Acetate Pathway (Polyketide Pathway)
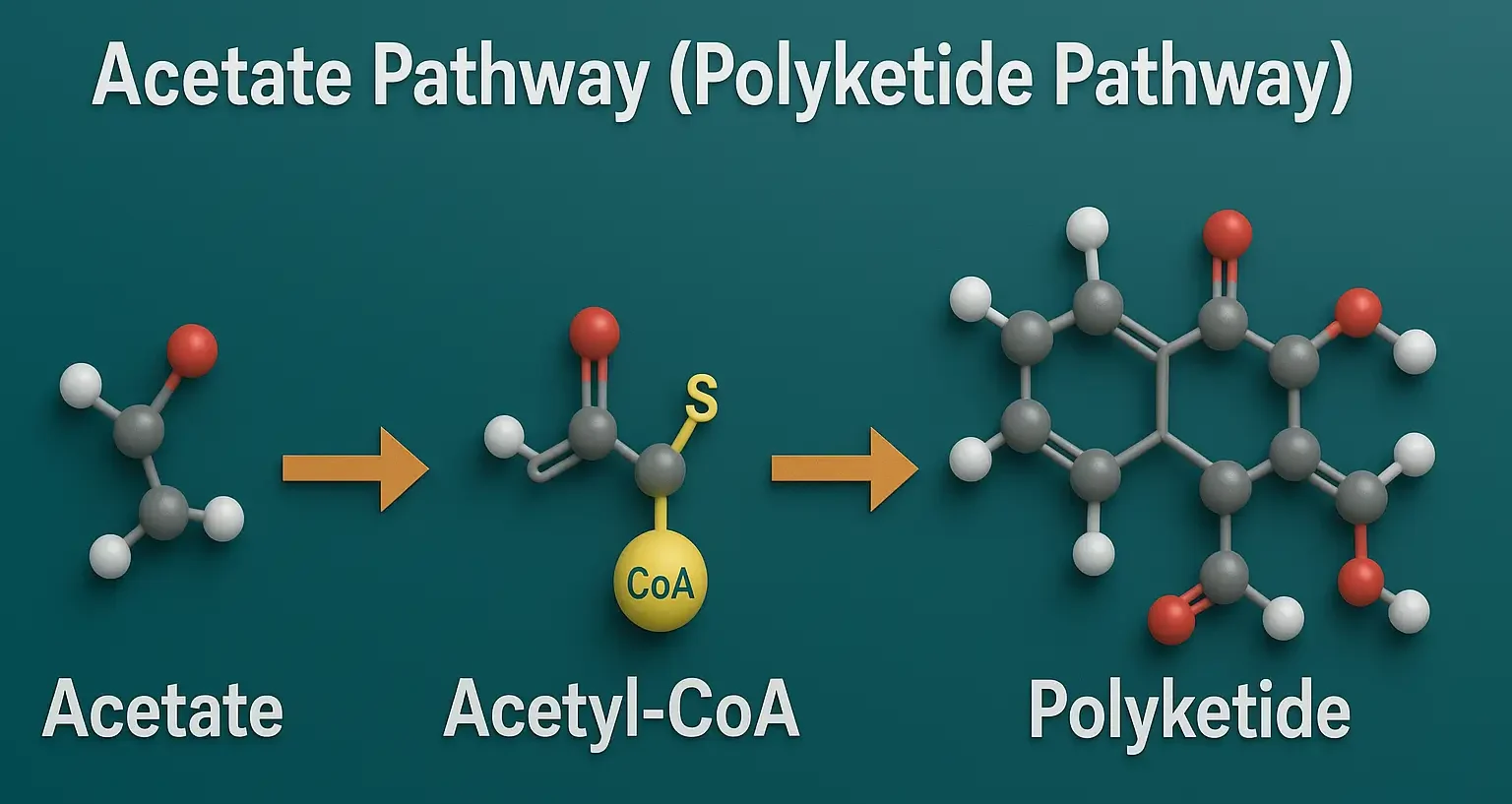
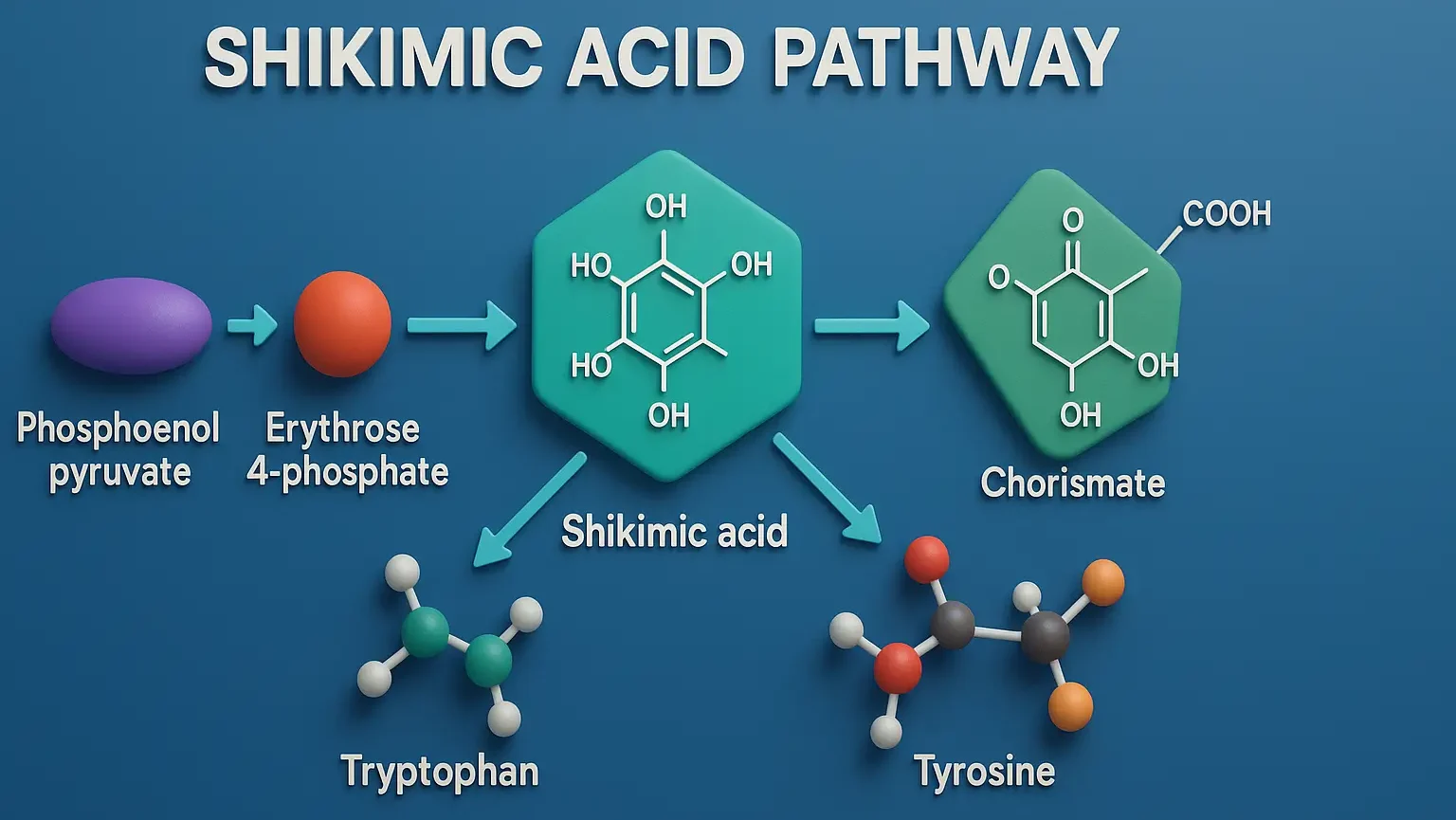
Overview of Acetate Pathway (Polyketide Pathways): The Acetate pathway, often referred to as the polyketide pathway, involves the polymerization of acetyl-CoA or malonyl-CoA units. It is crucial not only for primary metabolites like fatty acids but also for numerous plant secondary metabolites (e.g., flavonoids, certain antibiotics in microorganisms, and various phenolics in plants). Key Steps: … Read more