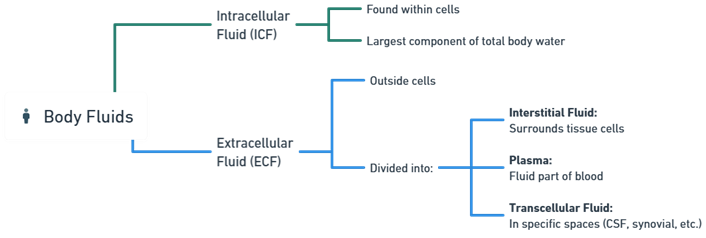
- Body fluids are essential liquids found within the human body that play vital roles in maintaining physiological functions and overall health.
- These fluids are distributed throughout the body’s tissues, cells, and cavities, and each type serves specific functions.
Types of Body Fluids and Their Functions
Blood
Blood is a vital fluid circulating within blood vessels.
Components
- Red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), platelets (thrombocytes), and plasma.
Advertisements
Functions
- Transportation: Carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
- Immune Response: White blood cells defend against infections and diseases.
- Clotting: Platelets help form clots to stop bleeding.
- Regulation: Helps regulate pH balance, temperature, and electrolyte levels.
Lymph
- A clear fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a network of vessels and nodes.
Functions
- Immune Function: Contains lymphocytes, which fight infections and diseases.
- Fluid Balance: Maintains fluid balance by collecting excess tissue fluid and returning it to the bloodstream.
Interstitial Fluid
- Fluid that surrounds and bathes cells in tissues throughout the body.
Functions
- Nutrient Exchange: Provides a medium for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between blood vessels and cells.
Advertisements
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- A clear fluid circulating within the brain’s ventricles and the spinal cord’s subarachnoid space.
Functions
- Protection: Cushions and protects the central nervous system (CNS).
- Buoyancy: Provides buoyancy to the brain.
Synovial Fluid
- Fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder).
Advertisements
Functions
- Lubrication: Acts as a lubricant and shock absorber, reducing friction between joint cartilage surfaces for smooth movement.
Serous Fluid
A watery, clear fluid found in the pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal cavities.
Functions
- Friction Reduction: Reduces friction between the layers of serous membranes surrounding vital organs like the lungs, heart, and abdominal organs.
Gastrointestinal Fluids
- Includes saliva, gastric juices, pancreatic juices, bile, and intestinal fluids.
Functions
- Digestion: Involved in the digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Urine
- A fluid produced by the kidneys and excreted through the urinary system.
Advertisements
Functions
- Waste Removal: Eliminates waste products and excess substances.
- Regulation: Helps maintain electrolyte balance and regulate blood pressure.
Sweat
A fluid produced by sweat glands in the skin.
Functions
- Temperature Regulation: Helps cool the body through evaporative heat loss.
- Waste Elimination: Removes small amounts of waste products and electrolytes.
These body fluids serve several important functions
- These body fluids serve several key functions:
- Transportation: Carry nutrients, oxygen, hormones, and waste. For example, blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and removes carbon dioxide.
- Temperature Regulation: Help regulate body temperature, such as sweat cooling the body.
- Protection: Contain white blood cells and antibodies to defend against pathogens, boosting the immune system.
- Lubrication: Provide lubrication in joints, like synovial fluid, reducing friction for smooth movement.
- Digestion: Aid in digestion, with fluids like saliva and gastric juices helping to break down food.