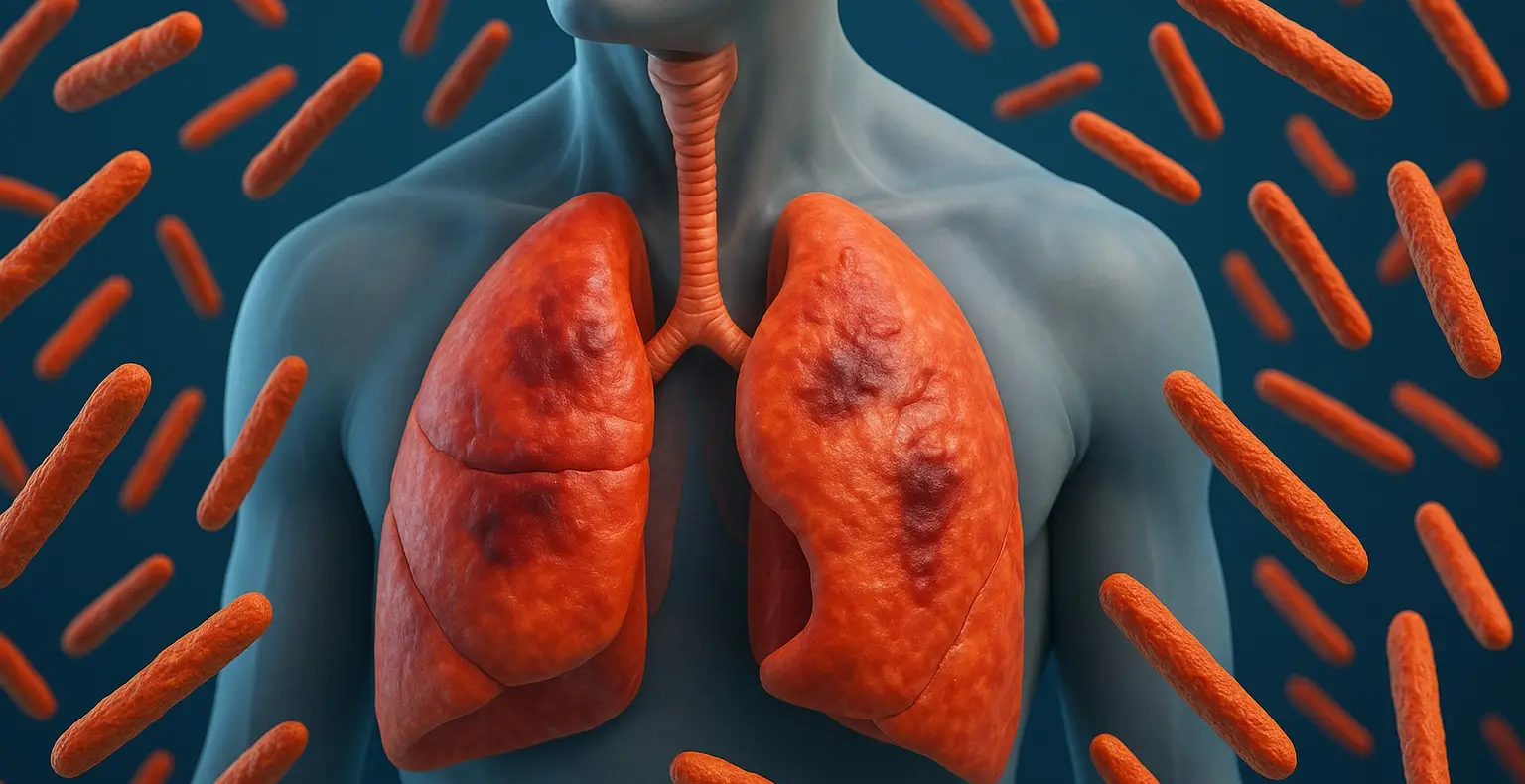
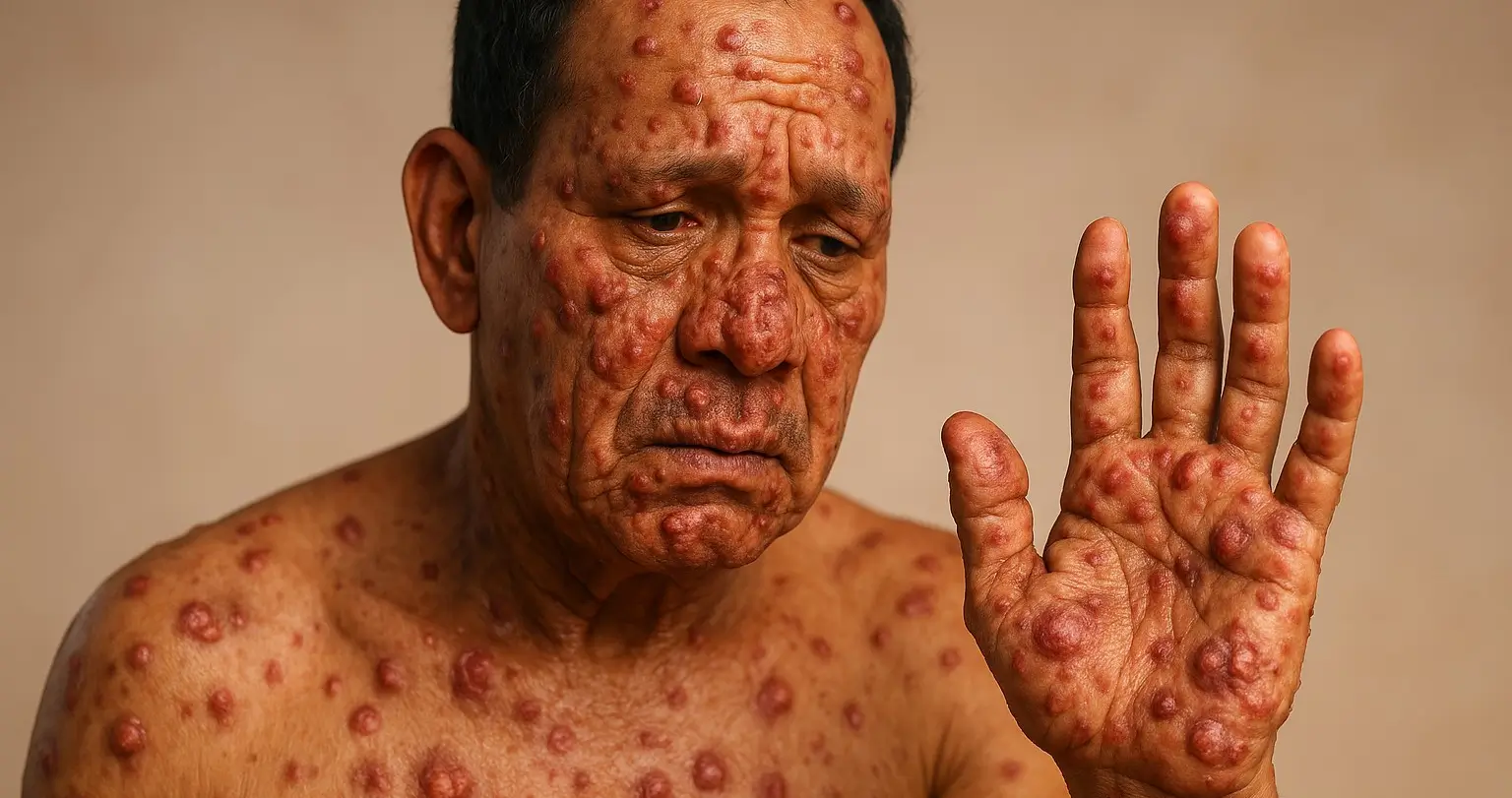
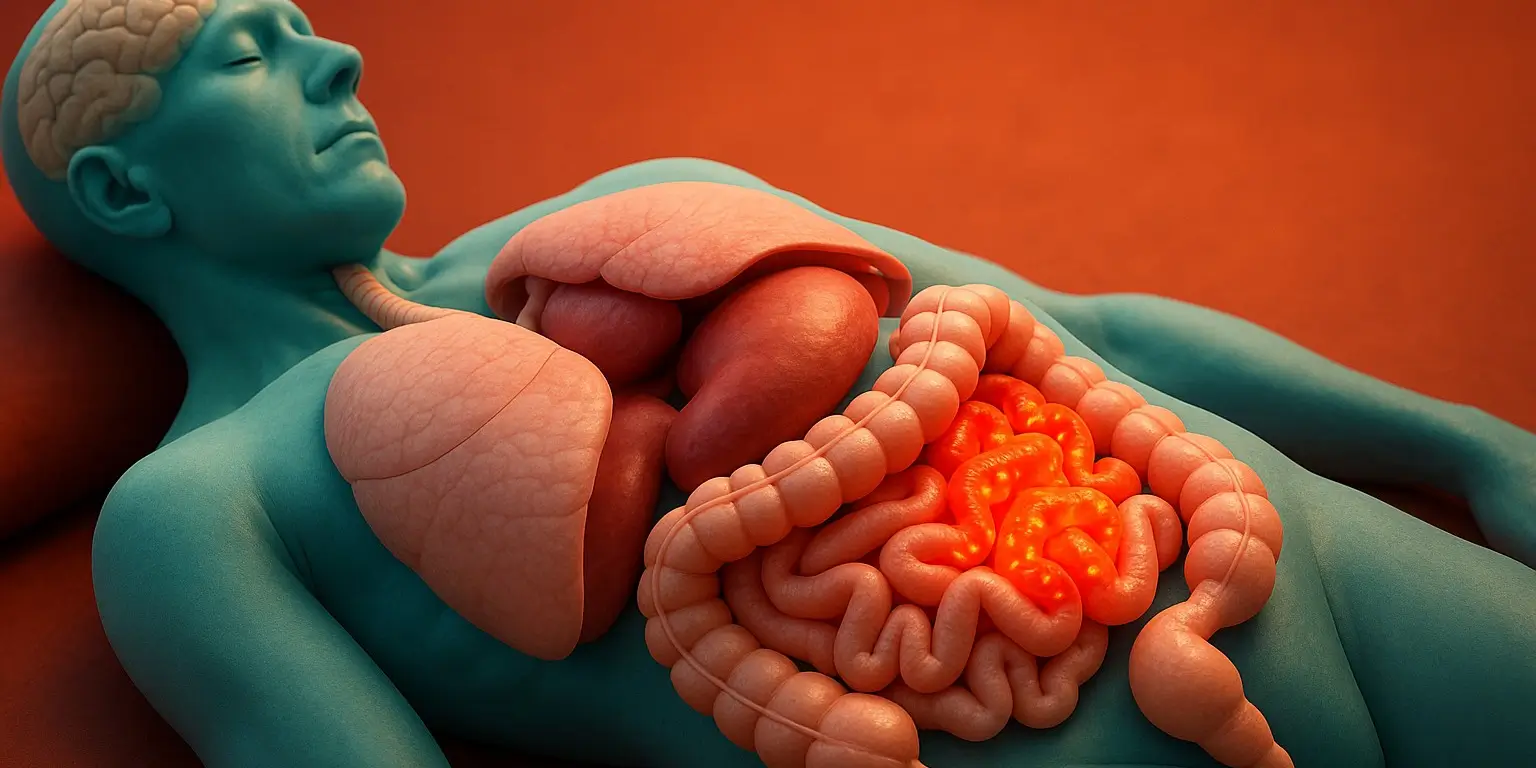
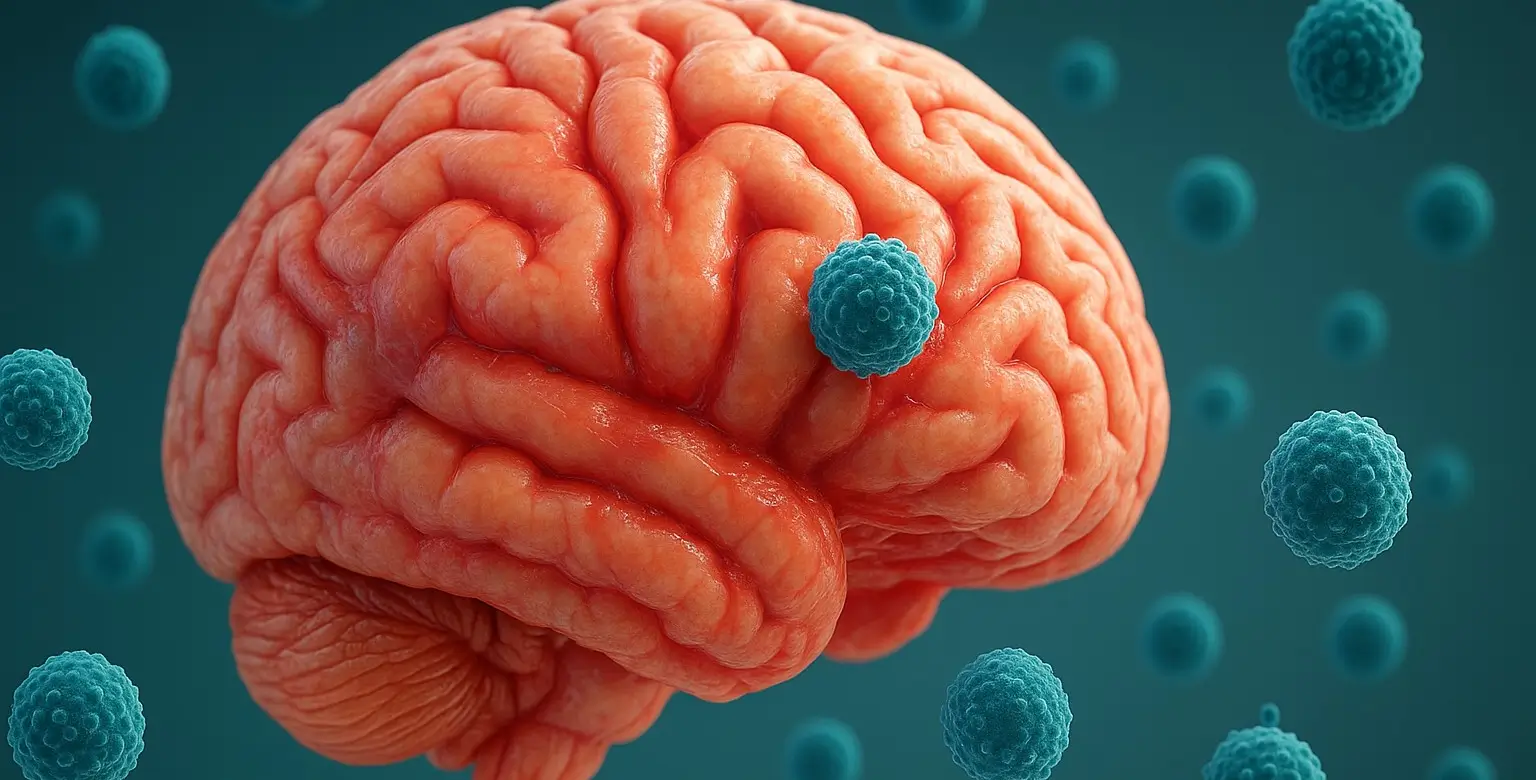
Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis is a potentially severe infectious disease primarily affecting the lungs (pulmonary TB) but can also affect other parts of the body (extrapulmonary TB). It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis Pulmonary TB: Persistent Cough: Lasting more than three weeks, sometimes producing blood (hemoptysis). Chest Pain: Painful breathing or … Read more