- Barbital (Veronal) was used as a sedative-hypnotic for insomnia and anxiety management.
- It is a barbiturate that depresses CNS activity, producing sedation and sleep.
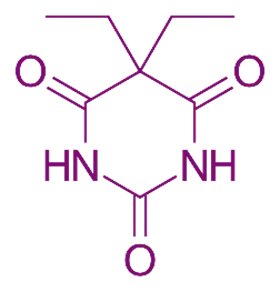
Chemical Formula:
- C₈H₁₂N₂O₃
Mechanism of Action:
- Enhances the action of GABA by prolonging the opening of Cl⁻ channels at the GABA-A receptor.
Therapeutic Uses:
- Historically used as a sedative/hypnotic (no longer in clinical use due to safety concerns).
Side Effects of Barbital:
- Drowsiness
- Respiratory depression
- Physical dependence
- Withdrawal symptoms
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR):
-
Barbituric acid core (pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione):
- Required for sedative-hypnotic activity.
-
Alkyl substitutions at position 5 (usually 2 groups):
- Increase lipid solubility and CNS activity.
- Optimal total carbon atoms = 6–10 for maximal hypnotic effect.
-
No substitution on the nitrogen:
- Barbital has unsubstituted N1 and N3; gives moderate onset and long duration.
-
Highly polar:
- Less lipophilic than others like phenobarbital; hence slower CNS penetration.
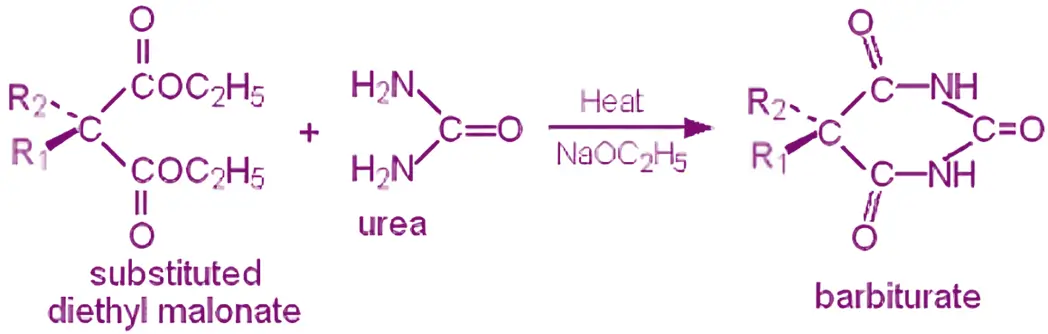
Synthesis of Barbital:
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos