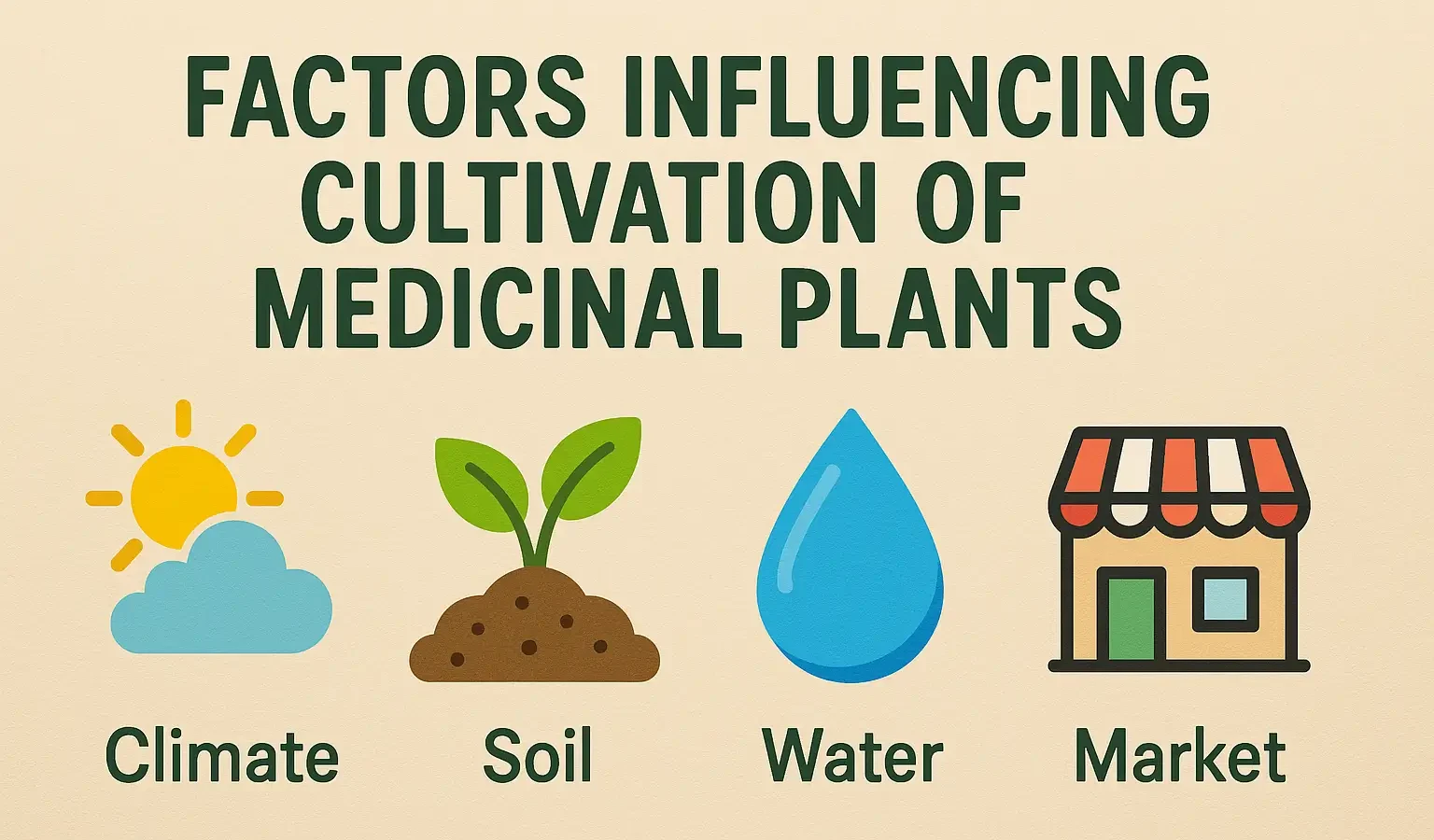
Factors Influencing Cultivation of Medicinal Plants
Factors Influencing Cultivation of Medicinal Plants include soil, climate, water, and light conditions. Factors Influencing Cultivation of Medicinal Plants impact yield, quality, and active constituent content. Cultivation of medicinal plants is also influenced by several environmental, biological, and agricultural factors that impact growth, yield, and the quality of bioactive compounds. Environmental Factors Climate – Temperature, … Read more