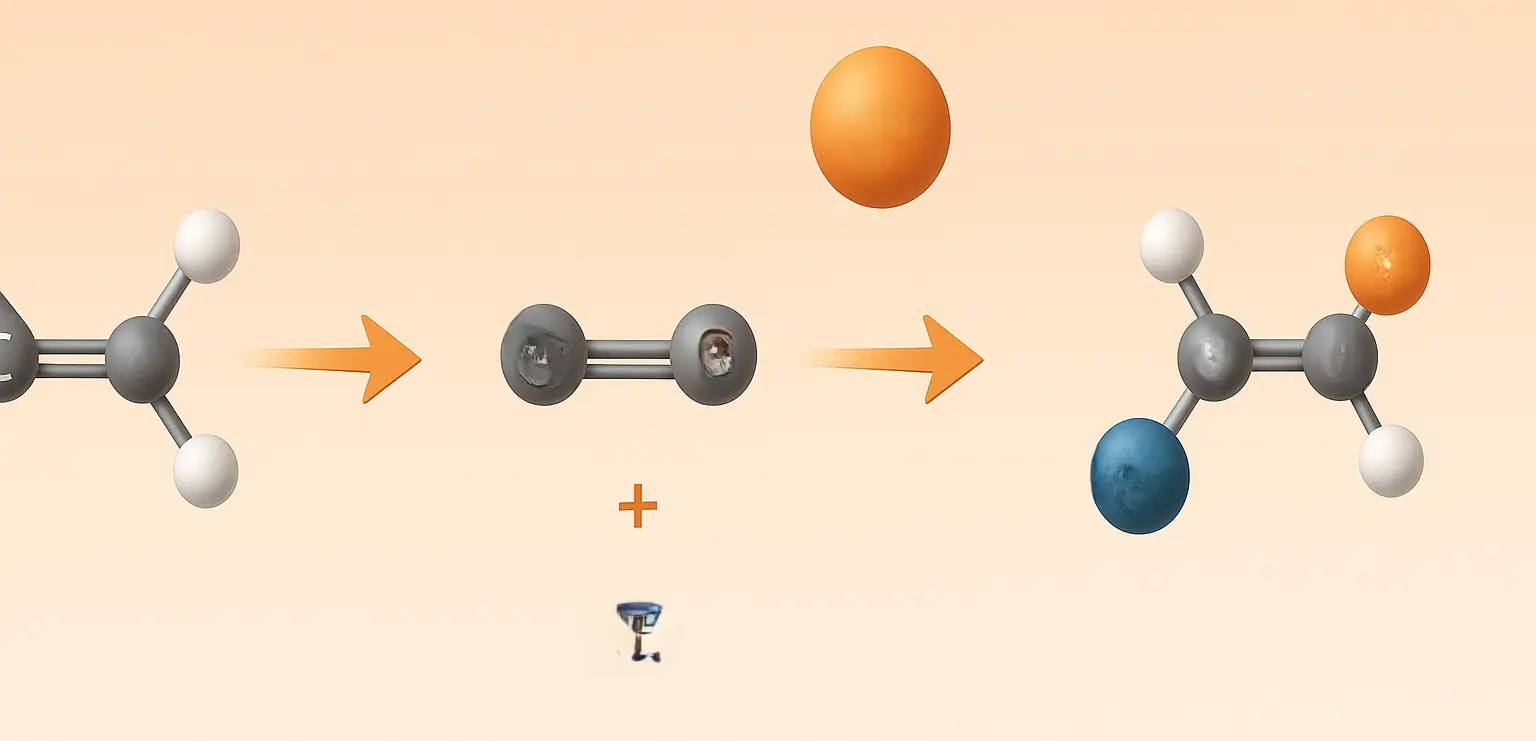
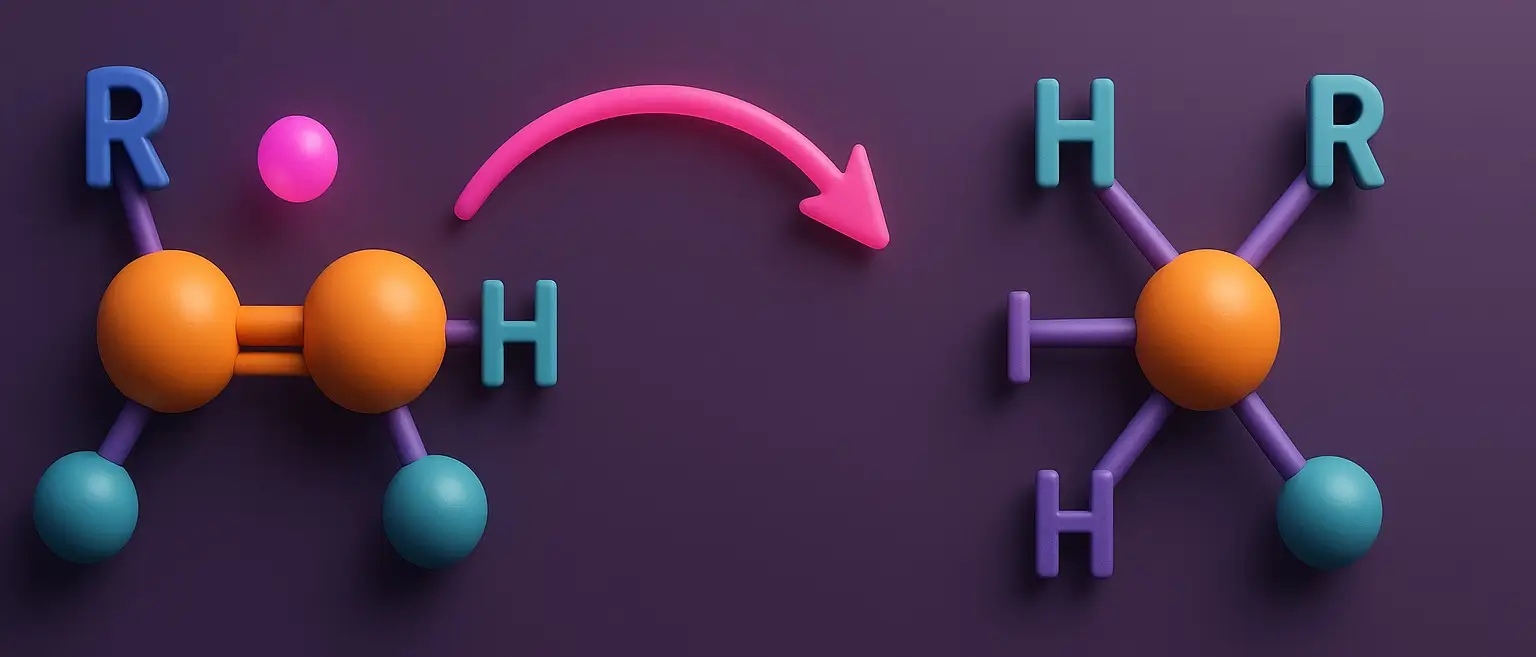
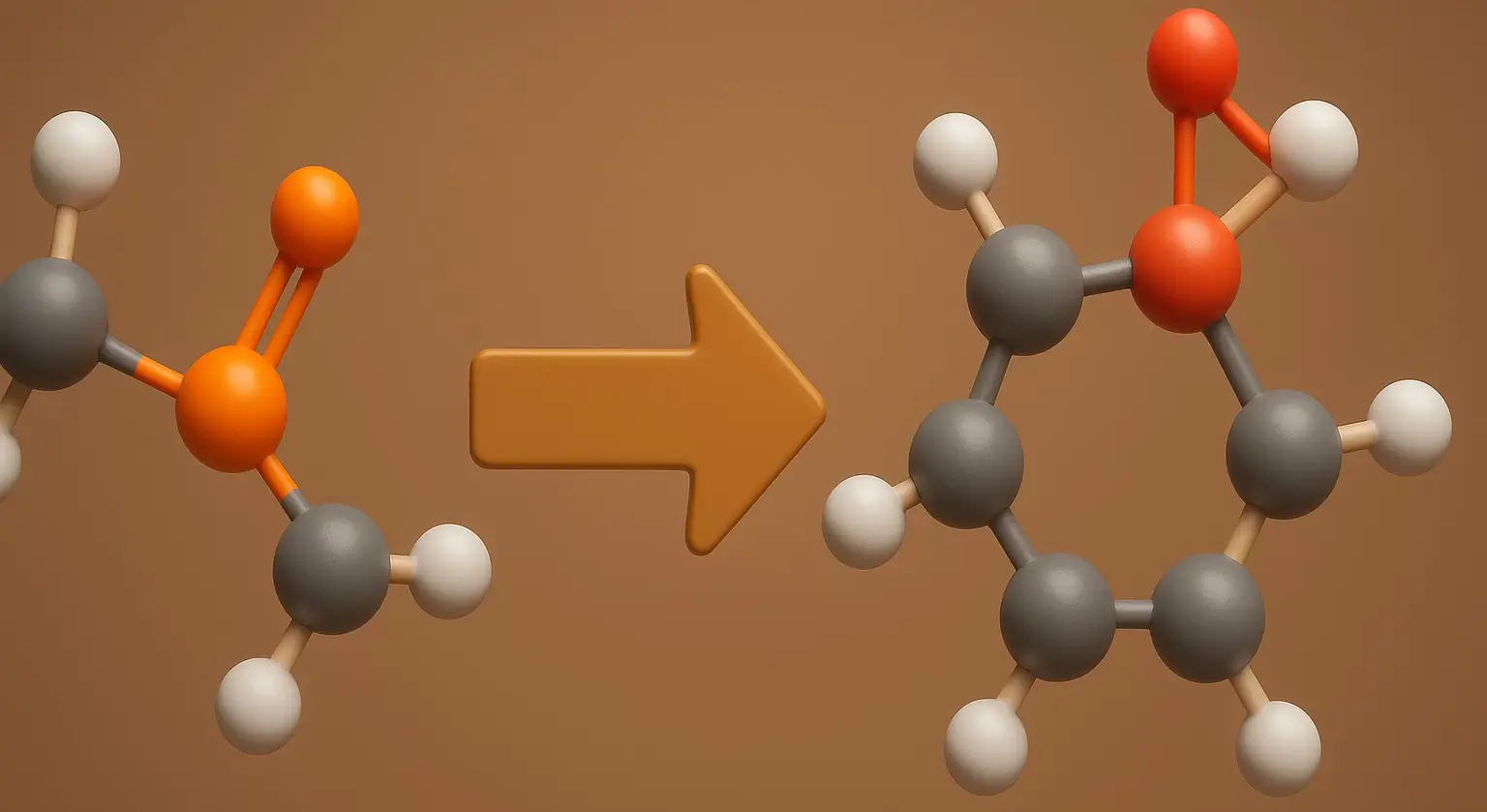
Electrophilic addition: an overview
Electrophilic addition is a fundamental chemical reaction where an electrophile and a nucleophile, typically an alkene or alkyne, combine to form a single bond. This process involves the conversion of a π bond into new σ bonds, playing a crucial role in the transformation of alkenes and alkynes into more complex organic compounds. Key Concepts … Read more