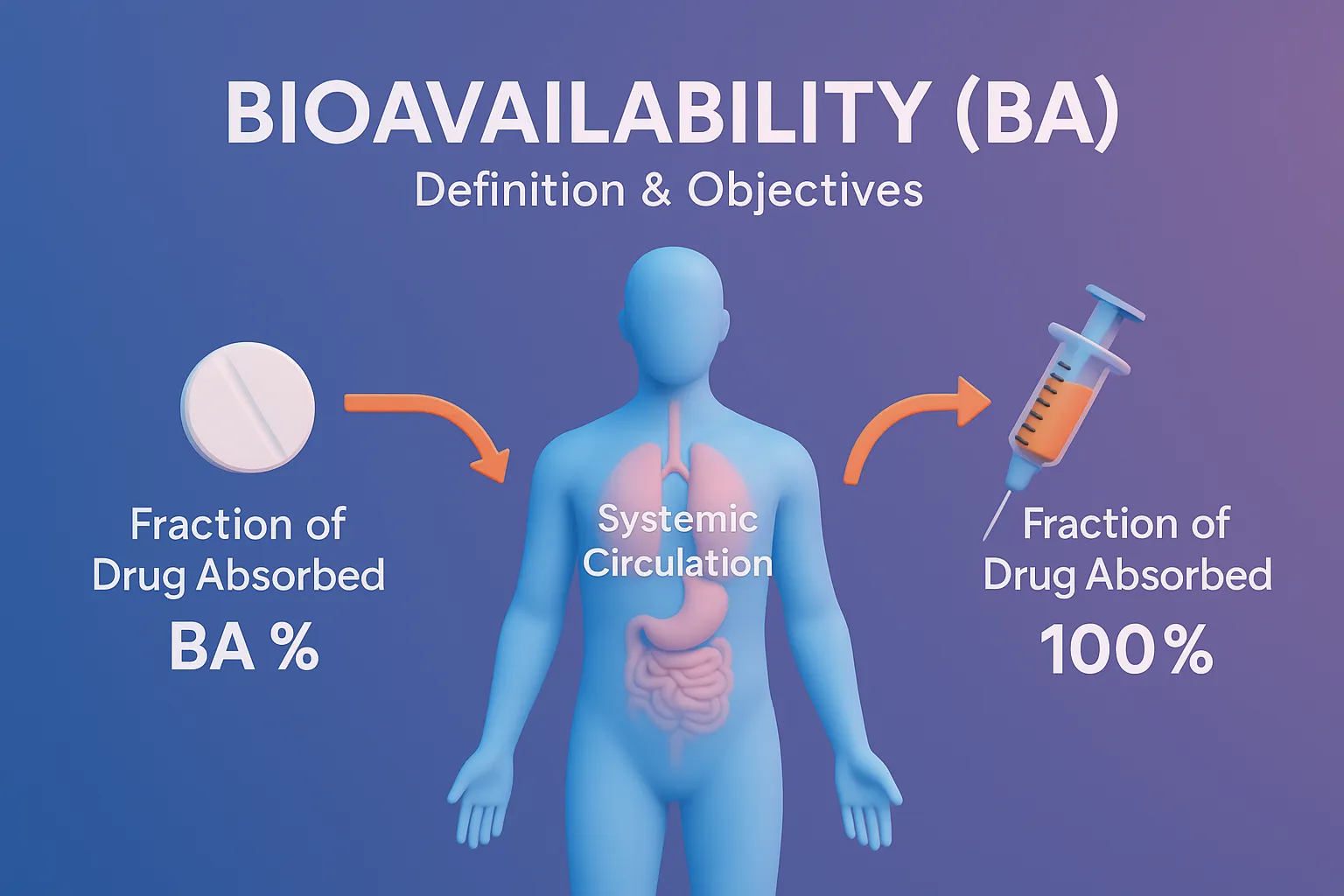
Bioavailability BA definition and objectives explain the rate and extent of drug absorption reaching systemic circulation.
Bioavailability (BA) definition and objectives
Definition of Bioavailability
- Bioavailability is defined as the fraction (F) of an administered drug dose that reaches systemic circulation in an unchanged form and is available for therapeutic action. It includes both:
- Extent of drug absorption (how much drug reaches systemic circulation)
- Rate of absorption (how quickly the drug reaches systemic circulation)
Objectives of Bioavailability Studies
- Bioavailability studies are conducted to:
- Compare Different Drug Formulations – Ensure consistency between different formulations of the same drug.
- Evaluate Drug Absorption – Assess how much drug enters the bloodstream after administration.
- Determine Optimal Dosage Forms – Choose the best formulation (tablet, capsule, solution, etc.).
- Assess the Impact of Food or Other Factors – Understand how food, pH, or metabolic variations affect drug absorption.
- Establish Therapeutic Equivalence – Ensure generic formulations provide the same therapeutic effect as brand-name drugs.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements