- Atenolol is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called beta-blockers. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), angina (chest pain), and to improve survival after a heart attack.
- Atenolol works by blocking the action of certain natural chemicals in the body, such as adrenaline, on the heart and blood vessels.
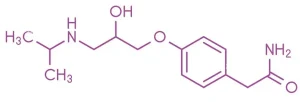
Chemical Structure & Formula:
- A beta₁-selective blocker featuring an aromatic ring linked to a hydroxypropanolamine side chain.
- Approximate Formula: C₁₄H₂₂N₂O₃

Mechanism of Action:
- Selectively blocks β₁ receptors, predominantly in cardiac tissue.
- This leads to a reduction in heart rate, contractility, and cardiac output with minimal impact on β₂ receptors.
Side Effects of Atenolol:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Cold extremities
- Mild bradycardia and hypotension
- Rare gastrointestinal disturbances
Clinical Uses of Atenolol:
- Employed for the management of hypertension, angina pectoris, and secondary prevention following myocardial infarction.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

Hi, I apologize for including a direct link, but I want to make it clearer which medication I’m referring to. I noticed that the page for Ternolol at https://pillintrip.com//medicine/ternolol returns a 404 error. Could you please clarify if Ternolol is similar to other beta-blockers like Atenolol, and do you have any reliable information about its proper use or indications? Thanks in advance!
Thanks for pointing that out! It looks like the link is broken — we’ll get that fixed. Ternolol is indeed similar to other beta-blockers like Atenolol and is used to manage things like high blood pressure and heart issues. Always best to check with a doctor or pharmacist for specific info on use. Appreciate your comment!