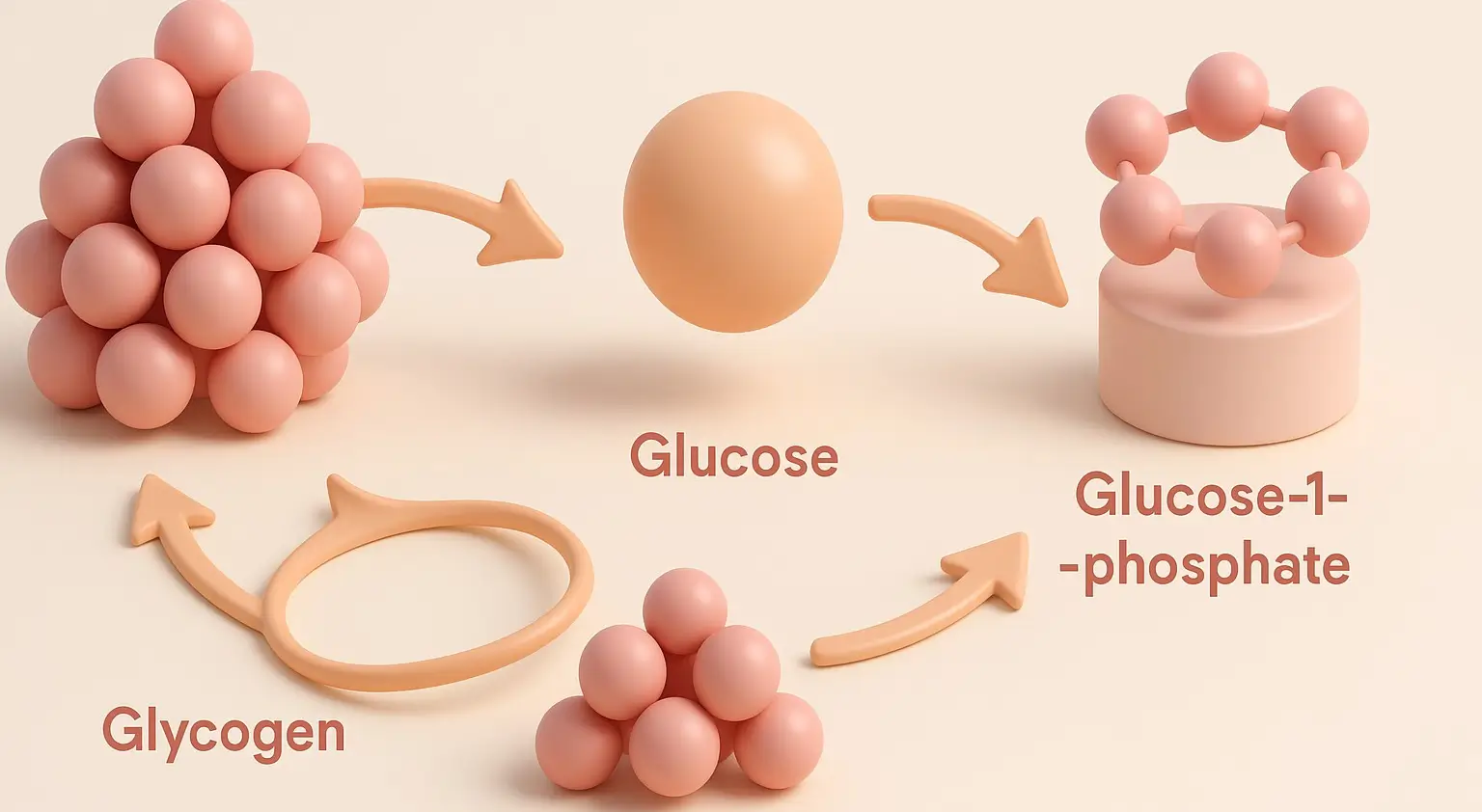
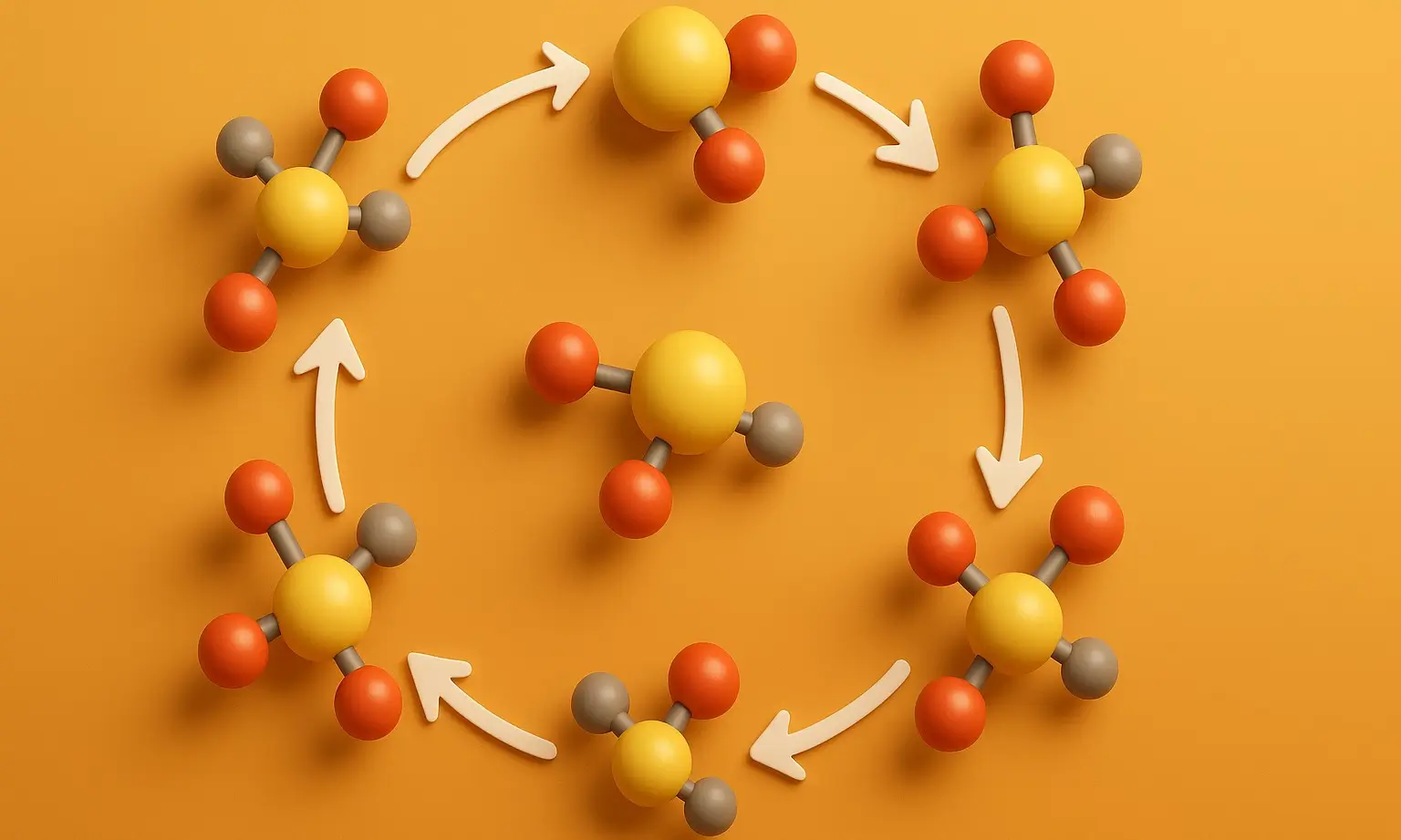
Electron Transport Chain (ETC) of Inhibitors
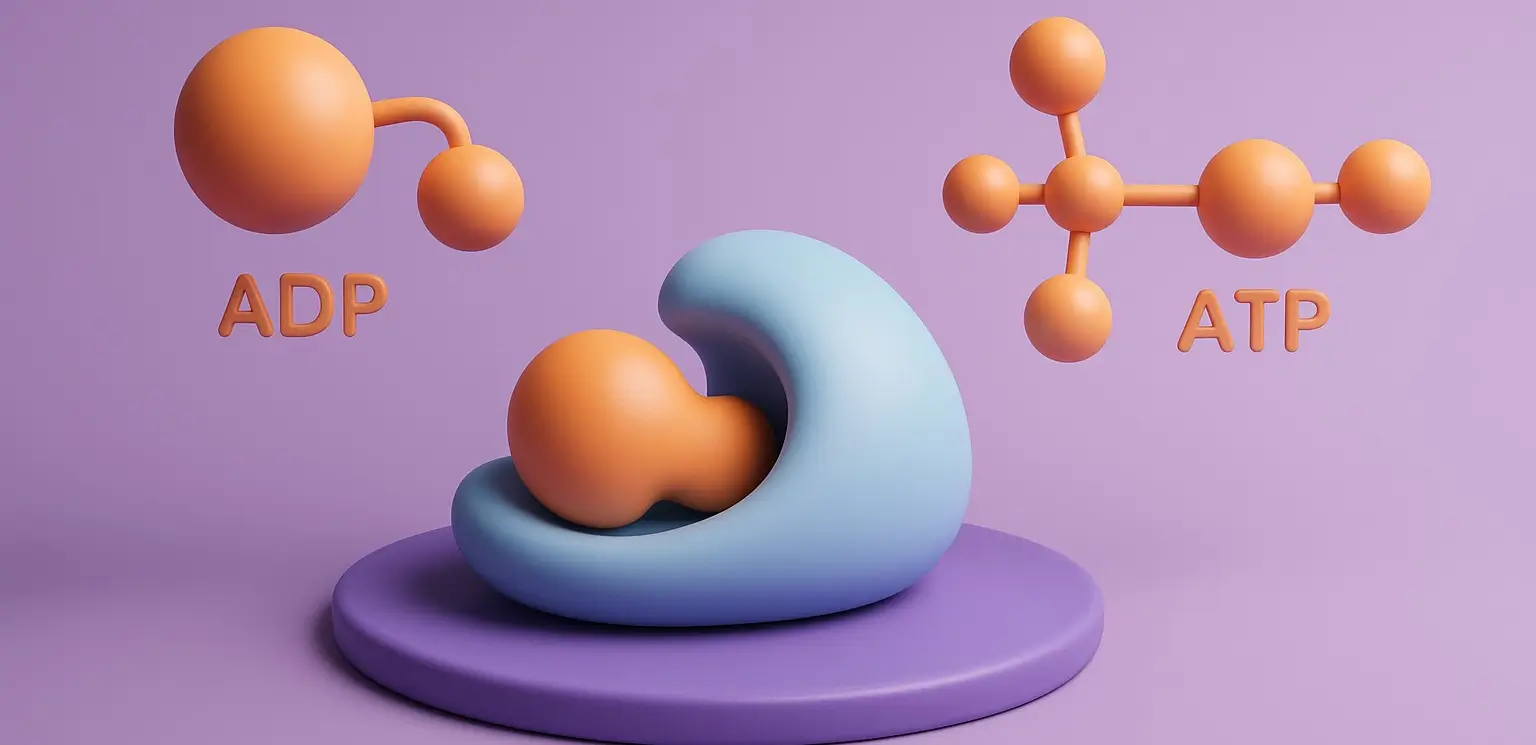
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a crucial component of cellular respiration, facilitating the transfer of electrons and the generation of a proton gradient essential for ATP synthesis. However, this process can be disrupted by various inhibitors, which interfere with the normal functions of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). These inhibitors are categorized based on … Read more