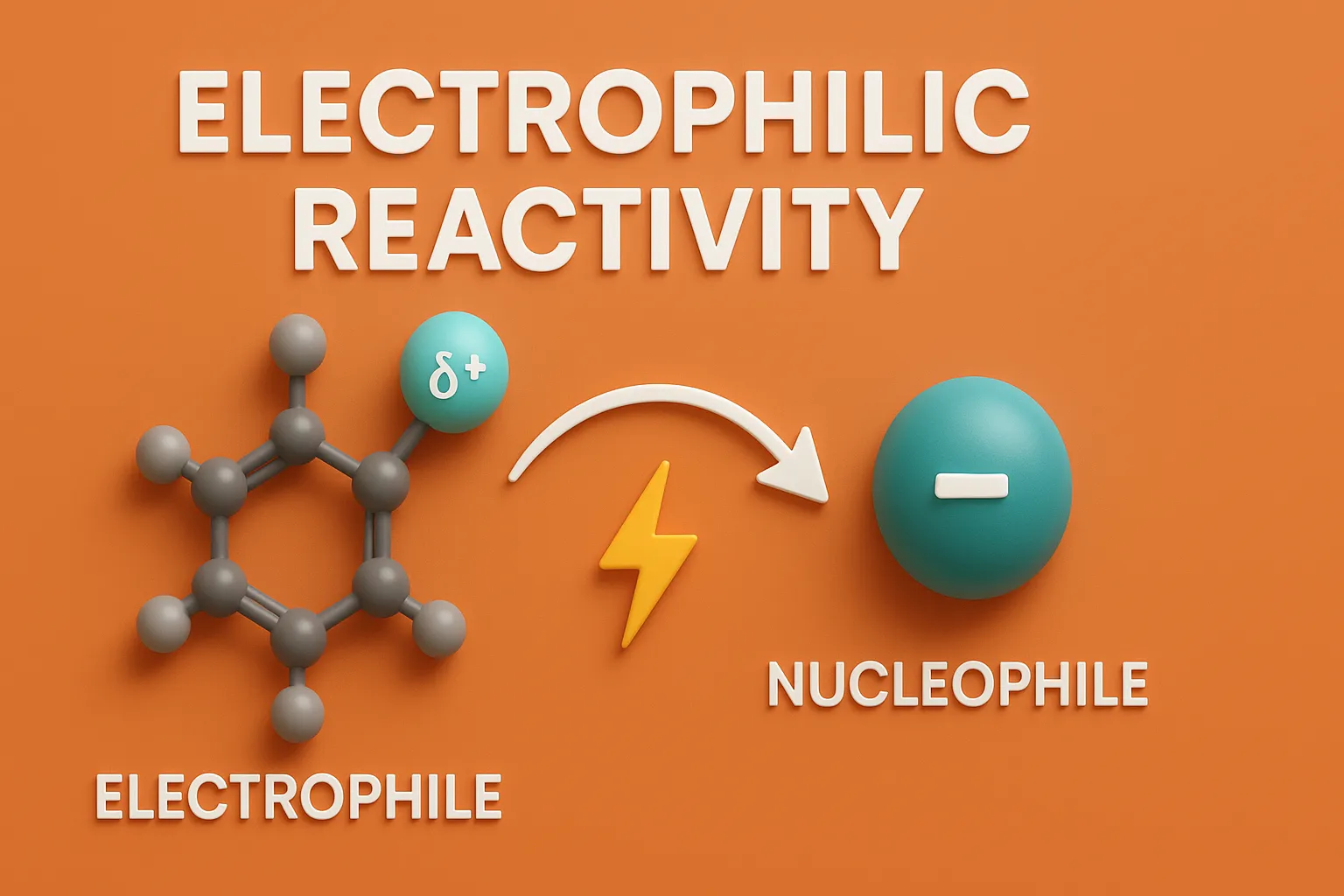
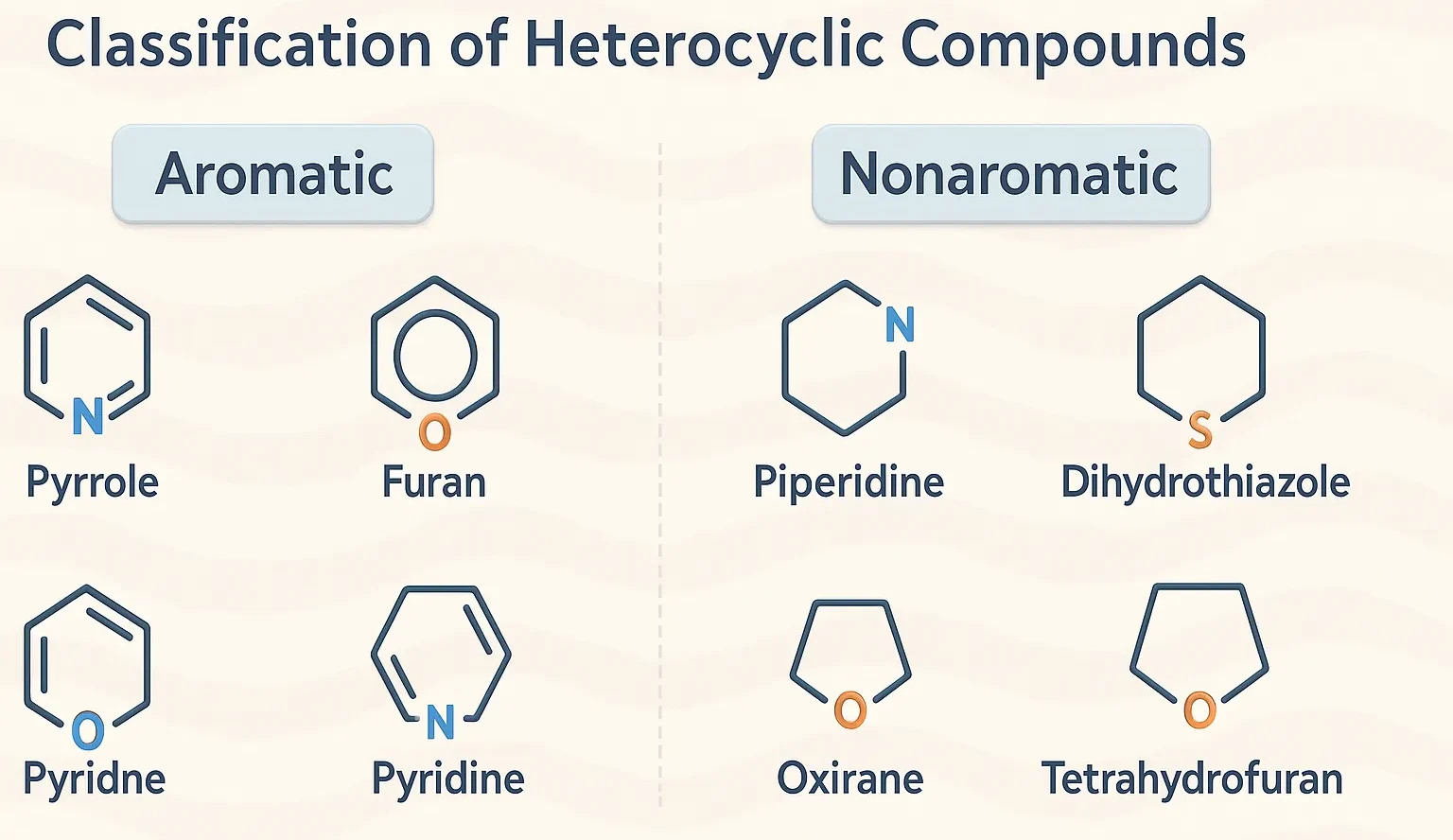
Electrophilic Reactivity
Electrophilic Reactivity is the tendency of aromatic or unsaturated compounds to undergo reactions with electron-seeking species (electrophiles). Reactivity toward EAS depends on electron density in the ring. More electron-rich rings react more easily. Comparison of EAS Reactivity Compound Electron Density Reactivity toward EAS Preferred Position of Attack Pyrrole Highest Most reactive Position-2 (α) Furan Moderate … Read more