- Catecholamines Biosynthesis (dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine) are synthesized from tyrosine in adrenergic neurons and the adrenal medulla.
Steps of Catecholamines Biosynthesis
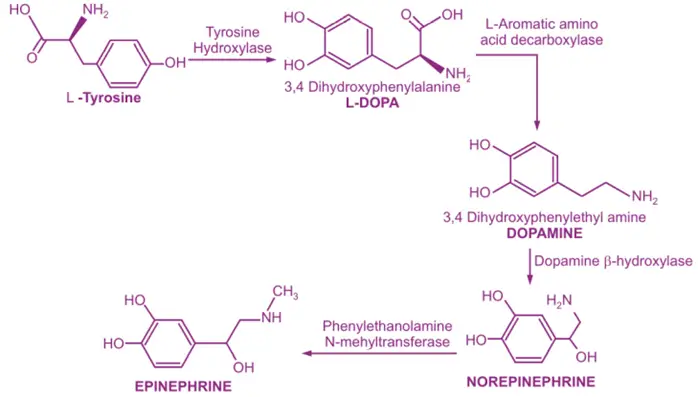
-
Tyrosine Transport & Hydroxylation:
- Tyrosine, derived from diet or synthesized from phenylalanine, is transported into neurons.
- Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) converts tyrosine into L-DOPA (Rate-limiting step).
-
Decarboxylation to Dopamine:
- DOPA decarboxylase converts L-DOPA into dopamine.
-
Hydroxylation to Norepinephrine:
- Dopamine is transported into vesicles via VMAT.
- Dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) converts dopamine into norepinephrine (NE) inside vesicles.
-
Methylation to Epinephrine (Adrenal Medulla Only):
- Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) converts NE into epinephrine in response to cortisol
Summary of Enzymes Involved
| Step | Substrate → Product | Enzyme |
| 1 | Tyrosine → L-DOPA | Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) |
| 2 | L-DOPA → Dopamine | DOPA Decarboxylase |
| 3 | Dopamine → Norepinephrine | Dopamine β-Hydroxylase (DBH) |
| 4 | Norepinephrine → Epinephrine | Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase (PNMT) |
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos