- Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways (bronchi) that carry air in and out of the lungs.
- This inflammation and constriction can cause episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing, particularly at night or early in the morning.
- Asthma affects people of all ages, but it often begins during childhood.
Pathophysiology and Mechanism
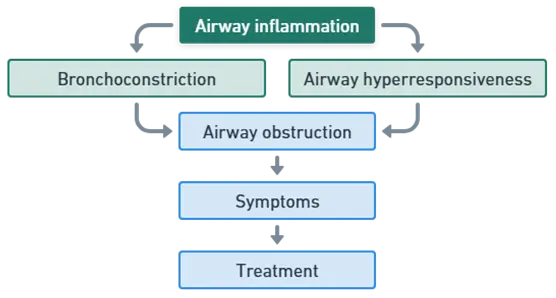
Asthma involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The pathophysiology includes three main processes:
-
Airway Inflammation
- The immune system overreacts to triggers like allergens, irritants, or infections.
- Causes increased mucus production and swelling of airway walls, narrowing the passages.
-
Bronchospasm
- Triggers cause the smooth muscles around the airways to contract.
- Further narrows the airways, leading to breathing difficulties.
-
Airway Hyperresponsiveness
- Airways are more sensitive to various stimuli.
- Increases the likelihood of bronchospasm and inflammation when exposed to triggers.
Advertisements
Triggers of Asthma
- Allergens: Pollen, mold spores, pet dander, dust mites.
- Respiratory Infections: Common cold, flu.
- Irritants: Tobacco smoke, air pollution, strong odors.
- Physical Activity: Exercise-induced asthma.
- Environmental Factors: Cold air, changes in temperature and humidity.
- Emotional Factors: Stress and strong emotions.
- Medications: Aspirin, NSAIDs.
- Other Conditions: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Symptoms of Asthma
- Wheezing: High-pitched whistling sound during breathing.
- Shortness of Breath
- Chest Tightness or Pain
- Coughing: Particularly at night or early morning.
- Difficulty Sleeping: Due to breathing problems or coughing.
Diagnosis
- Medical History and Physical Examination
- Lung Function Tests: Such as spirometry to assess airway obstruction.
Management of Asthma
- Asthma management involves medications and lifestyle adjustments to control symptoms and prevent attacks.
Medications
-
Quick-Relief Medications (Rescue)
- Provide rapid relief by relaxing airway muscles.
- Examples:
- Short-acting beta-agonists (e.g., albuterol)
- Anticholinergics (e.g., ipratropium)
-
Long-Term Control Medications
- Reduce inflammation and prevent symptoms over time.
- Taken daily, regardless of symptoms.
- Examples:
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Long-acting beta-agonists
- Leukotriene modifiers
Advertisements
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Healthy Diet
- Regular Exercise
- Avoiding Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure.
- Smoking Cessation
- Stress Management
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
- With proper management, individuals with asthma can control their symptoms and maintain normal activity levels.

Other subjects is unable to open sir /madam, can you please fix it so that everyone can use it
Hi Dheeraj, Other subject are still not ready on website, will be available after some time.