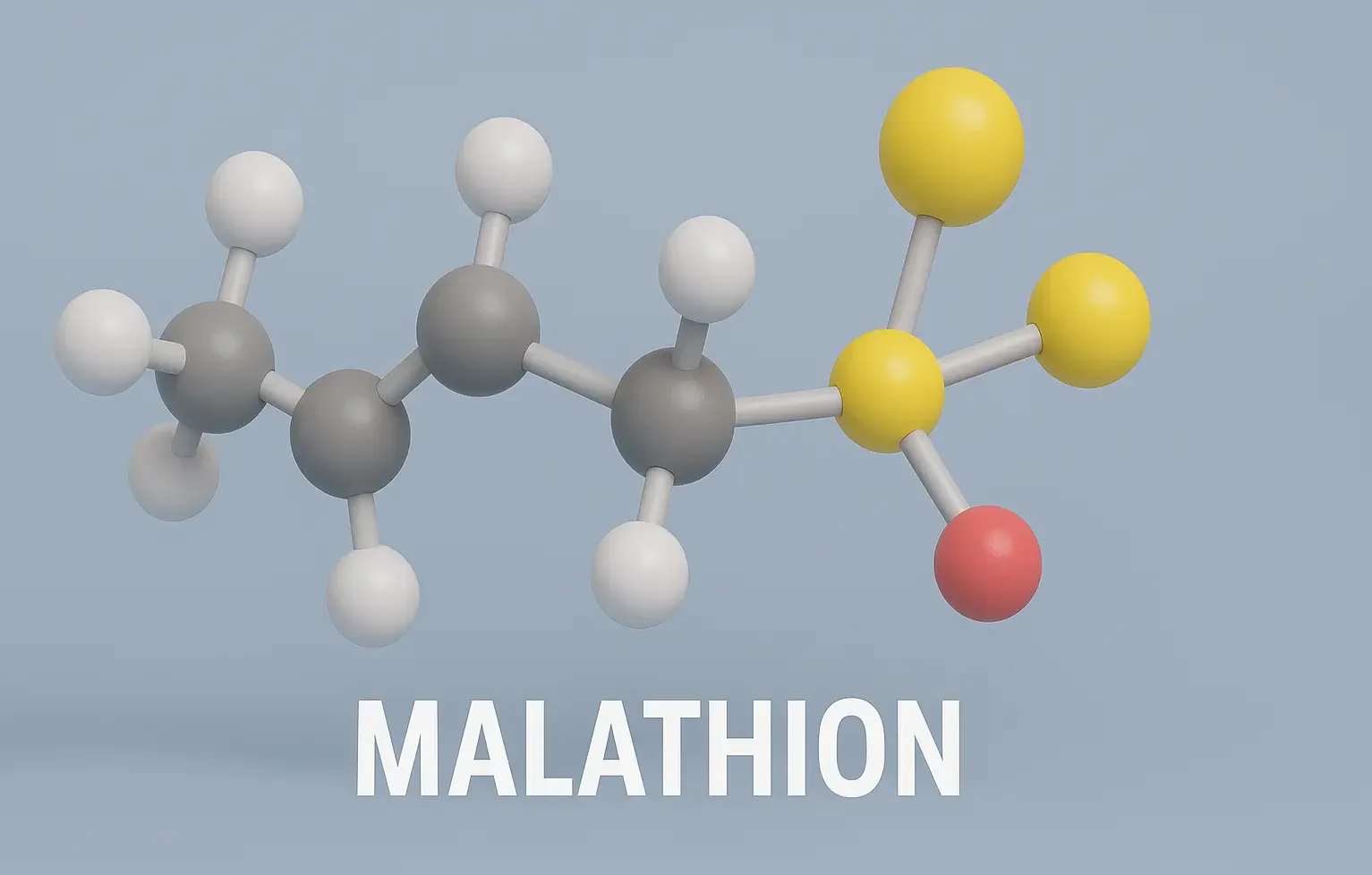
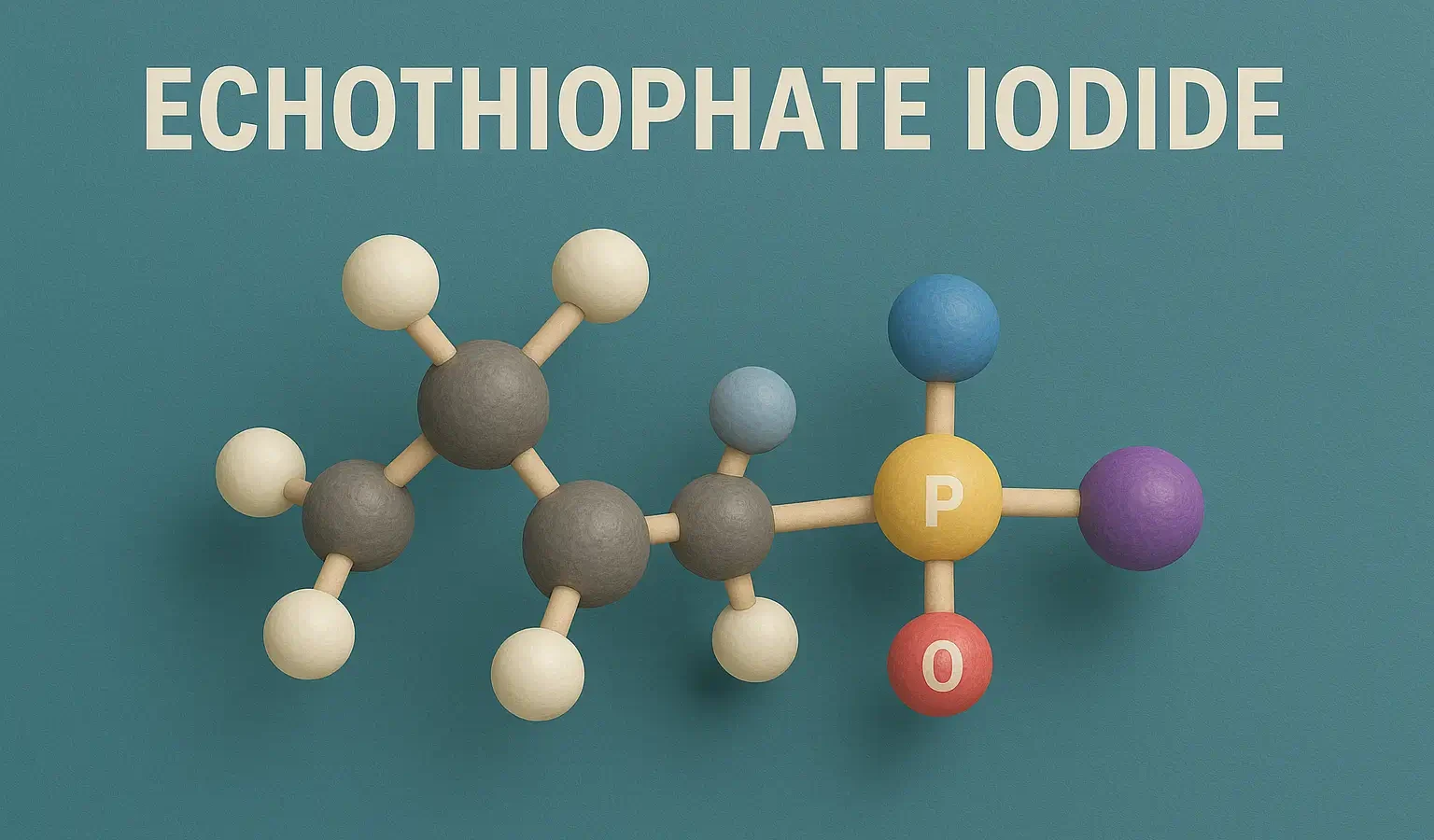
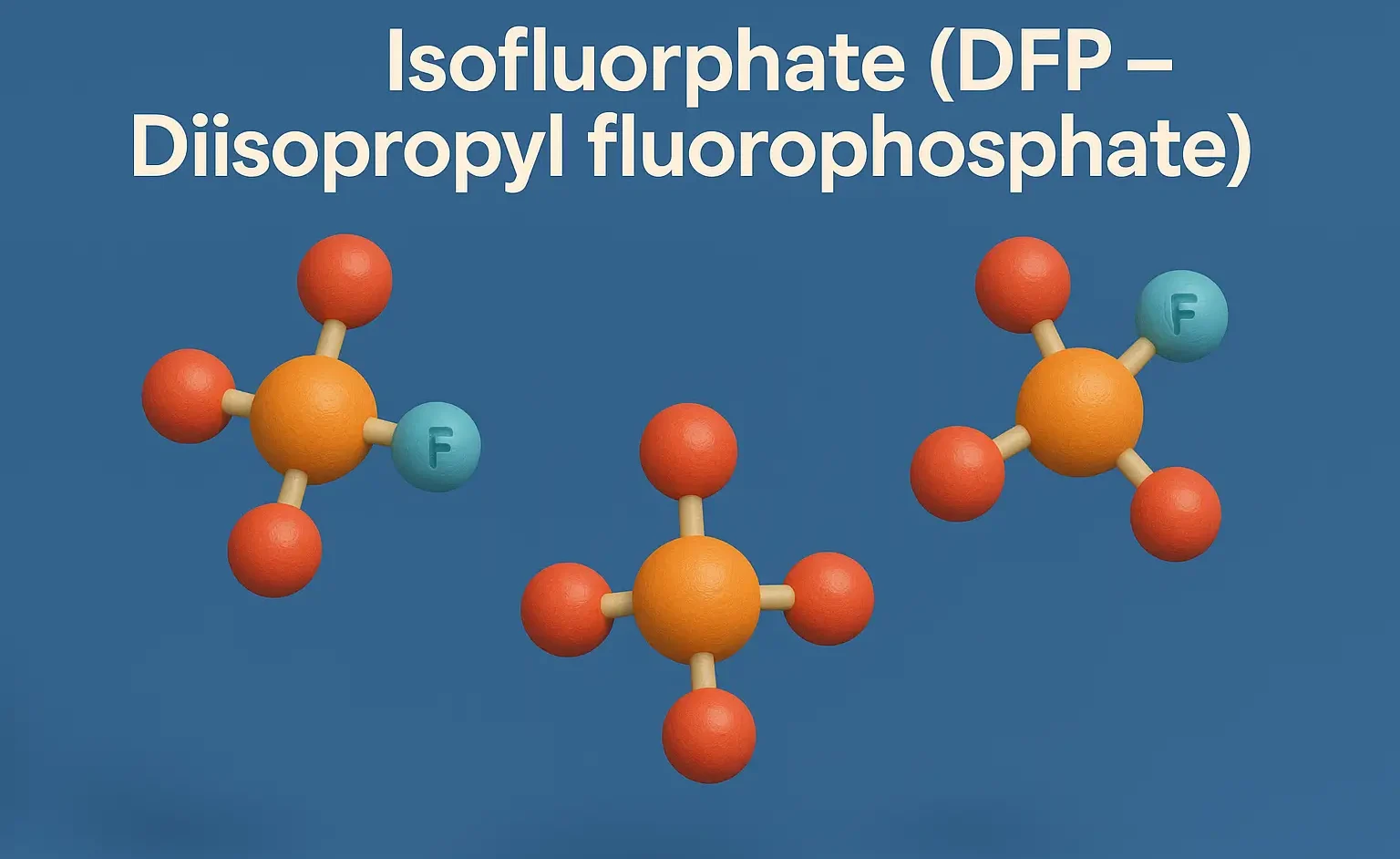
Homatropine Hydrobromide
Homatropine Hydrobromide acts as an anticholinergic with shorter action than atropine. Homatropine Hydrobromide relieves eye disorders by dilating pupils and reducing spasms. Formula: C₁₆H₂₁NO₃·HBr Mechanism of Homatropine Hydrobromide: Muscarinic antagonist, shorter acting than atropine Uses of Homatropine Hydrobromide: Mydriasis Cycloplegia (eye exams) Side Effects: Transient stinging Increased intraocular pressure Dry mouth, photophobia