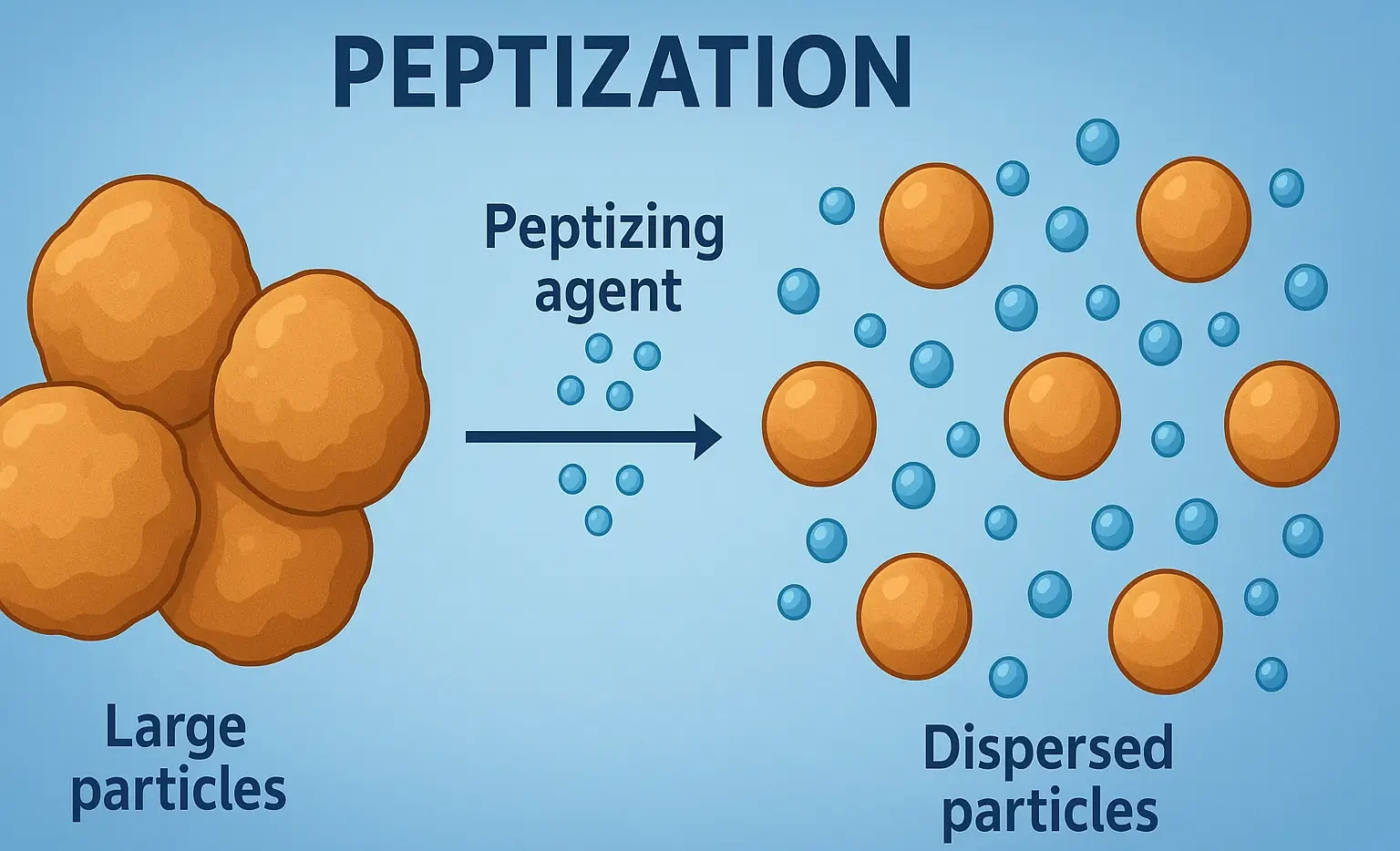
Synthesis of Acridine
Synthesis of Acridine covers Bernthsen condensation, Ullmann coupling, and intramolecular cyclization for dyes and drug discovery. Bernthsen Synthesis (Classical Method) Reactants: Diphenylamine + Carboxylic acid (or acid anhydride) Catalyst: Zinc chloride (ZnCl₂) Conditions: High temperature (~250–270 °C) Reaction: Diphenylamine + Formic acid → Acridine + Water Mechanism: Involves Friedel–Crafts acylation, cyclization, and dehydration. From Anthranilic … Read more