- Anterior Pituitary Hormones: Analogues and Their Inhibitors include GnRH analogues and dopamine agonists.
- Anterior Pituitary Hormones: Analogues and Their Inhibitors regulate growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
Physiology of the Anterior Pituitary
- The anterior pituitary secretes several key hormones regulated by hypothalamic-releasing and inhibiting factors.
Advertisements
Hormones Produced:
- Growth Hormone (GH)
- Prolactin
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Regulation:
- Stimulation: Releasing factors such as GHRH stimulate GH secretion.
- Inhibition: Inhibitory factors like somatostatin suppress GH release.
Advertisements
Key Anterior Pituitary Hormones
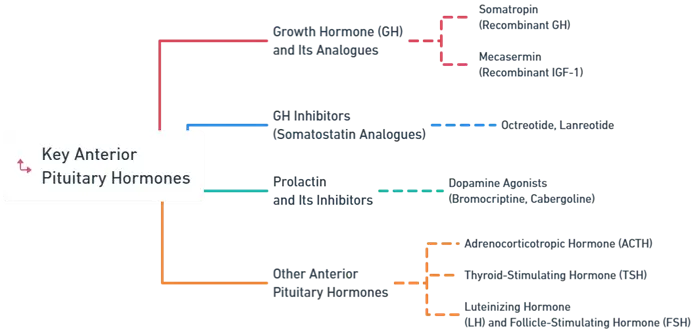
1. Growth Hormone (GH) and Its Analogues
- Somatropin (Recombinant GH):
- Uses: GH deficiency (children/adults), Turner syndrome, chronic kidney disease.
- Adverse Effects: Edema, arthralgia, hyperglycemia.
- Mecasermin (Recombinant IGF-1):
- Uses: GH insensitivity in children.
- Adverse Effects: Hypoglycemia (monitor glucose).
Advertisements
2. GH Inhibitors (Somatostatin Analogues):
- Octreotide, Lanreotide:
3. Prolactin and Its Inhibitors
- Dopamine Agonists (Bromocriptine, Cabergoline):
- Mechanism: Suppress prolactin secretion.
- Uses: Hyperprolactinemia (galactorrhea, infertility), prolactin-secreting adenomas, Parkinson’s disease.
- Adverse Effects: Nausea, headache, orthostatic hypotension, psychiatric disturbances.
4. Other Anterior Pituitary Hormones
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH):
- Analogues: Synthetic ACTH (cosyntropin) for adrenal insufficiency testing.
- Inhibitors: Indirectly inhibited by glucocorticoids via negative feedback.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH):
- Analogues/Inhibitors: Direct pharmacological agents are less common; instead, thyroid hormone analogues or antithyroid drugs indirectly influence TSH levels via feedback.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
- Analogues: GnRH analogues (e.g., leuprolide) for prostate cancer, fertility treatments.
- Inhibitors: GnRH antagonists (e.g., degarelix) suppress LH and FSH quickly.
Advertisements
Clinical Applications
- Acromegaly: Managed with GH inhibitors like octreotide.
- Prolactinomas: Treated with dopamine agonists.
- Diagnostic Testing: ACTH analogues used to assess adrenal function.
- Reproductive Disorders: GnRH analogues and antagonists used in fertility treatments and hormone-sensitive cancers.