Introduction of Atherosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaques made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances in the arteries, leading to narrowed and hardened arteries.
Types
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Affects the arteries supplying blood to the heart.
- Carotid Artery Disease: Affects the arteries supplying blood to the brain.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Affects the arteries supplying blood to the limbs.
- Renal Artery Stenosis: Affects the arteries supplying blood to the kidneys.
Etiology
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol contribute to plaque formation.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure damages the inner lining of arteries.
- Smoking: Damages the endothelium (inner lining) of arteries.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels increase the risk of plaque buildup.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can accelerate plaque development.
Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis
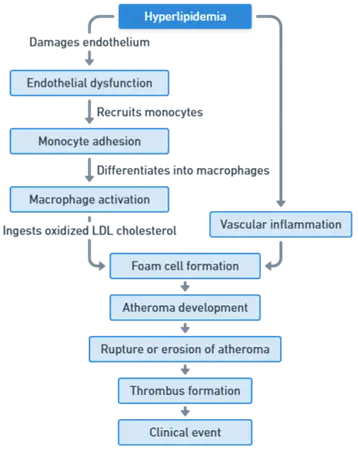
- Endothelial Injury: Damage to the inner lining of arteries initiates the process.
- Lipid Accumulation: Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol infiltrates the arterial wall.
- Inflammation: Immune response to lipid deposits leads to chronic inflammation.
- Plaque Formation: Smooth muscle cells and extracellular matrix proliferate, forming fibrous plaques.
Advertisements
Signs and Symptoms
- Asymptomatic: Often no symptoms until arteries are significantly narrowed or blocked.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Chest pain (angina) or heart attack.
- Carotid Artery Disease: Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Leg pain (claudication) during walking.
- Renal Artery Stenosis: Hypertension and kidney dysfunction.
Management and Treatment
-
Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Blood pressure and diabetes management
-
Medications:
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
- Antiplatelet Agents: Prevent blood clots.
- Antihypertensives: Control blood pressure.
- Diabetes Medications: Manage blood sugar levels.
-
Medical Procedures:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: Open narrowed arteries.
- Endarterectomy: Surgical removal of plaque.
- Bypass Surgery: Create new pathways for blood flow.

