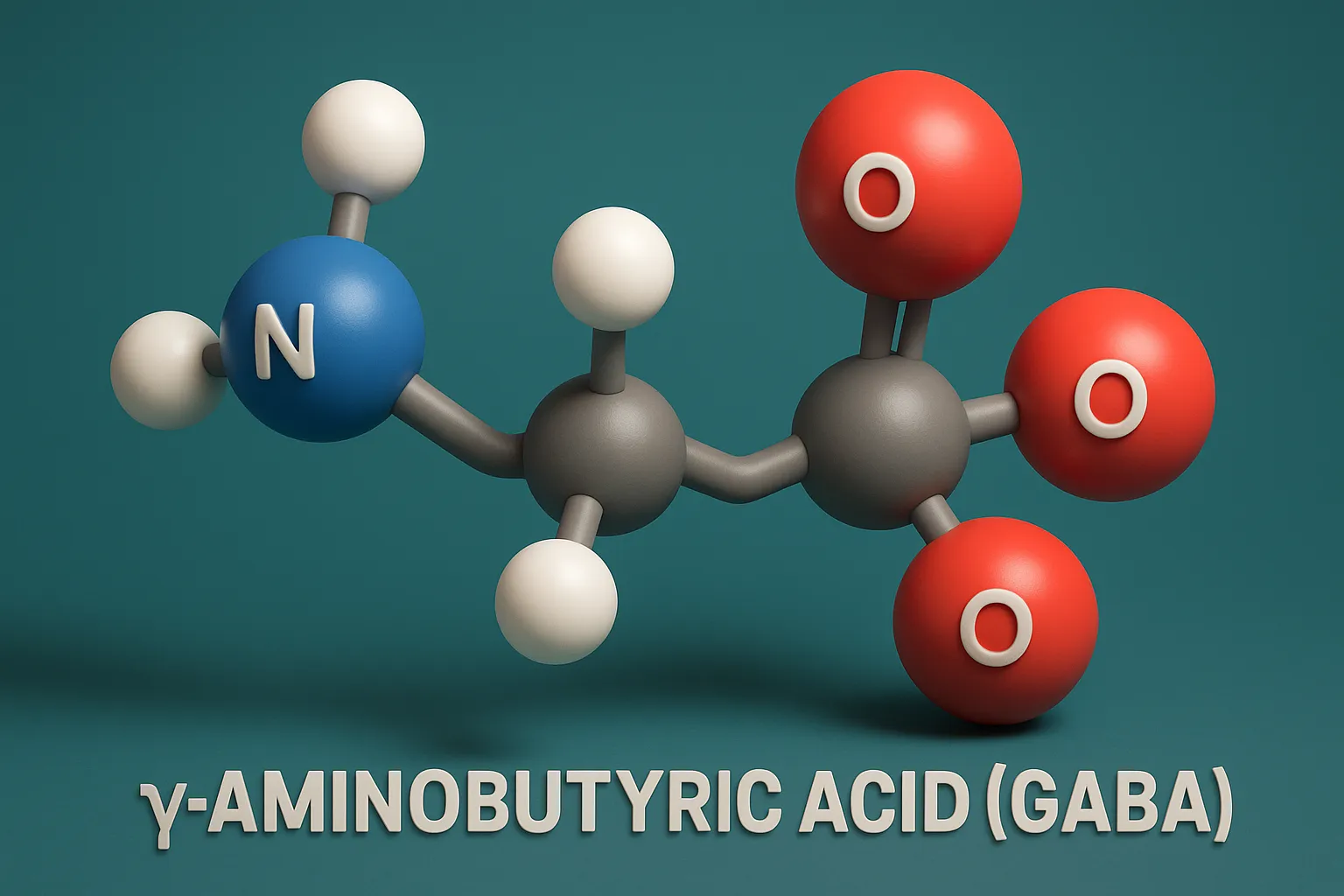
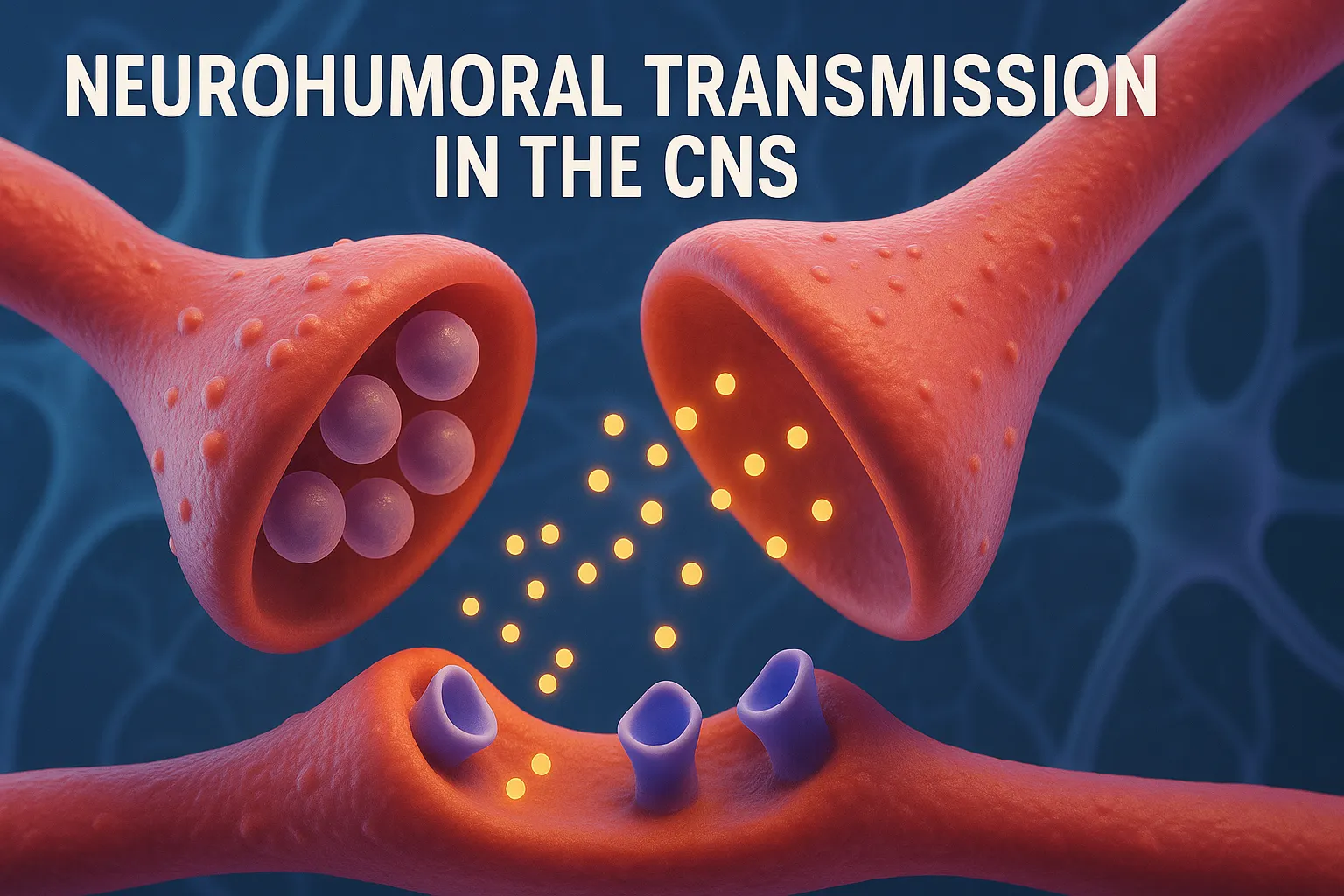
Serotonin (5-HT)
Serotonin (5-HT) is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and cognitive functions in the CNS. Function Serotonin (5-HT): Regulates mood, appetite, sleep, pain perception, and cognition. Receptors: Multiple subtypes (5-HT1 to 5-HT7) with distinct actions: 5-HT1A: mood, anxiety. 5-HT2A: hallucinations, platelet aggregation. 5-HT3: vomiting center (only ionotropic receptor). 5-HT4: GI motility. Synthesis Pathway: Tryptophan … Read more