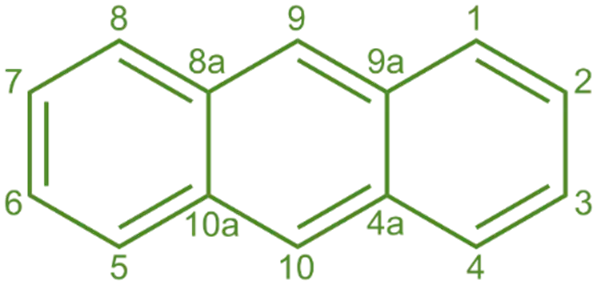
Structure of Anthracene:
- It is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with three fused benzene rings arranged in a linear structure.
- The molecular formula is C14H10, and it is isomeric with phenanthrene.
Advertisements
Synthesis of Anthracene:
-
From Coal Tar:
- Anthracenes are also isolated from the high boiling fraction of coal tar.
-
Laboratory Synthesis (Elbs Reaction):
- Cyclodehydration: Ortho-benzoyltoluene is cyclodehydrated to form anthracenes.
- Aromatization: The intermediate is aromatized to produce anthracenes.
- the intermediate is aromatized to produce anthracenes.
-
O-Benzoyltoluene → Cyclodehydration → Anthracenes
-
Reactions of Anthracene:
-
Electrophilic Substitution:
- Nitration: Anthracenes react with nitric acid to form 9-nitroanthracene.
- C14H10 + HNO3 → H2SO4 (reagents) → C14H9NO2 + H2O
- Sulfonation: Anthracenes react with sulfuric acid to form anthracene sulfonic acid.
-
C14H10 + H2SO4 (reagents) → C14H9SO3H + H2O
-
- Nitration: Anthracenes react with nitric acid to form 9-nitroanthracene.
-
Oxidation:
- Anthracenes can be oxidized to anthraquinone using chromic acid or other strong oxidizing agents.
-
C14H10 + 2[O] → C14H8(O)2
-
- Anthracenes can be oxidized to anthraquinone using chromic acid or other strong oxidizing agents.
Advertisements
Derivatives:
- Anthraquinone: An important industrial chemical used in the production of dyes and hydrogen peroxide.
- Dyes: Anthracene derivatives are the basis of various dyes, especially anthraquinone dyes.
Medicinal Uses:
- Anthraquinone Derivatives: Many anthraquinone derivatives are used in medicine as laxatives (e.g., senna, cascara), and some have been studied for their anti-cancer properties.
Advertisements

