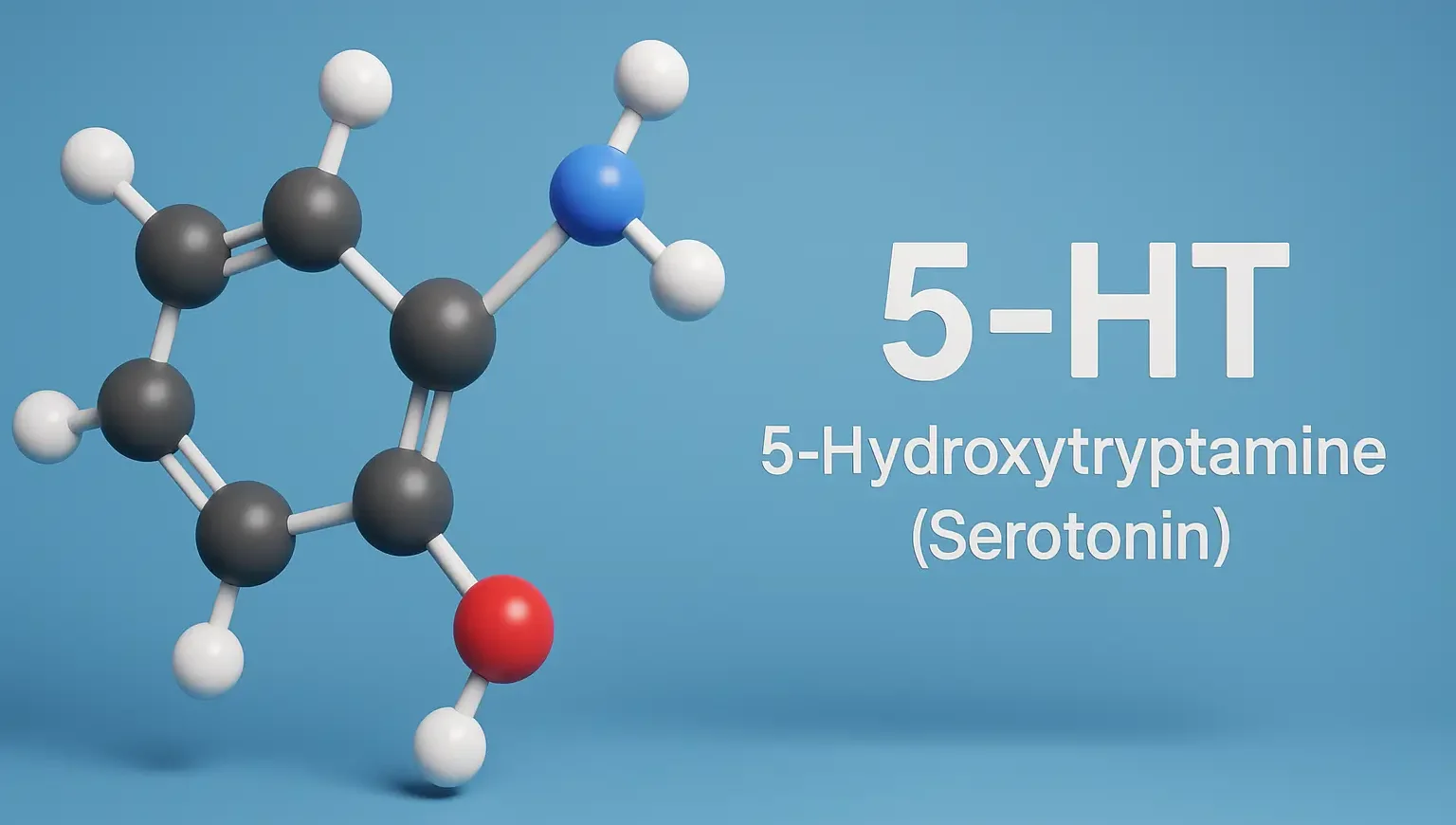
5-HT (5-Hydroxytryptamine) (Serotonin)
Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter derived from the amino acid tryptophan. 5-HT (5-Hydroxytryptamine) (Serotonin) influences a wide range of physiological and behavioral processes. Synthesis: From the amino acid tryptophan by tryptophan hydroxylase and subsequent decarboxylation. Storage: High concentration in enterochromaffin cells in the gut, platelets, and in the CNS as a neurotransmitter. … Read more