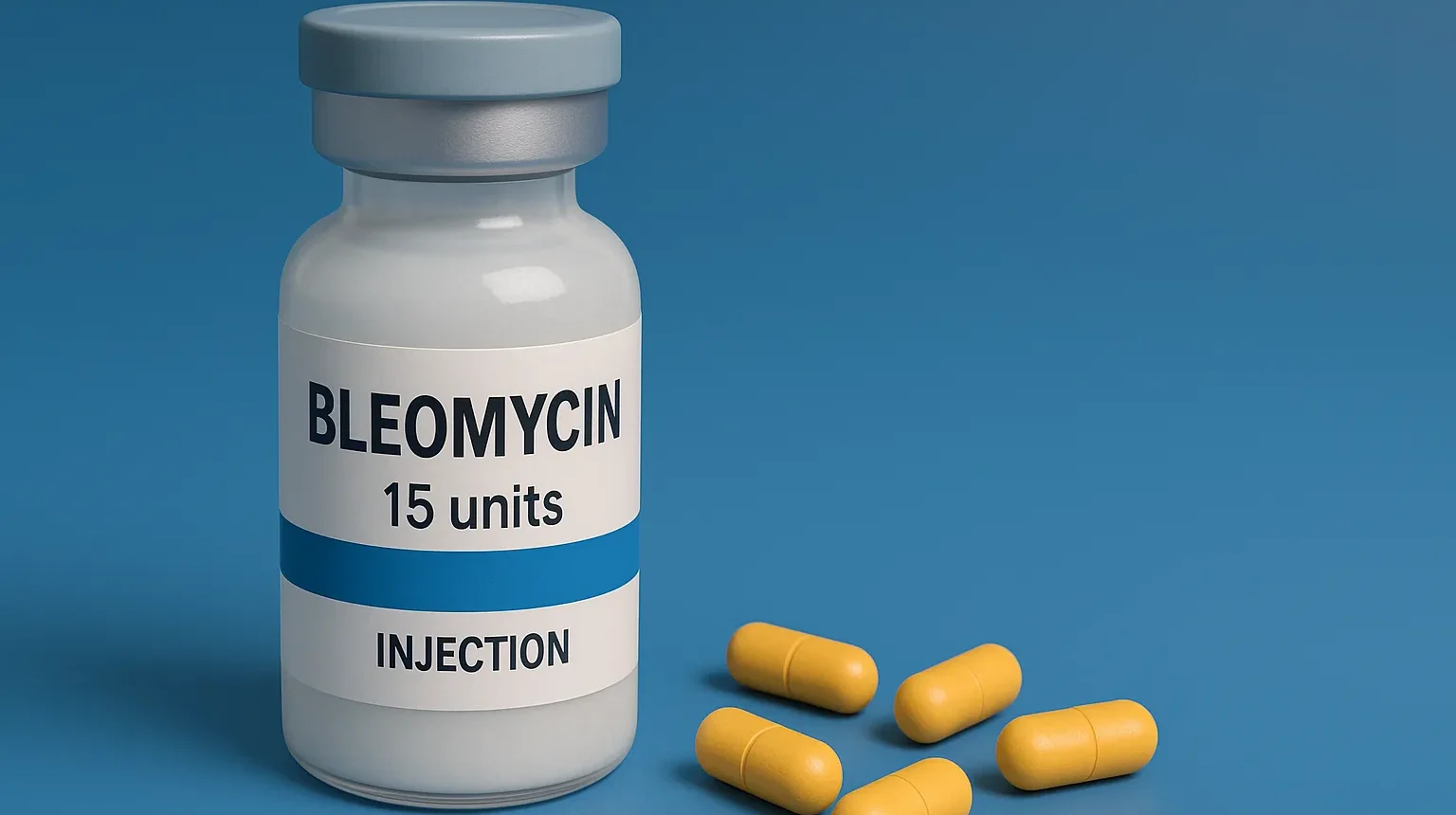
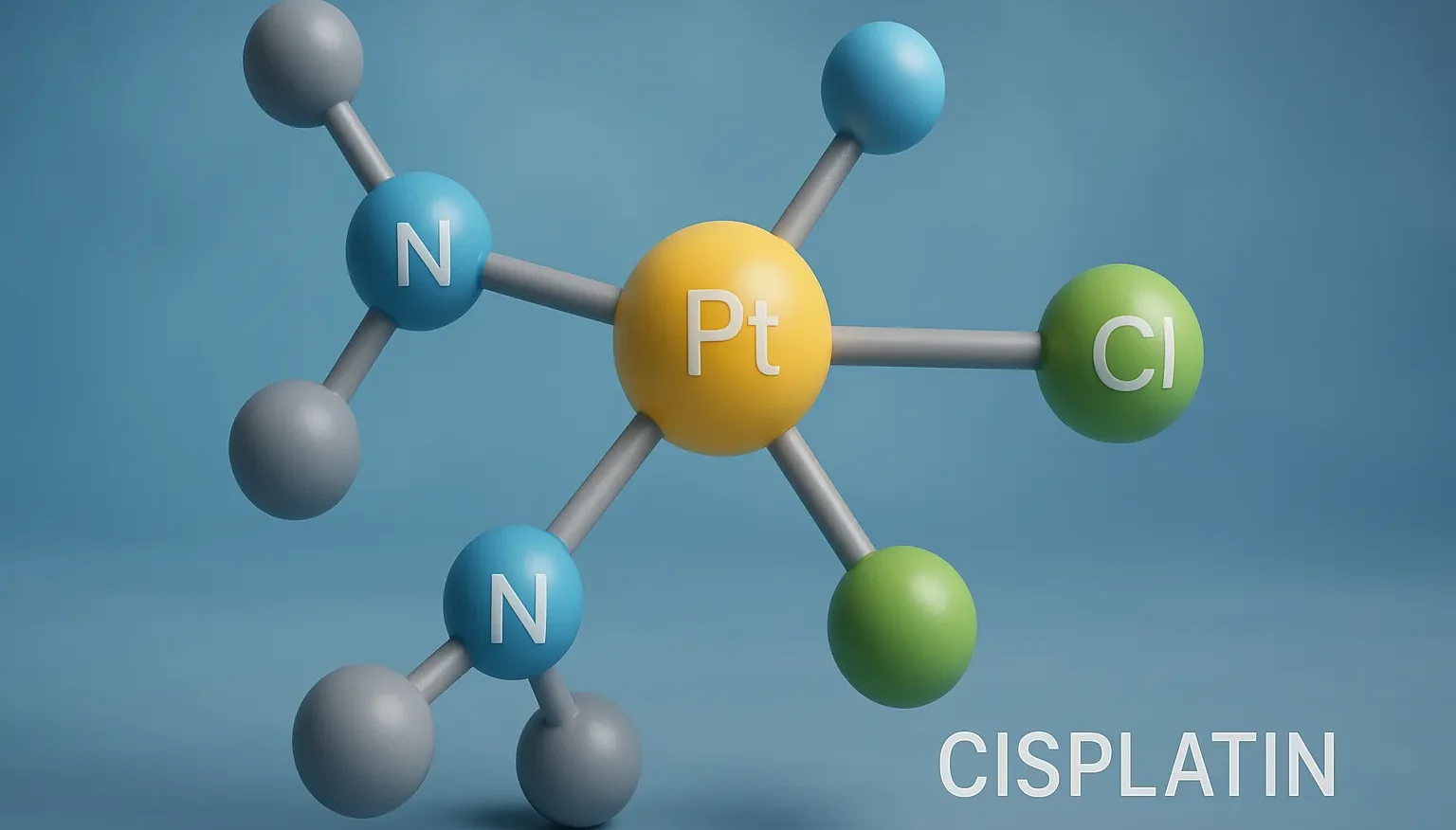
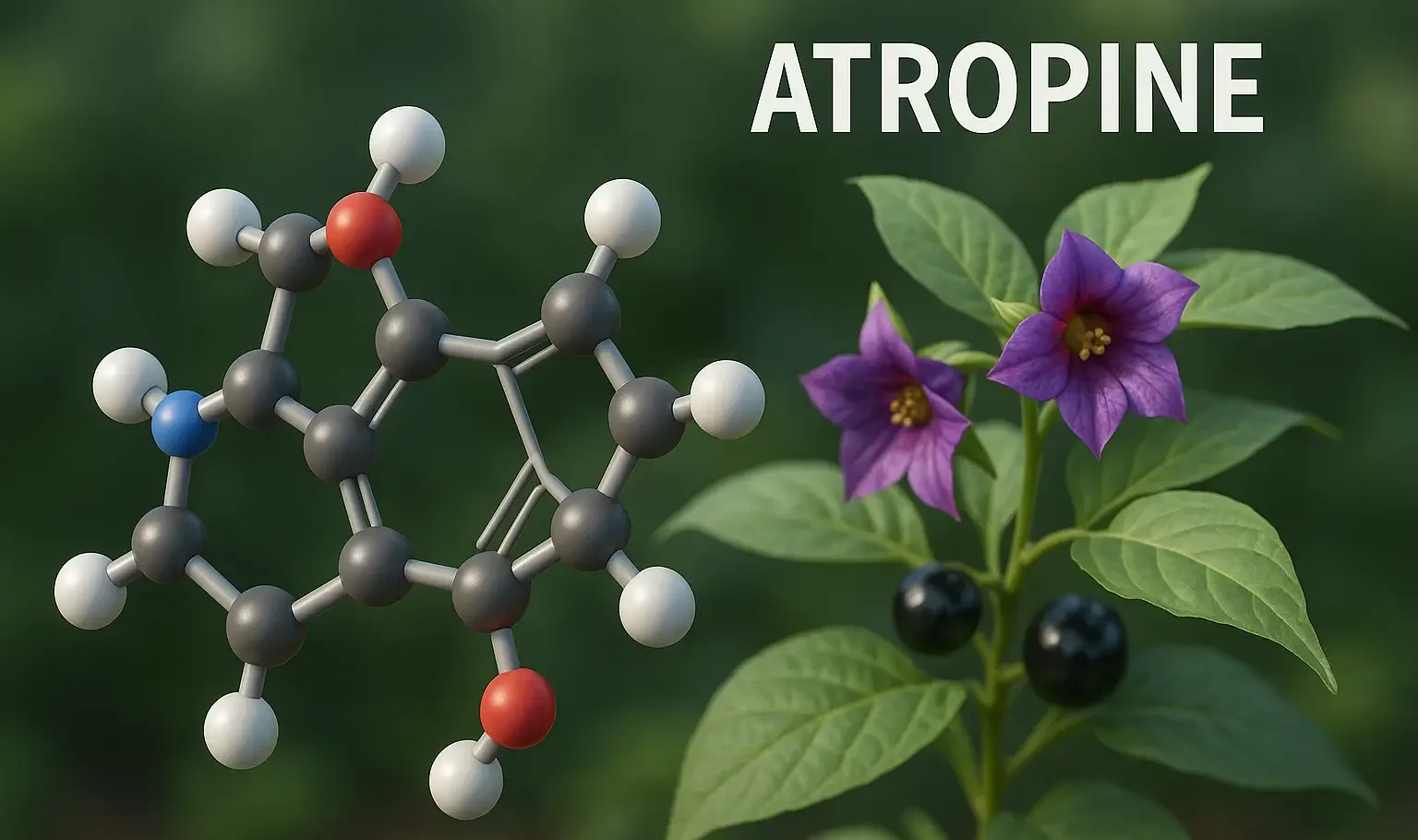
