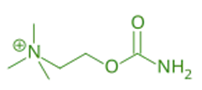
- Carbachol (Carbamoylcholine) is a cholinergic agonist that mimics the action of acetylcholine by stimulating both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
Chemical Formula:
- C₆H₁₅ClN₂O₂

Advertisements
Mechanism of Action:
- Direct agonist at muscarinic and nicotinic
- Longer duration due to resistance to AChE.
Uses of Carbachol:
- Used topically in glaucoma to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Also used to induce miosis during surgery.
Advertisements
Side Effects of Carbachol:
- Blurred vision
- Lacrimation
- Hypotension
- Diarrhea, nausea
SAR (Structure-Activity Relationship) of Carbachol:
-
Quaternary ammonium group:
- Essential for binding to muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
- The positive charge interacts with the anionic site of the receptor.
-
Ester group replaced with carbamate:
- Carbamate is more resistant to hydrolysis than an ester → longer duration of action than acetylcholine.
-
Ethylene bridge (2-carbon):
- Optimal for receptor activity. Alteration decreases potency.
-
Lack of selectivity:
- Due to similarity with acetylcholine, it activates both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
-
Increased enzymatic stability:
- More stable against acetylcholinesterase hydrolysis.
Advertisements
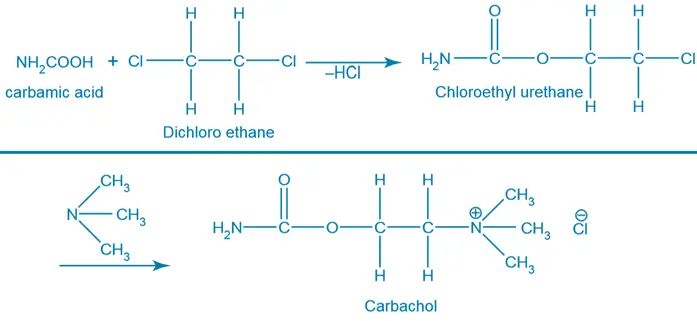
General Synthesis: