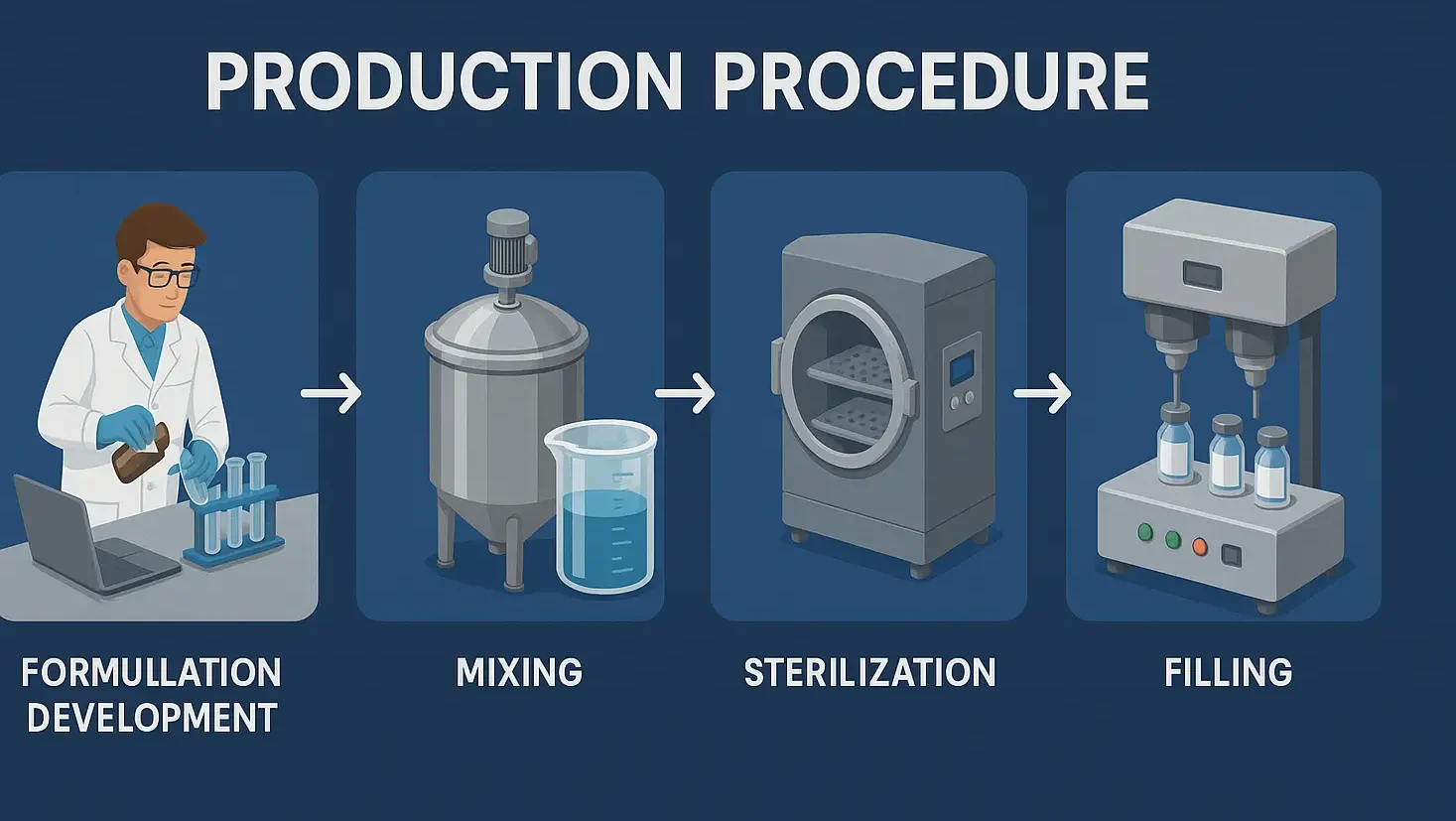
Classification of antihistamine
Below we have described the classification of antihistamine based on receptor type and generation with their roles in allergy relief and related conditions. Classification of antihistamine: The medications listed can be classified into three main categories: H1-antagonists (antihistamines), H2-antagonists (histamine H2 receptor blockers), and gastric proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs). Below is a proper classification of each: … Read more