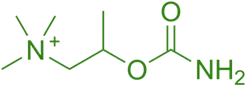
- Bethanechol is a synthetic choline ester and a direct-acting parasympathomimetic agent that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors (especially M3) in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and urinary bladder.
- It mimics the effect of acetylcholine on smooth muscle without significant effects on nicotinic receptors or the central nervous system.
Chemical Formula:
- C₇H₁₇NO₂

Mechanism of Action:
- Selective muscarinic agonist (very little nicotinic activity).
- Resistant to hydrolysis by AChE.
Uses of Bethanechol:
- Urinary retention
- Postoperative ileus
- Neurogenic bladder
Side Effects:
- Salivation
- Sweating
- Bronchospasm
- Bradycardia
- GI discomfort
SAR of Bethanechol:
- Beta-methyl substitution → increases selectivity for muscarinic
- Carbamate ester → resistant to AChE degradation.
- Quaternary amine → no CNS penetration (limited systemic effects).
General Synthesis:
- Beta-methylcholine is used as starting compound.
- React with methyl isocyanate or carbamoyl chloride to form carbamoyl ester.
- Quaternize to form chloride.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos