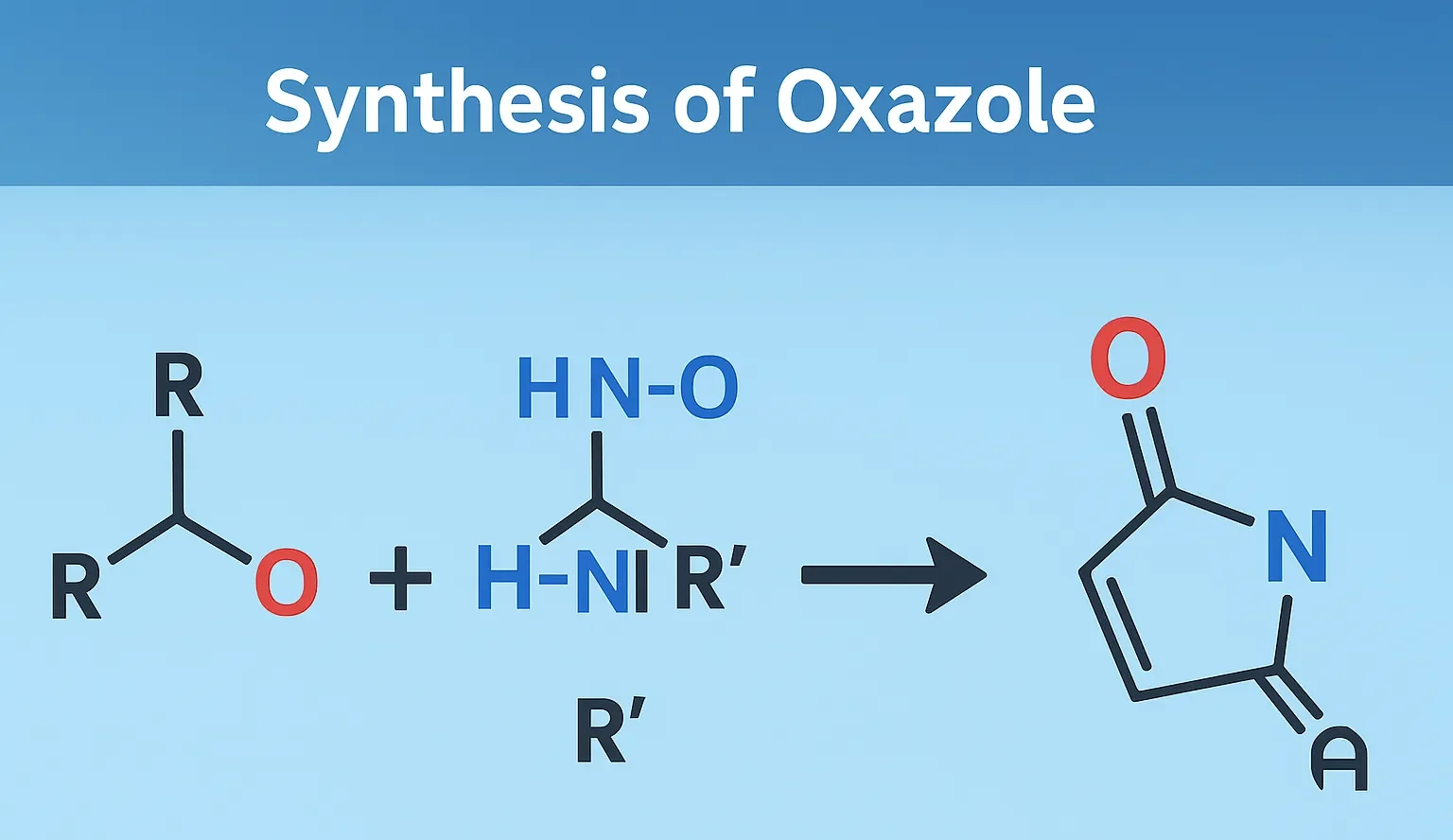
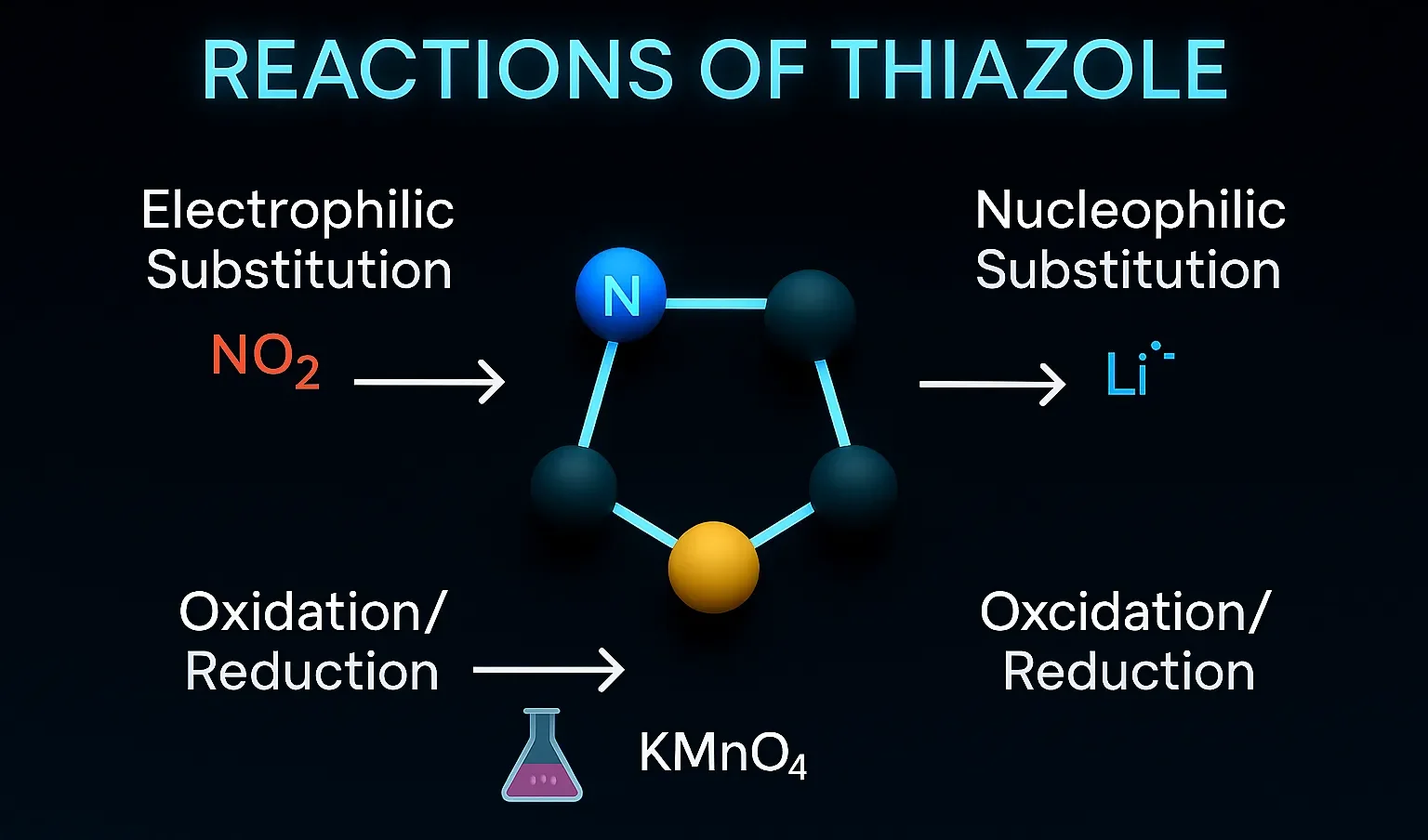
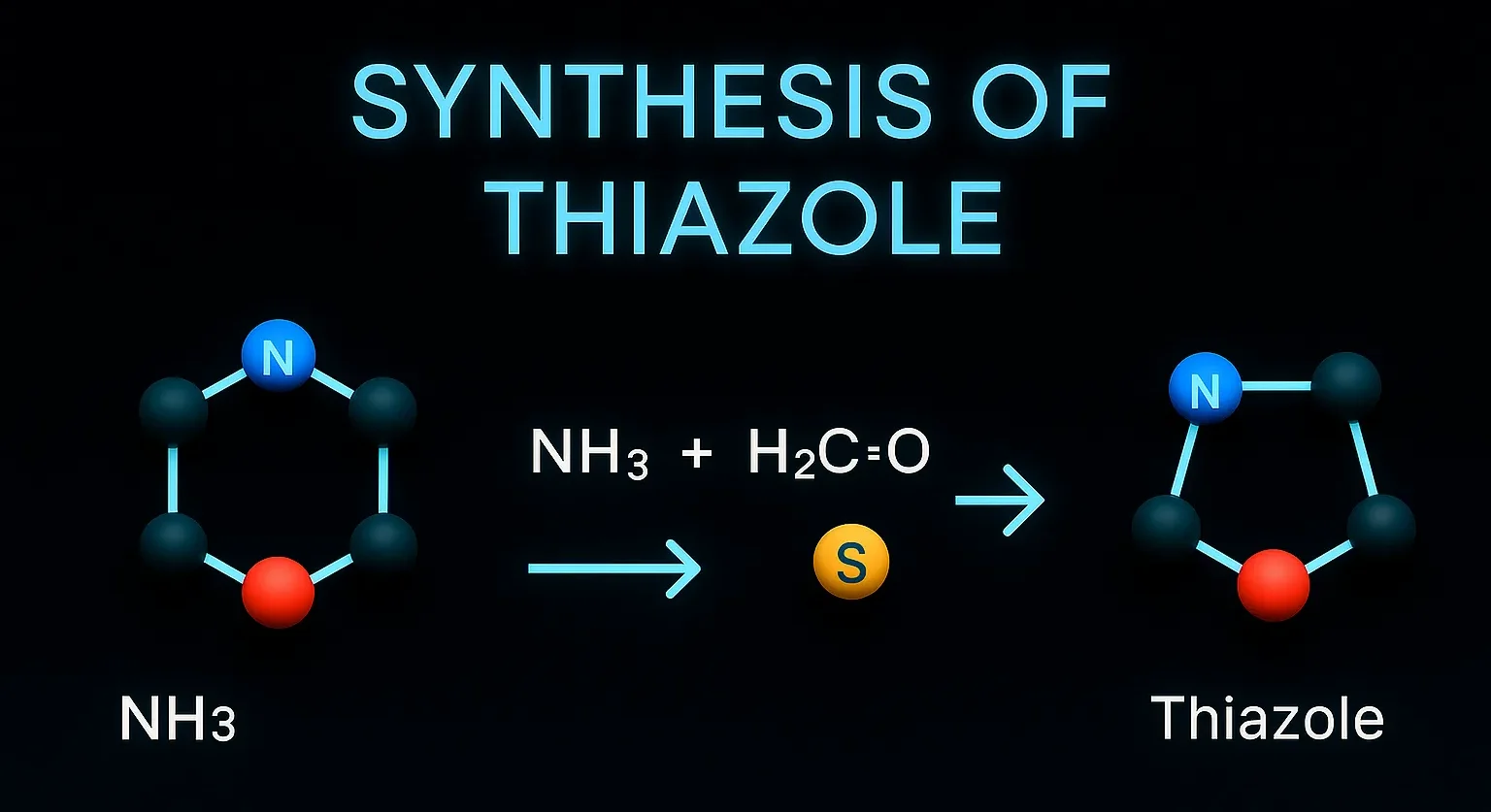
Piroxicam
Piroxicam blocks COX enzymes, reducing prostaglandin synthesis to relieve pain and swelling. It is an NSAID for long-term management of arthritis, pain, and inflammation. Chemical Formula: C₁₅H₁₃N₃O₄S Mechanism of Piroxicam: Non-selective COX inhibitor Long half-life (~50 hrs) Uses of Piroxicam: Chronic inflammatory conditions (OA, RA) Once-daily dosing Side Effects: GI irritation/ulceration Photosensitivity Headache Notes: Long-acting … Read more