- Carvedilol is a non-selective beta-blocker with alpha-1 blocking activity, used primarily to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), heart failure, and left ventricular dysfunction after a heart attack.
- By blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, it reduces heart rate and contractility, while its alpha-1 blocking effects help relax blood vessels, lowering blood pressure and improving blood flow.
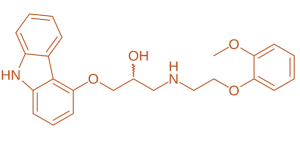
Chemical Structure & Formula:
- A nonselective beta blocker with additional α₁ receptor antagonism, containing a carbazole moiety linked to a propanolamine side chain.
- Approximate Formula: C₂₄H₂₆N₂O₄

Mechanism of Action:
- Blocks β receptors (reducing heart rate and contractility) and antagonizes α₁ receptors (causing vasodilation).
- The dual mechanism improves cardiac output and lowers peripheral resistance.
Side Effects of Carvedilol:
- Hypotension and dizziness
- Fatigue
- Weight gain in some cases
- Rarely, bronchospasm in predisposed individuals
Clinical Uses of Carvedilol:
- Used in treating hypertension, chronic heart failure, and post–myocardial infarction patients to improve survival and reduce hospitalizations.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos