SAR of Barbiturates
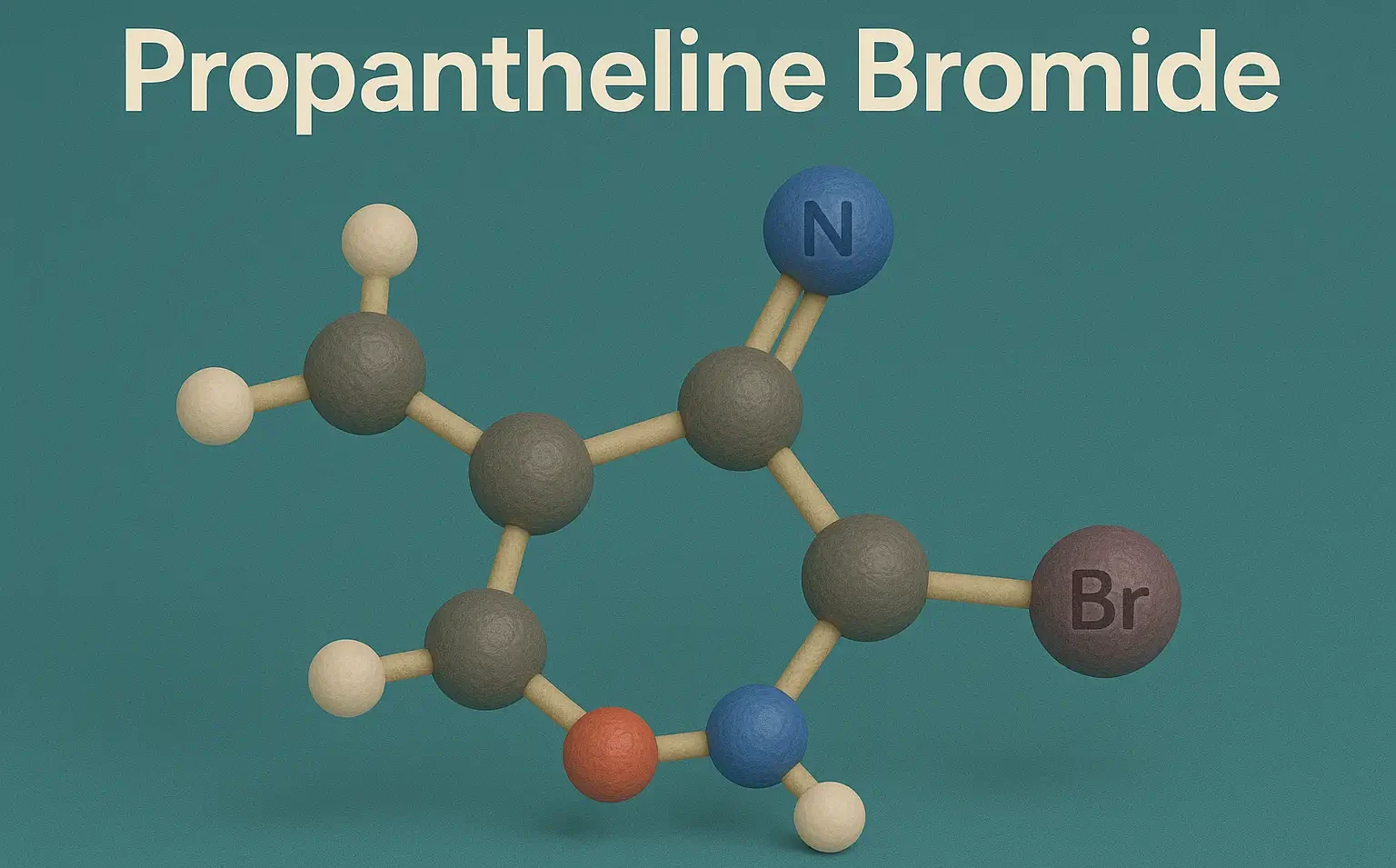
SAR of Barbiturates shows activity depends on substitutions at C5 and heteroatom modifications. SAR of Barbiturates reveals lipophilicity increases potency, while side chains alter duration. Barbiturates act by enhancing GABA-A activity and directly activating the GABA-A receptor at higher doses. Core Structure: Barbituric acid nucleus (pyrimidine ring with keto groups at C-2 and C-4, C-6). … Read more