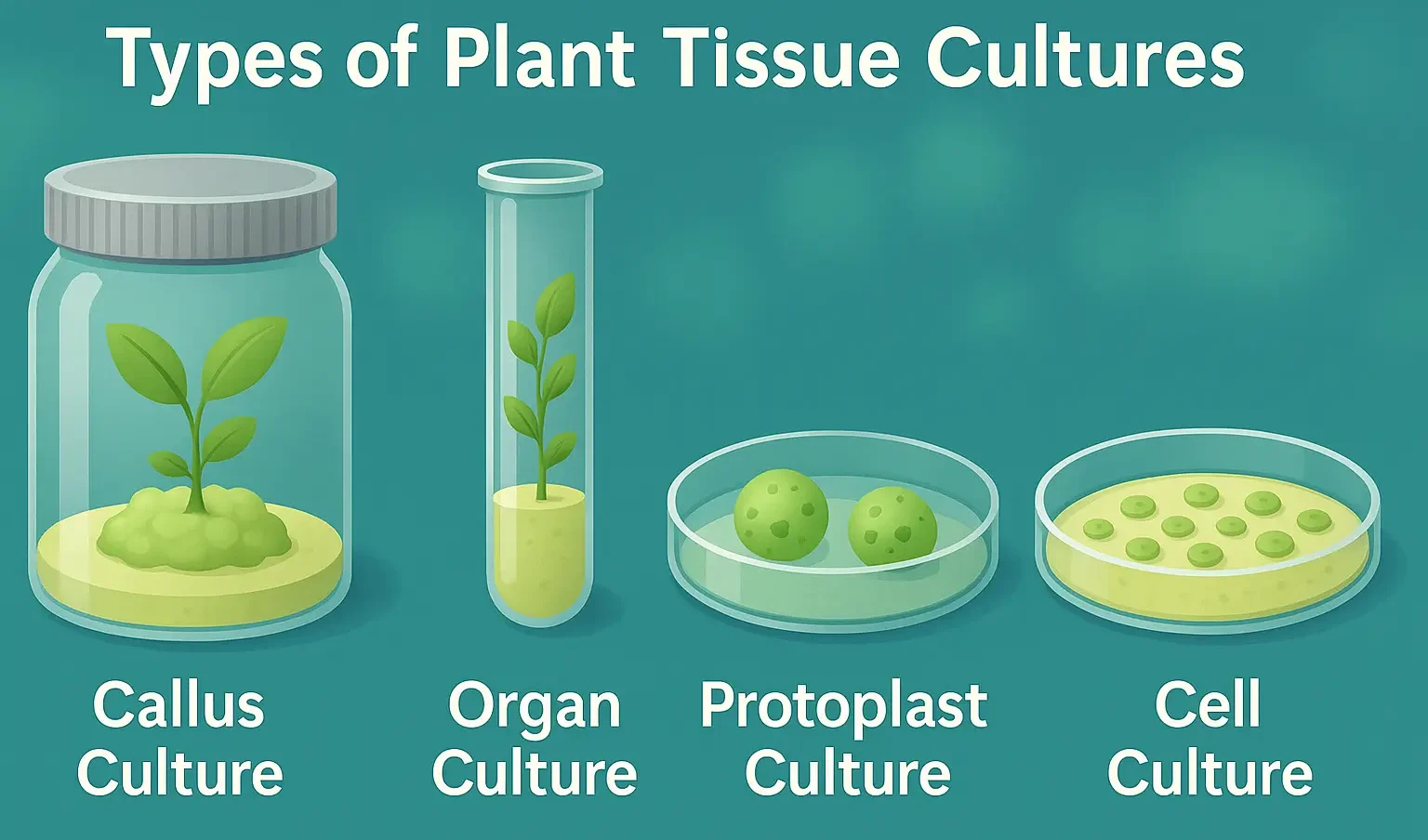
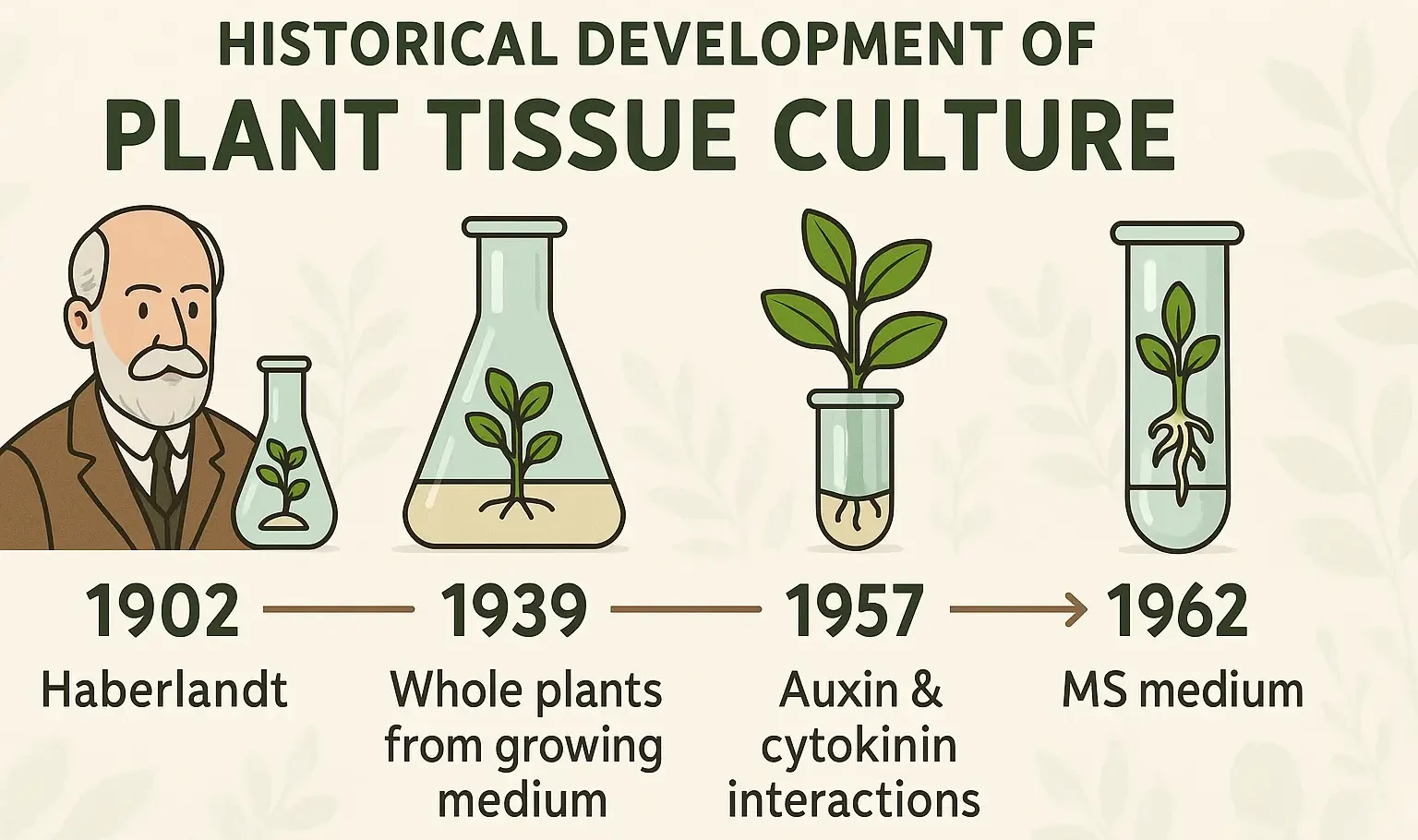
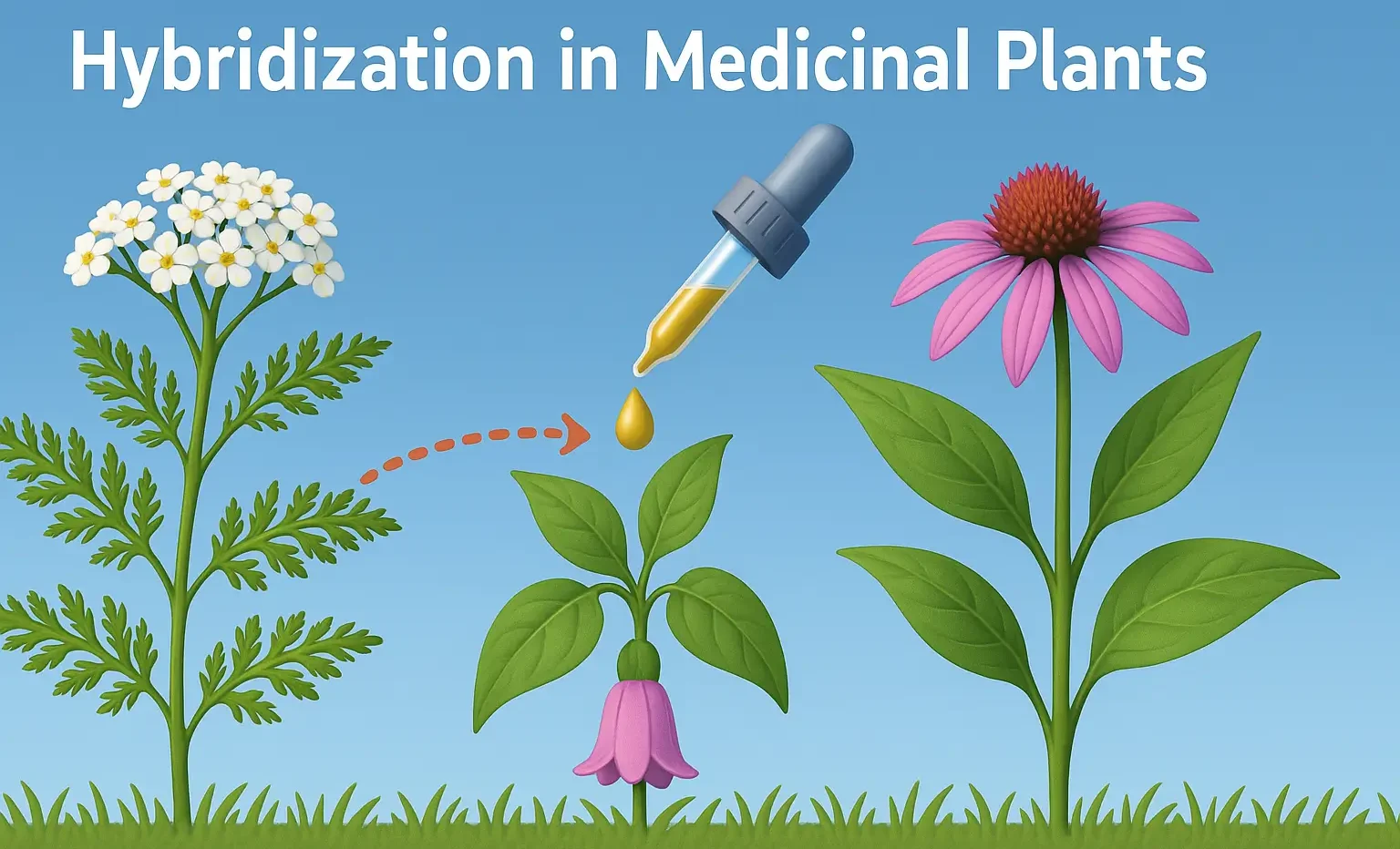
Ayurveda
Ayurveda is one of the oldest holistic healing systems, originating in India over 5,000 years ago. The term “Ayurveda” is derived from Sanskrit words: “Ayur” meaning life “Veda” meaning knowledge or science Ayurveda focuses on maintaining the balance of bodily functions through diet, lifestyle, herbal medicine, and spiritual practices. Principle The fundamental concept in Ayurveda … Read more