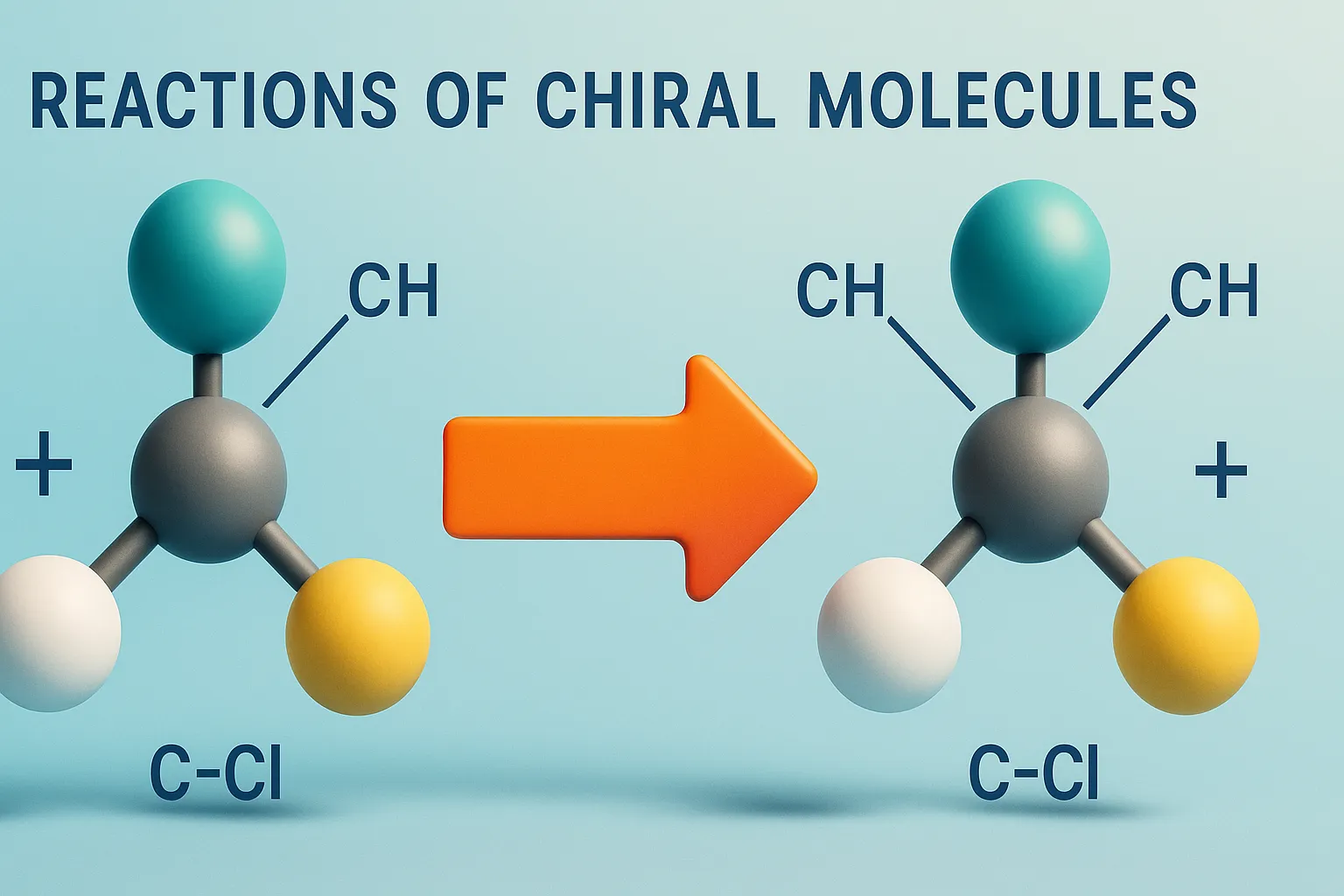
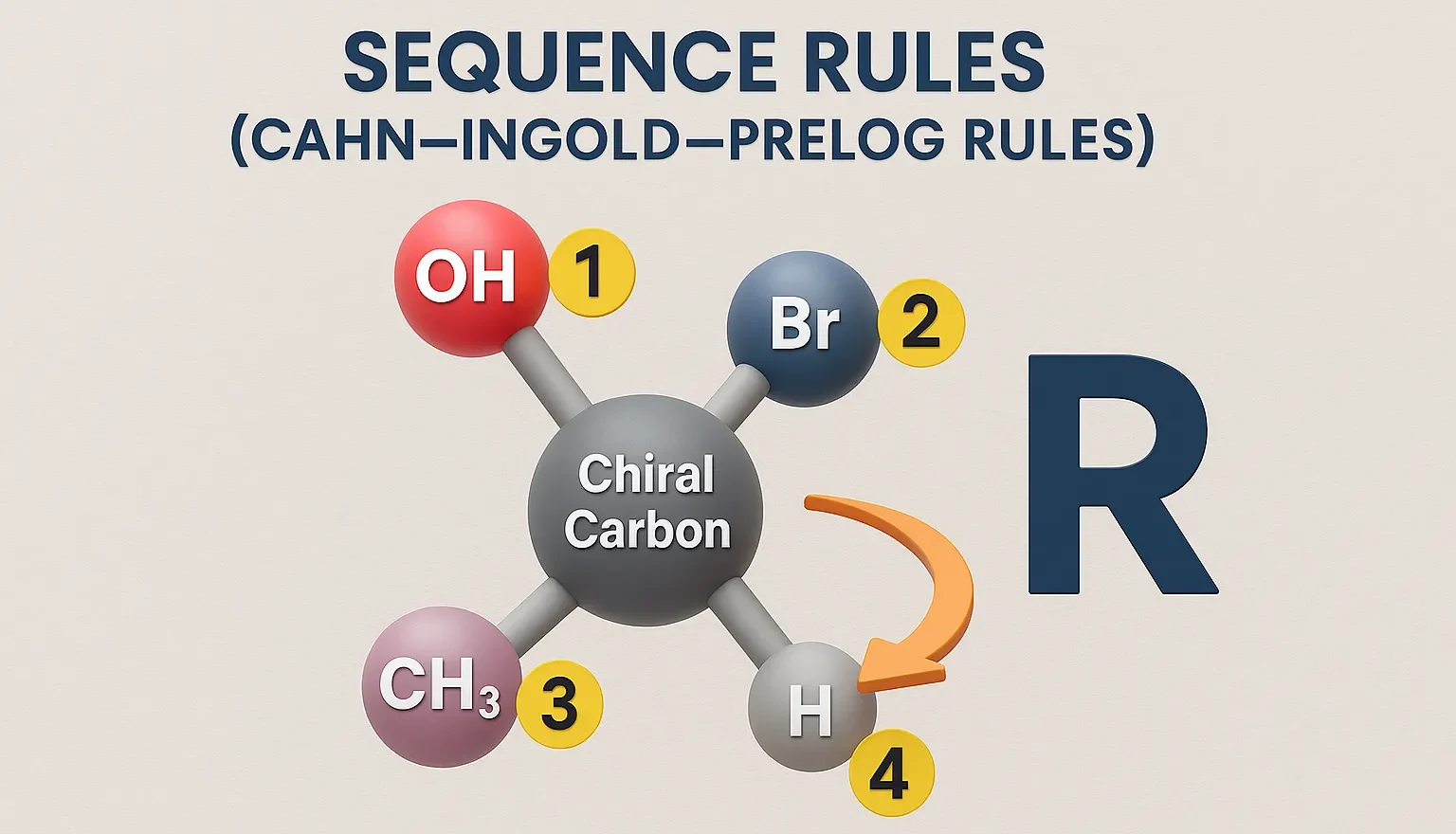
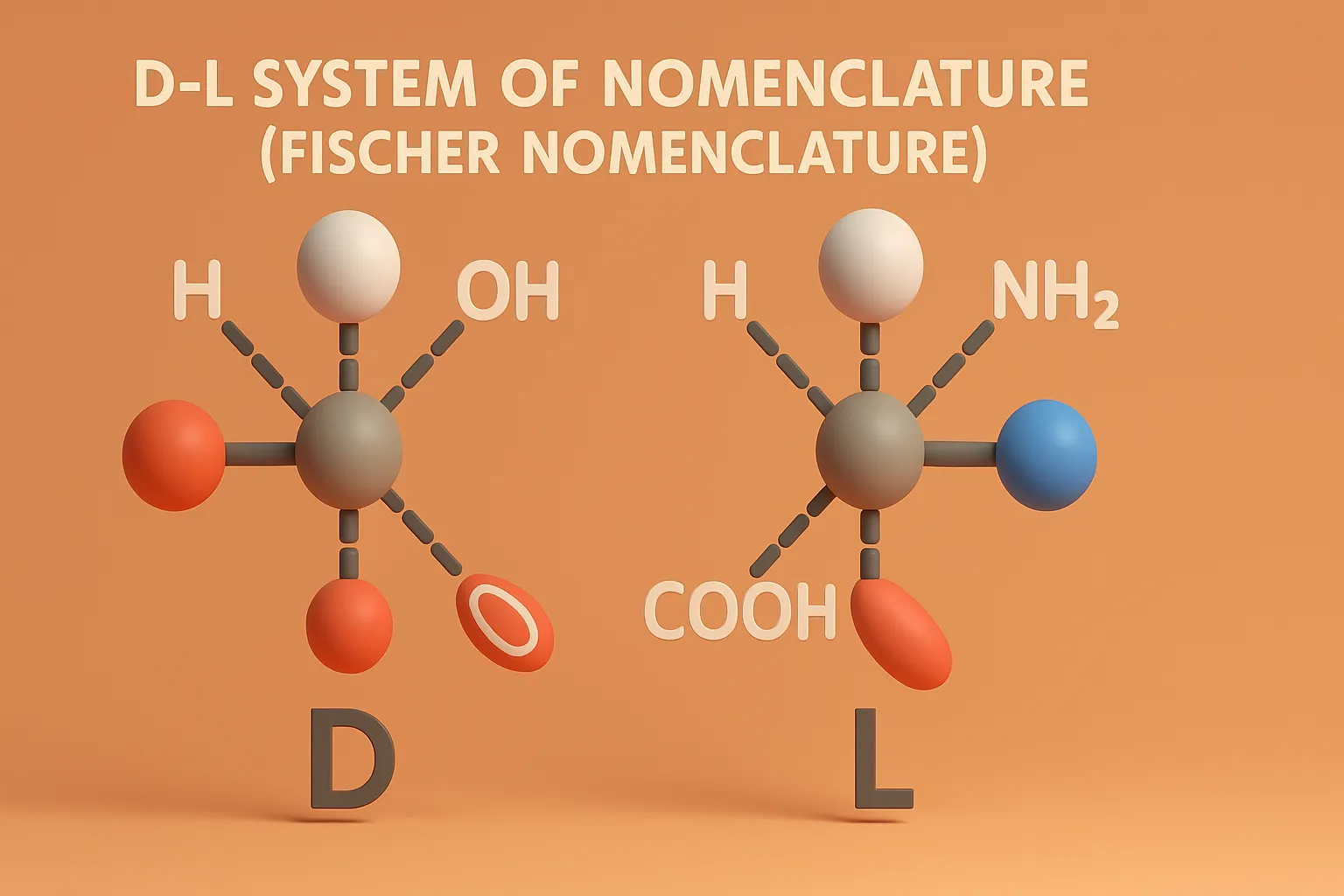
Reactions of Chiral Molecules
Reactions of Chiral Molecules involve changes where chirality may be retained, inverted, or lost, influencing drug activity and biological effects. Reactions involving chiral molecules are influenced by stereochemistry, leading to different outcomes based on the chirality. Racemization A reaction where a single enantiomer is converted into an equal mixture of both enantiomers (racemic mixture). Racemic … Read more