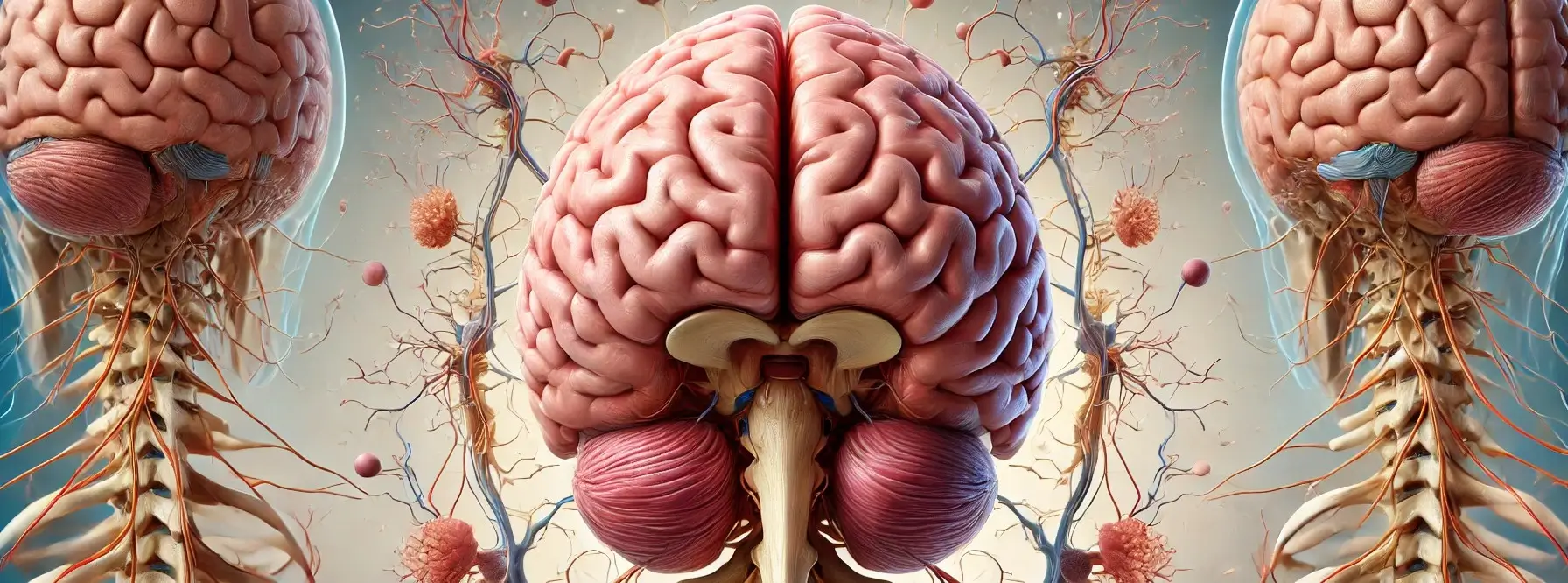
Cerebrum Structure And Functions
Cerebrum is the largest and most complex part of the human brain, responsible for higher cognitive functions such as thinking, learning, memory, language, and conscious perception. It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres (left and right) connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum, which enables communication between the two hemispheres. Cerebral … Read more