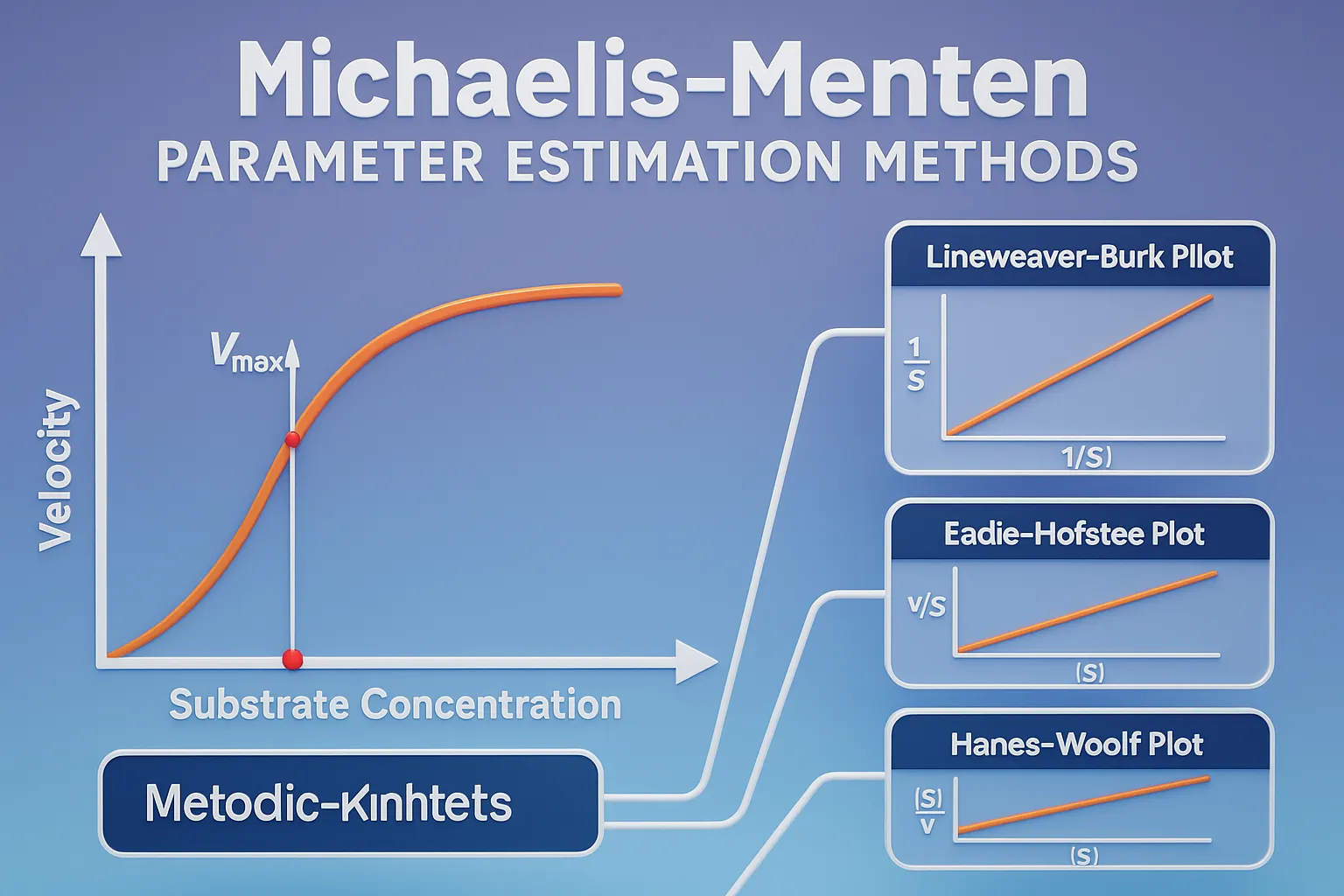
Michaelis-Menten Parameter Estimation Methods
Michaelis-Menten Parameter Estimation Methods determine Km and Vmax values using graphical and computational approaches. Michaelis-Menten Parameter Estimation Methods Several methods estimate Vmax and Km from experimental data: Lineweaver-Burk Plot (Double Reciprocal Plot) By taking the reciprocal of the Michaelis-Menten equation: $\frac{1}{V} = \frac{K_m}{V_{\text{max}}} \cdot \frac{1}{[S]} + \frac{1}{V_{\text{max}}}$ Plot 1/V 1/[S], resulting in a straight line. … Read more