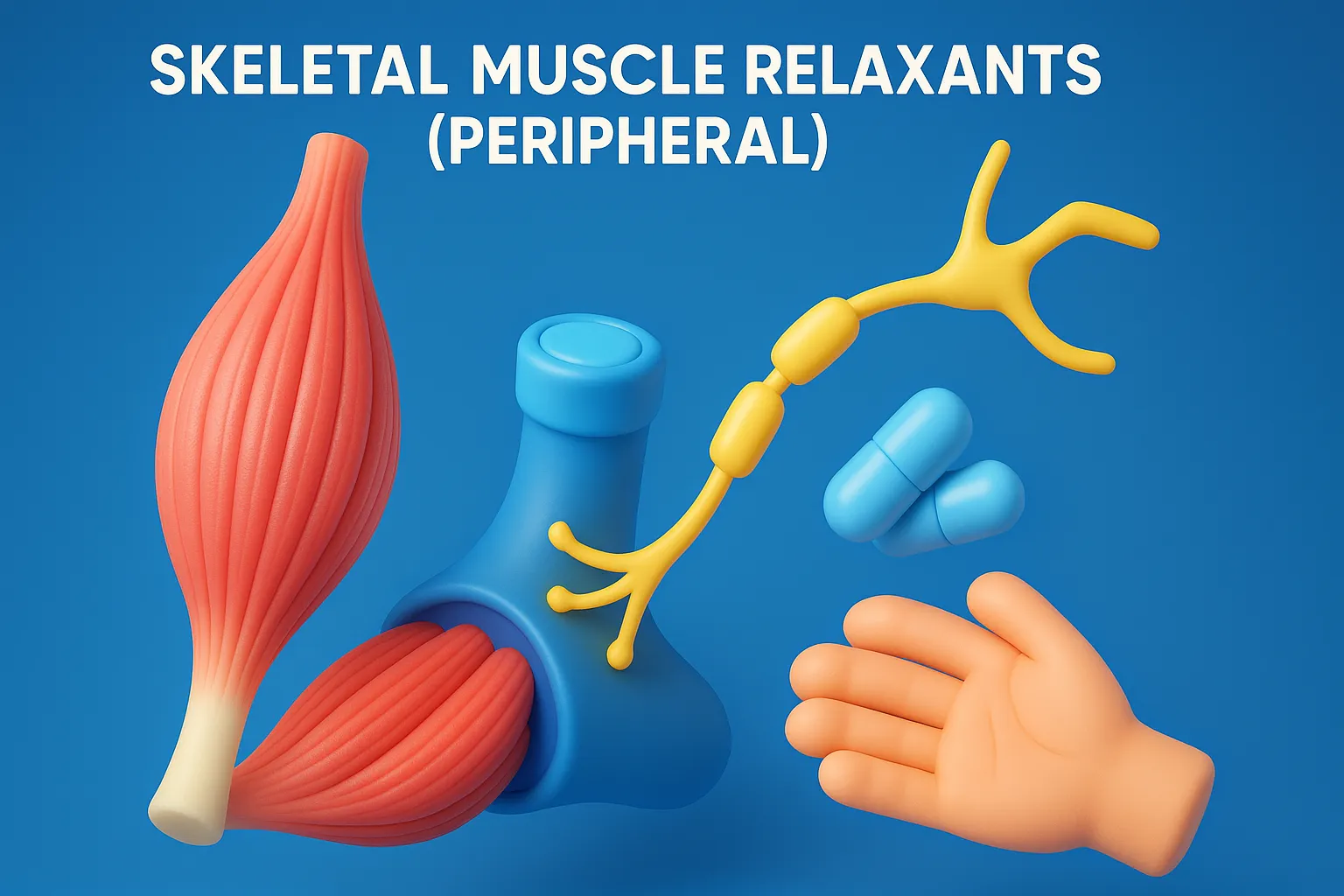
Diazepam
Diazepam treats anxiety, seizures, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal effectively. Diazepam enhances GABA action, producing sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant effects. Chemical Formula: C₁₆H₁₃ClN₂O Mechanism: Enhances GABAergic transmission at GABA-A receptors by increasing frequency of Cl⁻ channel opening Uses: Anxiety Muscle spasms Seizures (status epilepticus) Alcohol withdrawal Premedication for procedures Side Effects: Drowsiness, sedation Amnesia Muscle … Read more