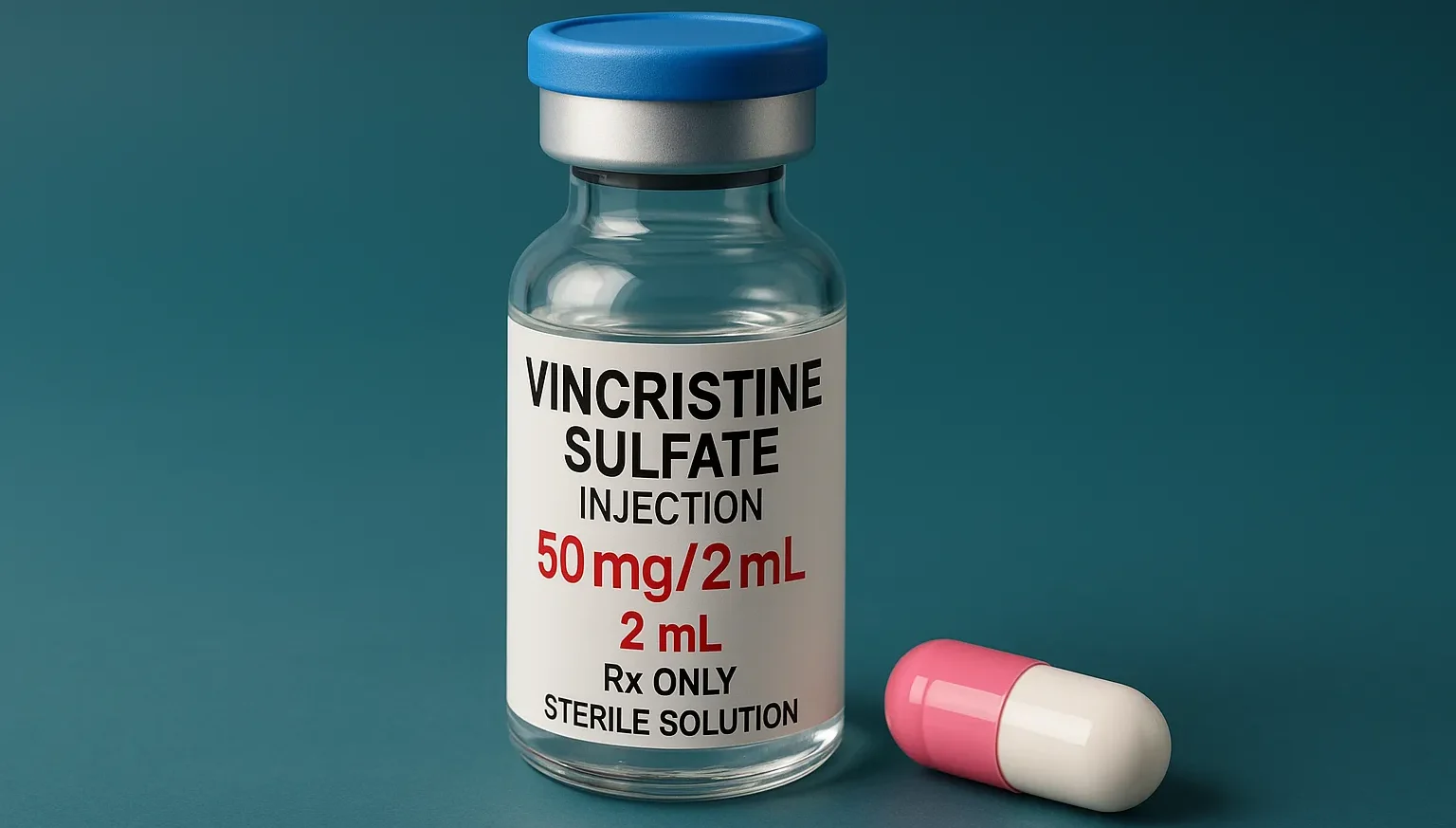
Quinine
Source and Occurrence of Quinine Quinine is obtained from the bark of the cinchona tree (Cinchona officinalis, Cinchona bark). It is a bitter alkaloid with antimalarial properties. Isolation Extraction: Bark Processing: The bark is dried and powdered. Alkaloid Extraction: Mixed with an acidic aqueous solution (e.g., dilute HCl) to convert quinine into its water-soluble salt. … Read more