- Catabolism of Purine Nucleotides involves the breakdown of nucleotides into their constituent components, ultimately leading to the formation of uric acid.
- Catabolism of Purine Nucleotides process occurs mainly in the liver and involves several key enzymes.
Steps in Purine Catabolism
-
Degradation of AMP and GMP:
-
AMP Catabolism:
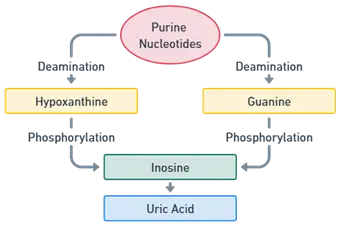
- AMP is deaminated to inosine monophosphate (IMP) by the enzyme AMP deaminase.
- IMP is hydrolyzed to inosine by the enzyme nucleosidase.
- Inosine is further hydrolyzed to hypoxanthine by purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP).
-
GMP Catabolism:
- GMP is hydrolyzed to guanosine by nucleosidase.
- Guanosine is converted to guanine by PNP.
- Guanine is deaminated to xanthine by the enzyme guanine deaminase.
-
Conversion to Uric Acid:
- Hypoxanthine and xanthine are oxidized to uric acid by the enzyme xanthine oxidase.
- Hypoxanthine is first converted to xanthine and then xanthine to uric acid.
-
Key Enzymes:
- AMP Deaminase
- Nucleotidases
- Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase (PNP)
- Guanine Deaminase
- Xanthine Oxidase
Pathway Summary of Catabolism of Purine Nucleotides:
- AMP → IMP → Inosine → Hypoxanthine → Xanthine → Uric Acid
- GMP → Guanosine → Guanine → Xanthine → Uric Acid
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos