Intracellular Receptors Regulating Transcription Factors
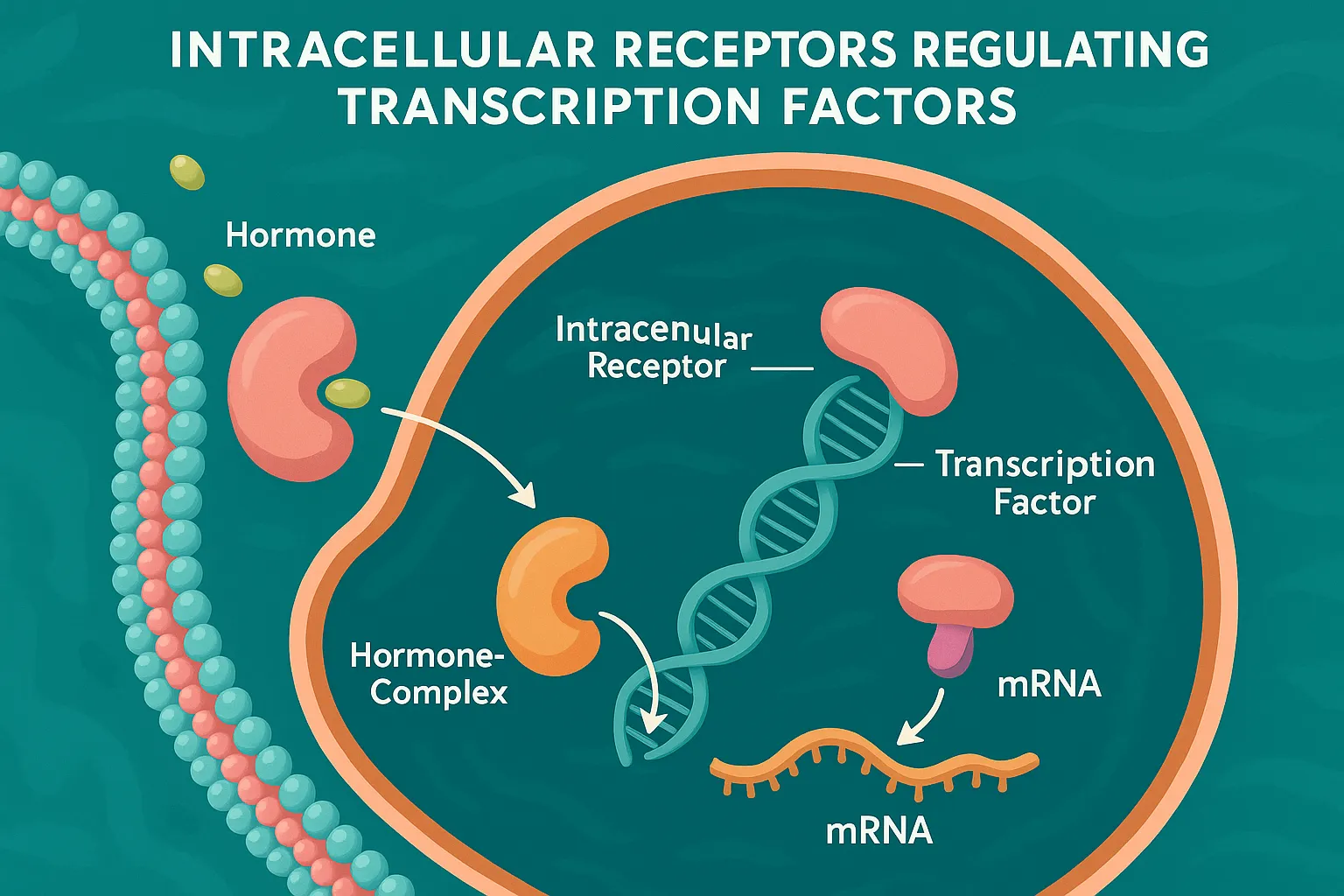
Intracellular Receptors Regulating Transcription Factors are receptors inside cells that bind ligands and directly influence gene expression. These receptors are located inside the cell, either in the cytoplasm or nucleus. They bind lipid-soluble ligands that cross the plasma membrane. Structure of Intracellular Receptors Regulating Transcription Factors: Ligand-binding domain DNA-binding domain (zinc finger motifs) Transcriptional regulatory … Read more