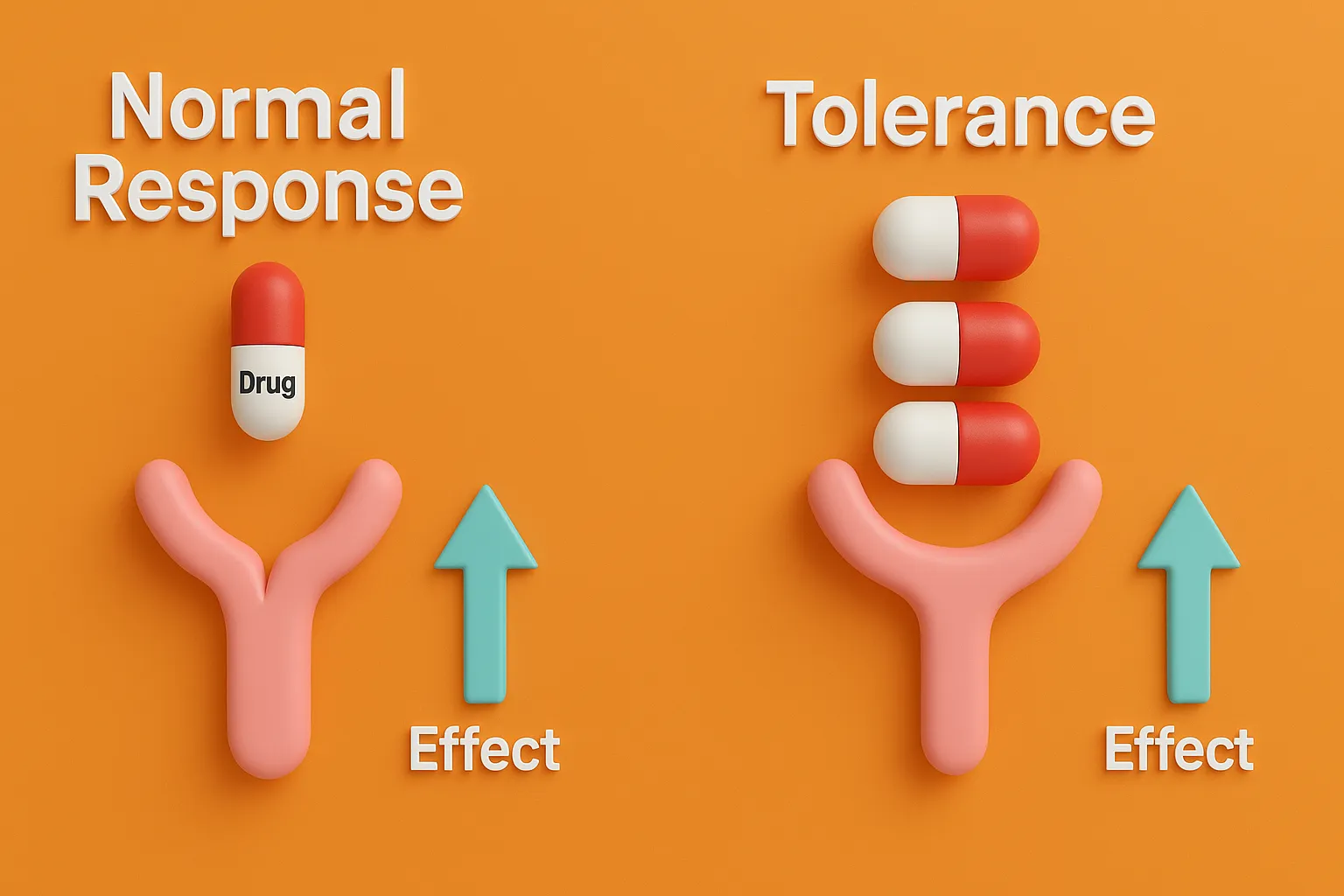
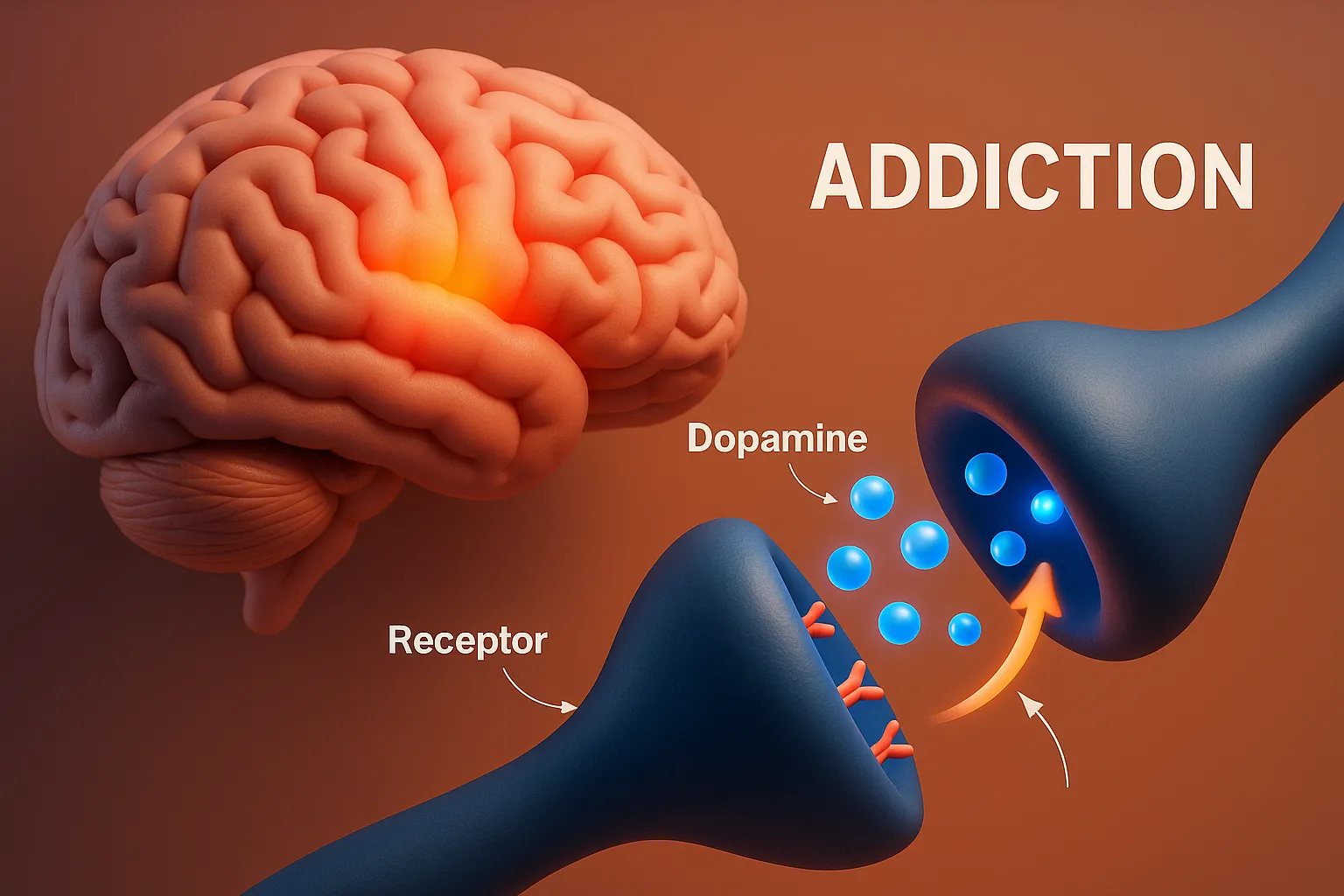
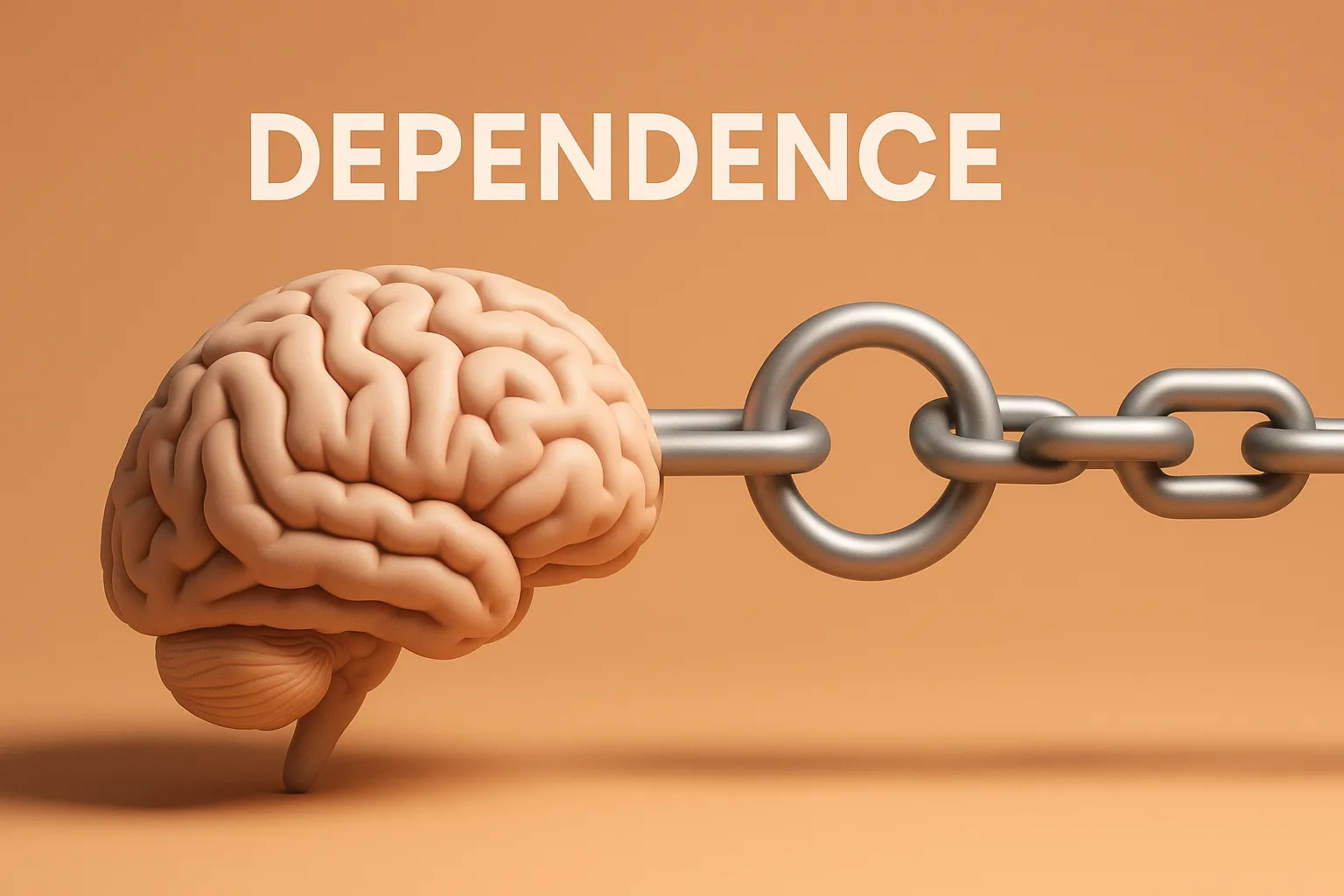
Distribution of Drugs
Distribution is the reversible transfer of a drug from the bloodstream to various tissues and organs. Once absorbed, drugs distribute throughout the body, moving into different tissues and fluids. Distribution depends on: Blood Flow (Perfusion Rate) Organs with higher blood flow (brain, liver, kidneys) get drug supply more rapidly. Skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and skin … Read more