The Anatomy of pancreas is a glandular organ behind the stomach that aids digestion and regulates blood sugar by producing insulin and other hormones.
Anatomy of Pancreas:
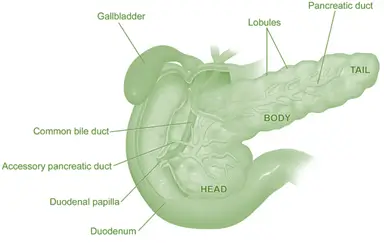
- The pancreas is a glandular organ located behind the stomach and near the duodenum.
- It is elongated and has a head, body, and tail. It is composed of two types of tissue: exocrine and endocrine.
- Exocrine tissue makes up the majority of the pancreas and consists of small, grape-like clusters called acini.
- The endocrine tissue is found in small clusters called islets of Langerhans.
Advertisements
Functions:
The pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine functions.
1. Endocrine function:
- The islets of Langerhans produce hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels in the body.
2. Exocrine function:
- The acini secrete digestive enzymes, and an alkaline fluid called pancreatic juice.
- These enzymes include proteases for protein digestion, amylases for carbohydrate digestion, and lipases for fat digestion.
- The alkaline fluid neutralizes the acidic chyme from the stomach, creating a suitable environment for the enzymes to function effectively in the duodenum.
Advertisements