Ethchlorvynol
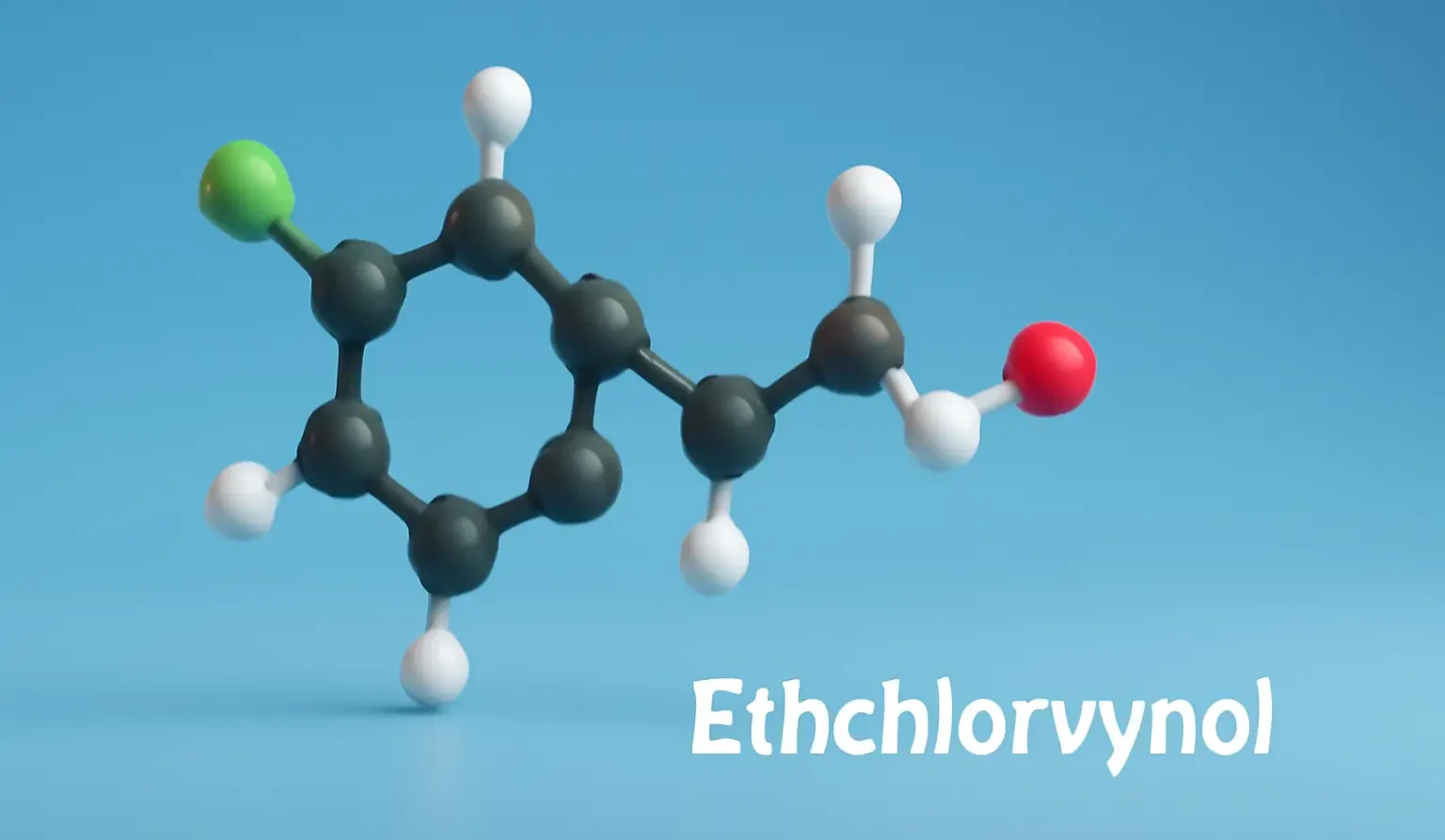
Ethchlorvynol acts on the CNS, enhancing inhibitory pathways to induce sleep and relaxation. It is used as a sedative-hypnotic for short-term relief of insomnia. Chemical Formula: C₇H₁₁ClO Mechanism of Action: CNS depressant with barbiturate-like action Potentiates GABA-mediated chloride currents Therapeutic Uses of Ethchlorvynol: Insomnia (short-term) Side Effects of Ethchlorvynol: Dizziness Euphoria Nausea Risk of dependence, … Read more