Overview of Amino Acid Pathways:
- Amino acid-derived pathways leverage the plant’s pool of protein-building amino acids (e.g., lysine, tyrosine, tryptophan, ornithine) to construct a wide array of nitrogen-containing secondary metabolites, especially alkaloids.
Essential and Non-Essential Amino Acids:
| Category | Definition | Examples |
| Essential Amino Acids | Cannot be synthesized by the body or plants and must be obtained from external sources (e.g., diet). | Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Lysine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Threonine, Methionine, Histidine |
| Non-Essential Amino Acids | Can be synthesized internally from other metabolic precursors. | Glutamate, Aspartate, Alanine, Glycine, Proline, Serine, Tyrosine, Asparagine, Glutamine, Cysteine, Arginine |
Key Steps and Main Routes:
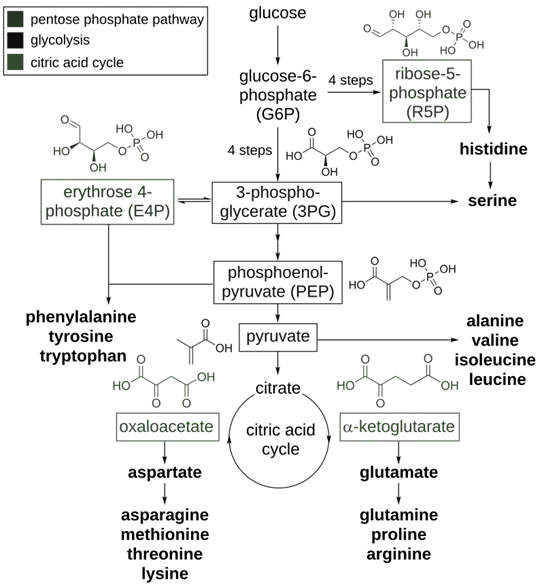
-
Transamination and Amino Acid Pool Formation
- Amino acids are synthesized from:
- Shikimic acid pathway (e.g., phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan).
- Glutamate and aspartate families.
- These amino acids serve as precursors for nitrogen-containing secondary metabolites.
- Amino acids are synthesized from:
-
Alkaloid Biosynthesis
- Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing ring structures derived from specific amino acids:
- Tryptophan → Indole alkaloids (e.g., vinblastine).
- Tyrosine → Isoquinoline alkaloids (e.g., morphine).
- Ornithine/Arginine → Tropane alkaloids (e.g., atropine) and pyrrolidine alkaloids.
- Biosynthesis involves decarboxylation and cyclization of amino acids into complex structures.
- Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing ring structures derived from specific amino acids:
-
Cyanogenic Glycosides and Glucosinolates
- Cyanogenic glycosides: Derived from amino acids like tryptophan or phenylalanine and release cyanide upon tissue damage, aiding in plant defense (e.g., amygdalin in stone fruits).
- Glucosinolates: Sulfur-containing compounds derived from amino acids like methionine and play a role in pest and pathogen resistance (e.g., in Brassicaceae plants).
Major Secondary Metabolites from Amino Acid Pathways:
- Alkaloids: Morphine, nicotine, vinblastine.
- Sulfur Compounds: Glucosinolates.
- Cyanogenic Glycosides: Amygdalin.
Biological Significance:
- Defense: Alkaloids deter herbivory (e.g., nicotine).
- Pharmacology: Medicinal alkaloids (e.g., morphine, vincristine).
- Signaling: Nitrogen-containing compounds function as signals or hormonal precursors.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos