Parasympathomimetic Agents
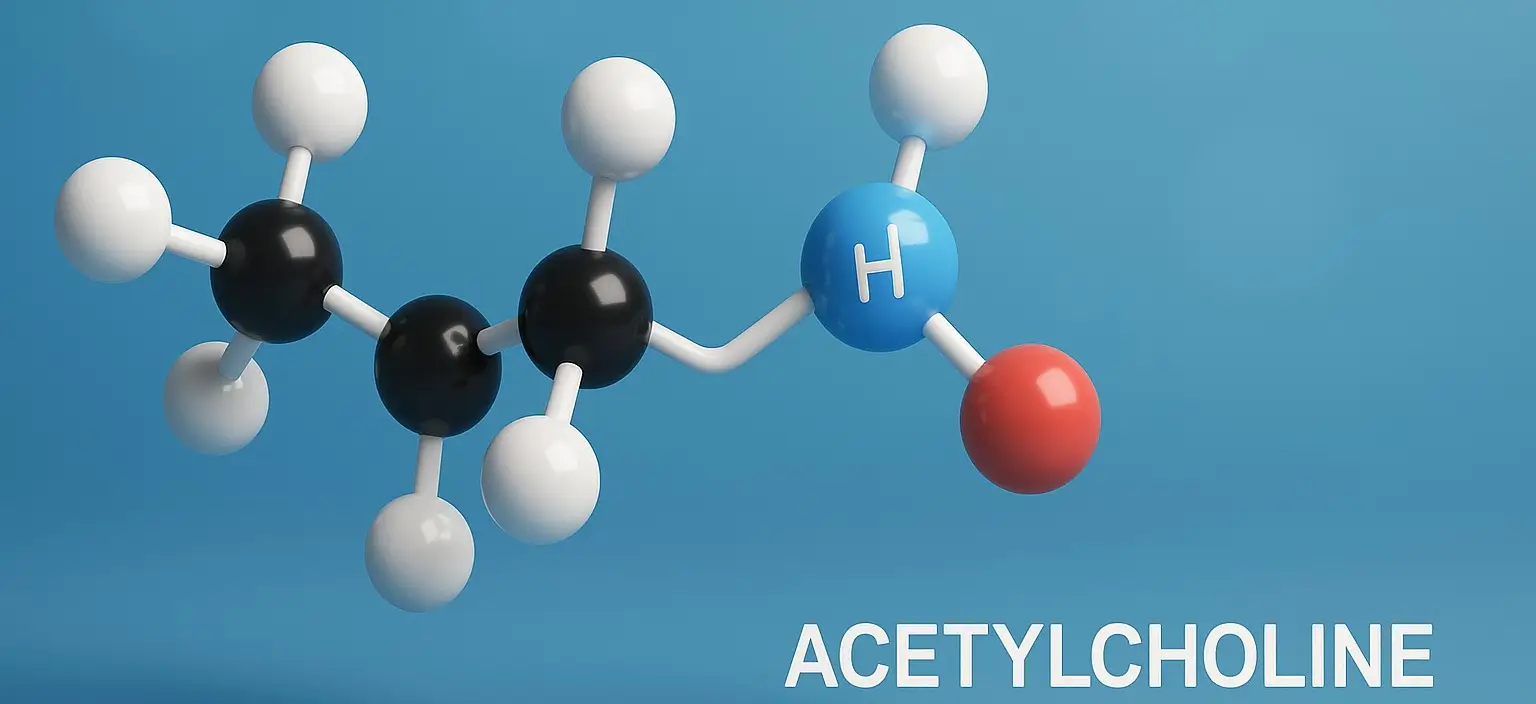
Parasympathomimetic agents are drugs that mimic the actions of acetylcholine (ACh) on parasympathetic nervous system These agents stimulate cholinergic receptors, resulting in increased secretions, smooth muscle contraction, slowed heart rate, and other parasympathetic effects. They are classified into two main groups: Direct-acting cholinergic agonists Indirect-acting cholinesterase inhibitors A third category includes cholinesterase reactivators, used to … Read more