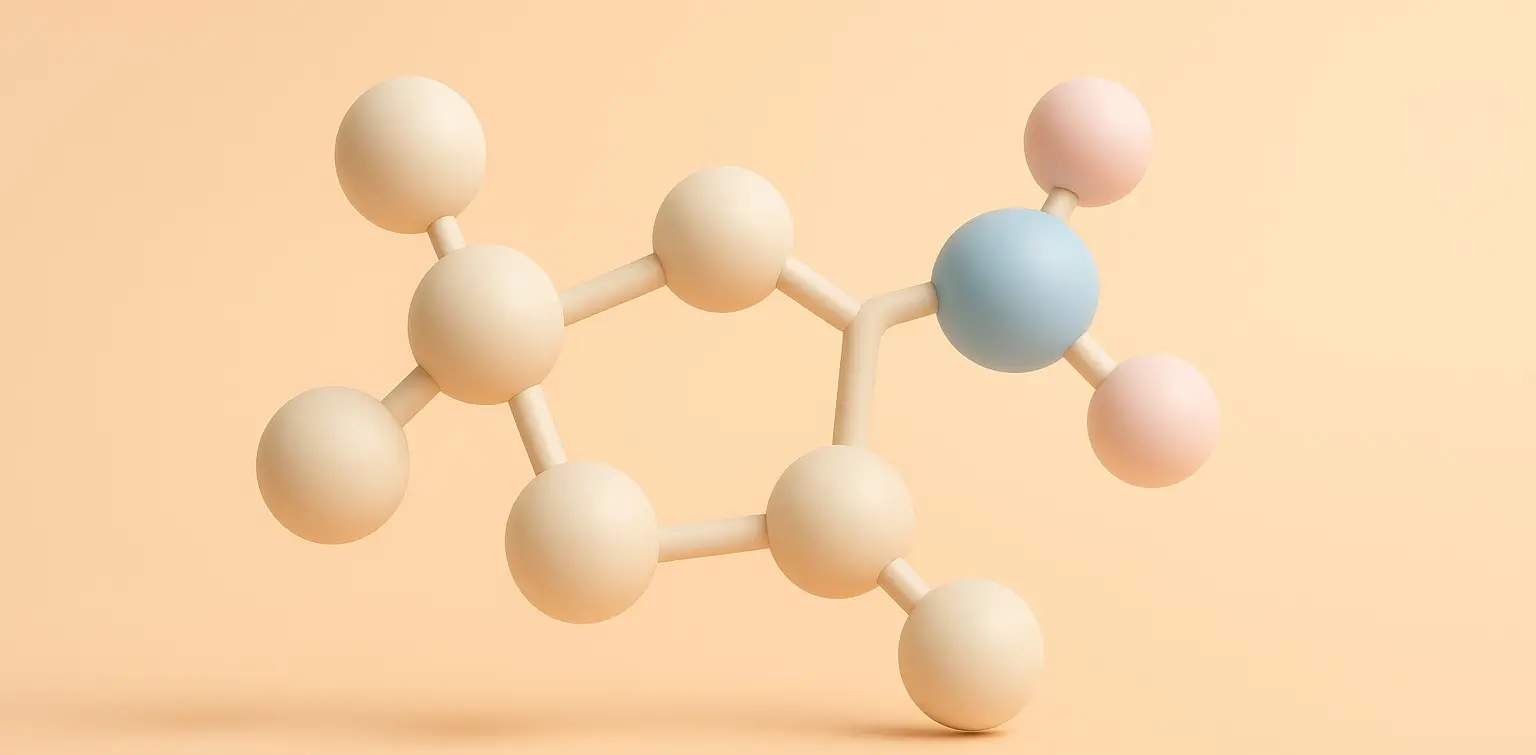
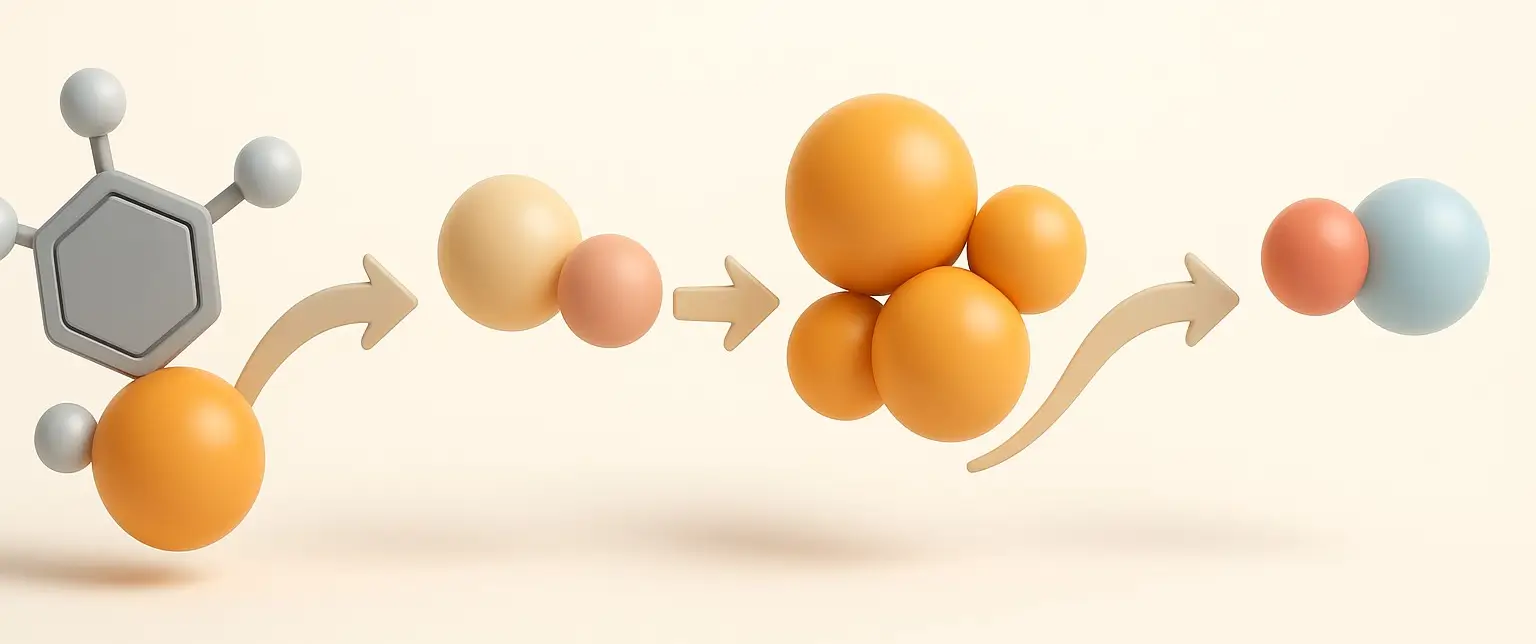
Melatonin
Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain that helps regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm. Synthesis of Melatonin: Step 1: Conversion to N-acetylserotonin: Enzyme: Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT). Process: Serotonin is acetylated to form N-acetylserotonin. Mechanism: AANAT transfers an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to serotonin, … Read more